A five-year plan provides a structured roadmap for career goals with clear milestones, offering long-term stability and direction. Agile career planning emphasizes flexibility and adaptability, allowing for continuous learning and adjustments based on evolving opportunities and market trends. Balancing both approaches can help professionals stay focused while remaining responsive to unexpected changes in their career paths.
Table of Comparison
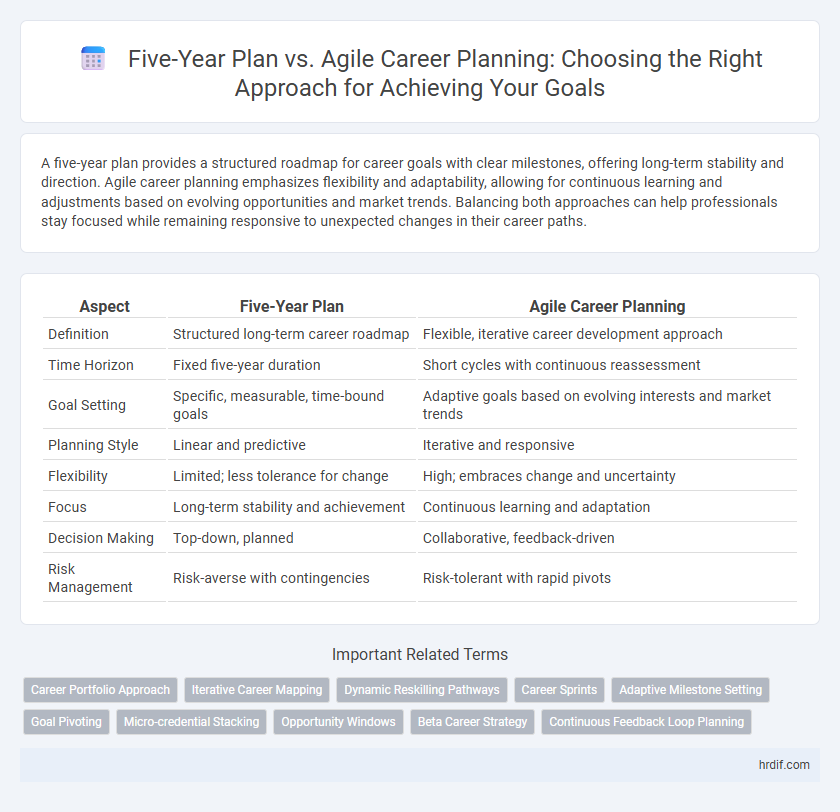
| Aspect | Five-Year Plan | Agile Career Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured long-term career roadmap | Flexible, iterative career development approach |
| Time Horizon | Fixed five-year duration | Short cycles with continuous reassessment |
| Goal Setting | Specific, measurable, time-bound goals | Adaptive goals based on evolving interests and market trends |
| Planning Style | Linear and predictive | Iterative and responsive |
| Flexibility | Limited; less tolerance for change | High; embraces change and uncertainty |
| Focus | Long-term stability and achievement | Continuous learning and adaptation |
| Decision Making | Top-down, planned | Collaborative, feedback-driven |
| Risk Management | Risk-averse with contingencies | Risk-tolerant with rapid pivots |
Overview of Five-Year Career Plans
Five-year career plans provide a structured roadmap outlining long-term professional goals, skill development, and milestones to achieve within a specified timeframe, typically five years. This approach emphasizes clear objectives, measurable progress, and strategic alignment with industry trends and personal aspirations. Despite its rigidity, the five-year plan offers clarity and direction crucial for careers in stable, hierarchical industries where predictability is valuable.
Introduction to Agile Career Planning
Agile career planning emphasizes flexibility and continuous learning, adapting goals to changing market conditions and personal growth. Unlike traditional five-year plans that set fixed milestones, Agile methods encourage iterative goal-setting and regular reassessment, promoting resilience and responsiveness. This approach aligns with dynamic career landscapes, fostering proactive skill development and opportunity exploration.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Five-Year Plans
Traditional five-year plans provide clear, long-term career goals and structured development paths, which can enhance focus and resource allocation. However, they often lack flexibility to adapt to rapidly changing job markets and personal interests, potentially leading to decreased motivation or missed opportunities. The rigidity of these plans contrasts with the dynamic nature of modern careers, where adaptability and continuous learning are crucial.
Advantages of Agile Career Approaches
Agile career planning offers the advantage of flexibility, allowing professionals to adapt to dynamic market conditions and emerging opportunities more effectively than rigid five-year plans. This approach encourages continuous learning and iterative goal-setting, which enhances skill development and responsiveness to industry trends. Emphasizing adaptability, Agile career strategies improve resilience and promote sustained career growth in uncertain and rapidly evolving job markets.
Flexibility vs Predictability in Career Planning
Five-year plans emphasize predictability by setting clear, long-term career milestones, ensuring structured progress toward specific goals. Agile career planning prioritizes flexibility, allowing professionals to adapt to changing opportunities and industry shifts rapidly. Balancing predictability with adaptability enhances career resilience and maximizes success in an evolving job market.
Adapting to Rapid Job Market Changes
Five-year plans often lack flexibility, making it difficult to adjust goals amid rapid job market changes. Agile career planning emphasizes continuous skill development, frequent reassessment, and adaptability to evolving industry demands. Embracing agile methods enhances resilience and better positions professionals to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Case Studies: Five-Year Plans vs Agile Planning
Case studies reveal that traditional Five-Year Plans provide structured milestones and clear long-term objectives, beneficial for industries with stable environments such as manufacturing and engineering. In contrast, Agile career planning emphasizes adaptability and continuous learning, proving effective in dynamic sectors like technology and marketing where rapid changes require frequent course adjustments. These findings highlight the strategic advantage of combining structured long-term goals with flexible, iterative planning to optimize career growth and resilience.
Skills Development in Different Planning Models
Five-year plans emphasize structured skills development aligned with long-term career goals, promoting deep specialization and mastery in chosen fields. Agile career planning prioritizes adaptability, continuous learning, and rapid skill acquisition to respond to evolving industry demands and personal interests. Combining both approaches enhances professional growth by balancing strategic skill investment with flexibility to pivot as opportunities arise.
Decision-Making for Your Career Strategy
Five-year plans provide structured, long-term career goals with clear milestones that help in systematic decision-making and resource allocation. Agile career planning emphasizes flexibility, allowing you to adapt quickly to market changes and emerging opportunities by reassessing decisions frequently. Combining both strategies enhances your career outlook by balancing strategic foresight with adaptive responsiveness in decision-making processes.
Choosing the Right Planning Method for Your Outlook
Choosing the right planning method for your career outlook hinges on aligning goals with flexibility and long-term vision. Five-year plans provide structured milestones and measurable objectives to guide steady progress, ideal for careers requiring predictable trajectories. Agile career planning embraces adaptability and continuous learning, allowing rapid adjustments in response to evolving opportunities and industry trends.
Related Important Terms
Career Portfolio Approach
The Career Portfolio Approach emphasizes flexibility and skill diversification, contrasting with the rigid structure of traditional five-year plans by promoting continuous adaptation to evolving job markets and technologies. Agile career planning leverages iterative goal-setting and real-time feedback, enabling professionals to respond dynamically to opportunities and challenges while building a versatile, evidence-based portfolio.
Iterative Career Mapping
Iterative career mapping enhances adaptability and responsiveness by continuously refining professional goals through regular feedback and reflection, contrasting the rigid structure of traditional five-year plans. Agile career planning emphasizes short-term milestones and skill development, enabling dynamic adjustments that align with evolving industry demands and personal growth trajectories.
Dynamic Reskilling Pathways
Five-year plans offer structured long-term goals, whereas Agile career planning emphasizes dynamic reskilling pathways that adapt to rapidly evolving job markets and technologies. Leveraging continuous learning platforms and micro-credentialing enables professionals to pivot skills efficiently, ensuring career resilience and alignment with emerging industry demands.
Career Sprints
Five-year plans provide long-term career vision but often lack flexibility to adapt to market changes, while Agile career planning emphasizes iterative Career Sprints that enable continuous skill development and rapid pivoting based on real-time opportunities. Career Sprints focus on short, achievable goals with regular evaluation, optimizing personal growth and aligning with evolving industry demands for a more resilient career trajectory.
Adaptive Milestone Setting
Adaptive milestone setting in Agile career planning emphasizes flexibility and continuous reassessment, allowing professionals to pivot goals based on evolving industry trends and personal growth. Unlike rigid five-year plans, this approach prioritizes iterative progress tracking and real-time adjustments to maximize career development opportunities.
Goal Pivoting
Five-year plans provide structured long-term goals, but Agile career planning emphasizes flexibility and frequent goal pivoting to adapt to changing opportunities and industry trends. Embracing Agile methods allows professionals to reassess objectives regularly, ensuring alignment with evolving skills and market demands for a more dynamic career outlook.
Micro-credential Stacking
Micro-credential stacking offers a flexible alternative to traditional five-year career plans by enabling continuous skill acquisition aligned with dynamic industry demands. Agile career planning leverages this approach, allowing professionals to adapt goals and competencies rapidly, ensuring relevance and competitive advantage in evolving job markets.
Opportunity Windows
Five-year plans offer structured, long-term career goals but may overlook evolving Opportunity Windows driven by market shifts and emerging technologies. Agile career planning enables professionals to pivot quickly and capitalize on these dynamic Opportunity Windows, enhancing adaptability and maximizing growth potential.
Beta Career Strategy
Beta Career Strategy emphasizes adaptability by combining the structure of a five-year plan with the flexibility of Agile career planning, allowing professionals to pivot based on evolving market trends and personal growth metrics. This approach leverages iterative goal-setting and continuous feedback, ensuring alignment with dynamic industry demands and individual skill development trajectories.
Continuous Feedback Loop Planning
Continuous feedback loop planning in Agile career approaches enables regular skill assessments and goal adjustments, enhancing adaptability and professional growth. Unlike rigid five-year plans, this dynamic process fosters ongoing development aligned with evolving industry demands and personal aspirations.
Five-year plan vs Agile career planning for outlook. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com