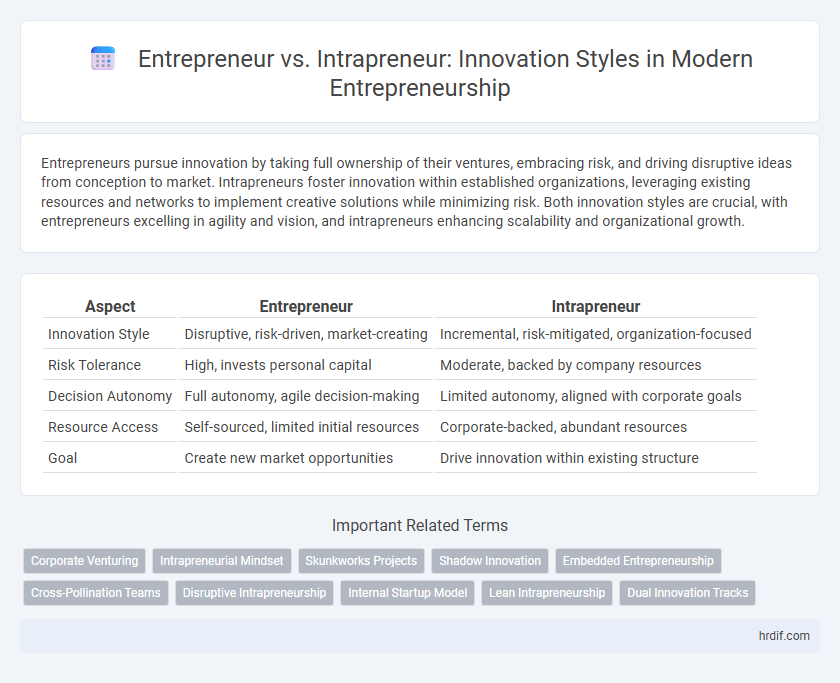
Entrepreneurs pursue innovation by taking full ownership of their ventures, embracing risk, and driving disruptive ideas from conception to market. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations, leveraging existing resources and networks to implement creative solutions while minimizing risk. Both innovation styles are crucial, with entrepreneurs excelling in agility and vision, and intrapreneurs enhancing scalability and organizational growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Innovation Style | Disruptive, risk-driven, market-creating | Incremental, risk-mitigated, organization-focused |
| Risk Tolerance | High, invests personal capital | Moderate, backed by company resources |
| Decision Autonomy | Full autonomy, agile decision-making | Limited autonomy, aligned with corporate goals |
| Resource Access | Self-sourced, limited initial resources | Corporate-backed, abundant resources |
| Goal | Create new market opportunities | Drive innovation within existing structure |
Defining Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs are individuals who create and manage new business ventures, driving innovation through risk-taking and independent decision-making. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources to innovate and develop new products or processes while adhering to corporate structures. Both play crucial roles in fostering innovation, with entrepreneurs focusing on market creation and intrapreneurs enhancing organizational growth.
Key Differences in Innovation Approaches
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating and scaling entirely new ventures, emphasizing risk-taking and market disruption through novel products or services. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging existing resources to improve processes, products, or business models, focusing on incremental or radical innovation without the external risks entrepreneurs face. Key differences lie in ownership, risk tolerance, and the scope of impact, where entrepreneurs pursue independent innovation ventures while intrapreneurs foster innovation aligned with corporate goals.
Risk Tolerance: Entrepreneurs vs Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs demonstrate higher risk tolerance by investing personal capital and pursuing disruptive innovations, embracing uncertainty to achieve significant market impact. Intrapreneurs exhibit moderate risk tolerance, operating within organizational boundaries and leveraging existing resources to foster incremental innovation while minimizing potential losses. Understanding these distinct risk profiles enables businesses to effectively harness both entrepreneurial agility and intrapreneurial stability for sustained innovation growth.
Resource Allocation Strategies
Entrepreneurs allocate resources by identifying market opportunities and securing external funding to drive innovation with high risk and autonomy. Intrapreneurs leverage existing organizational resources and internal networks to innovate within company constraints, emphasizing efficiency and alignment with corporate goals. Resource allocation strategies differ as entrepreneurs prioritize flexibility and scalability, while intrapreneurs focus on optimizing internal assets and managing stakeholder expectations.
Organizational Support and Autonomy
Entrepreneurs thrive on high autonomy, leveraging minimal organizational support to drive groundbreaking innovation through risk-taking and independent decision-making. Intrapreneurs benefit from robust organizational support, accessing resources, networks, and structured environments that enable innovation within company boundaries while balancing autonomy with strategic alignment. The distinct innovation styles highlight that entrepreneurial success hinges on freedom and self-direction, whereas intrapreneurial effectiveness depends on collaboration and organizational integration.
Impact on Business Growth and Scalability
Entrepreneurs drive business growth by introducing disruptive innovations and creating scalable ventures with high market impact. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing organizations by leveraging internal resources to enhance processes and expand product lines, supporting sustainable scalability. Both roles significantly influence business success, with entrepreneurs accelerating market entry and intrapreneurs optimizing operational growth.
Motivation and Reward Systems
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by leveraging intrinsic motivation and personal financial risk, seeking substantial ownership rewards and autonomy in decision-making. Intrapreneurs operate within corporate structures, motivated by organizational incentives such as performance bonuses, recognition, and career advancement, aligning innovation goals with company objectives. Both roles require tailored reward systems that balance creativity encouragement with accountability to maximize innovative output.
Case Studies: Successful Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs like Elon Musk revolutionize industries by founding companies such as Tesla and SpaceX, showcasing innovation through risk-taking and vision-driven leadership. Intrapreneurs inside established firms, exemplified by Google's development of Gmail led by Paul Buchheit, drive breakthrough innovations while leveraging existing organizational resources. Case studies highlight that entrepreneurial success often stems from autonomy and resource control, whereas intrapreneurial innovation thrives through collaboration and strategic alignment within corporate ecosystems.
Challenges and Barriers to Innovation
Entrepreneurs face challenges like securing funding, market uncertainty, and resource limitations when driving innovation independently. Intrapreneurs often encounter organizational bureaucracy, risk aversion, and limited autonomy within established companies, hindering rapid innovation. Both roles must navigate distinct barriers such as resistance to change and balancing creativity with practical constraints to successfully implement innovative ideas.
Choosing the Right Path: Entrepreneur or Intrapreneur?
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new businesses and taking full ownership of risks and rewards, often leading to disruptive market breakthroughs. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging existing resources and infrastructure to develop new products or processes with less financial risk but limited autonomy. Choosing the right path depends on one's appetite for risk, desire for independence, and preference for structural support in fostering innovation.
Related Important Terms
Corporate Venturing
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by launching new ventures with high risk and autonomy, while intrapreneurs innovate within established corporations through corporate venturing, leveraging organizational resources to accelerate product development and market expansion. Corporate venturing enables intrapreneurs to create startup-like agility inside the company, fostering breakthrough innovations without the constraints faced by traditional corporate structures.
Intrapreneurial Mindset
An intrapreneurial mindset drives innovation within established organizations by promoting risk-taking, proactive problem-solving, and resourcefulness, enabling employees to act like entrepreneurs while leveraging company resources. Unlike entrepreneurs who create ventures from scratch, intrapreneurs accelerate digital transformation and competitive advantage by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and internal innovation.
Skunkworks Projects
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by independently launching Skunkworks projects with high risk tolerance and autonomy, whereas intrapreneurs initiate similar confidential, experimental ventures within established organizations, leveraging existing resources for disruptive innovation. Skunkworks projects exemplify rapid prototyping and breakthrough development, enabling both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs to bypass traditional bureaucratic barriers and accelerate innovation cycles.
Shadow Innovation
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures that disrupt markets, while intrapreneurs foster shadow innovation within existing organizations by experimenting stealthily beyond formal processes. Shadow innovation enables intrapreneurs to prototype novel ideas confidentially, accelerating creative solutions without immediate management oversight.
Embedded Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by founding new ventures, leveraging embedded entrepreneurship to integrate startup agility with established organizational resources, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing companies by applying entrepreneurial thinking to internal projects. Embedded entrepreneurship enables organizations to harness intrapreneurs' creativity, accelerating innovation cycles and reducing market entry risks by blending entrepreneurial initiative with corporate support.
Cross-Pollination Teams
Entrepreneurs drive innovation through independent vision and risk-taking, while intrapreneurs leverage organizational resources to implement ideas within established companies; cross-pollination teams combine these approaches by integrating diverse perspectives from both roles to accelerate creativity and breakthrough solutions. This synergy enhances problem-solving capabilities and fosters disruptive innovation by blending entrepreneurial agility with intrapreneurial insight.
Disruptive Intrapreneurship
Disruptive intrapreneurship drives innovation within established organizations by leveraging internal resources to challenge market norms and create breakthrough solutions, contrasting with entrepreneurs who independently initiate ventures outside existing corporate structures. Intrapreneurs navigate organizational constraints to implement radical ideas, fostering transformative change without the risks associated with startup environments.
Internal Startup Model
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by building external startups, leveraging market opportunities to create disruptive products, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing organizations through the Internal Startup Model, promoting agile, startup-like environments that accelerate internal product development and reduce risk. The Internal Startup Model enables intrapreneurs to apply entrepreneurial principles, such as rapid prototyping and customer feedback loops, to innovate efficiently without the constraints of traditional corporate structures.
Lean Intrapreneurship
Lean intrapreneurship emphasizes iterative experimentation and resource efficiency within established organizations, contrasting with entrepreneurs who independently drive innovation by assuming full risk and ownership. By leveraging Lean principles, intrapreneurs accelerate product development and market validation while minimizing waste, fostering agile innovation cultures inside corporations.
Dual Innovation Tracks
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by independently creating disruptive products and business models from scratch, leveraging risk-taking and market agility. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within organizations by applying entrepreneurial thinking to improve existing processes, products, or services, balancing creativity with corporate resources and strategic objectives.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for innovation style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com