Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new businesses and taking full ownership of risks and rewards, often disrupting existing markets with novel ideas. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging company resources and structures to implement creative solutions while managing internal challenges. Both roles are essential for fostering innovation, with entrepreneurs focusing on external market opportunities and intrapreneurs enhancing internal processes and products.
Table of Comparison
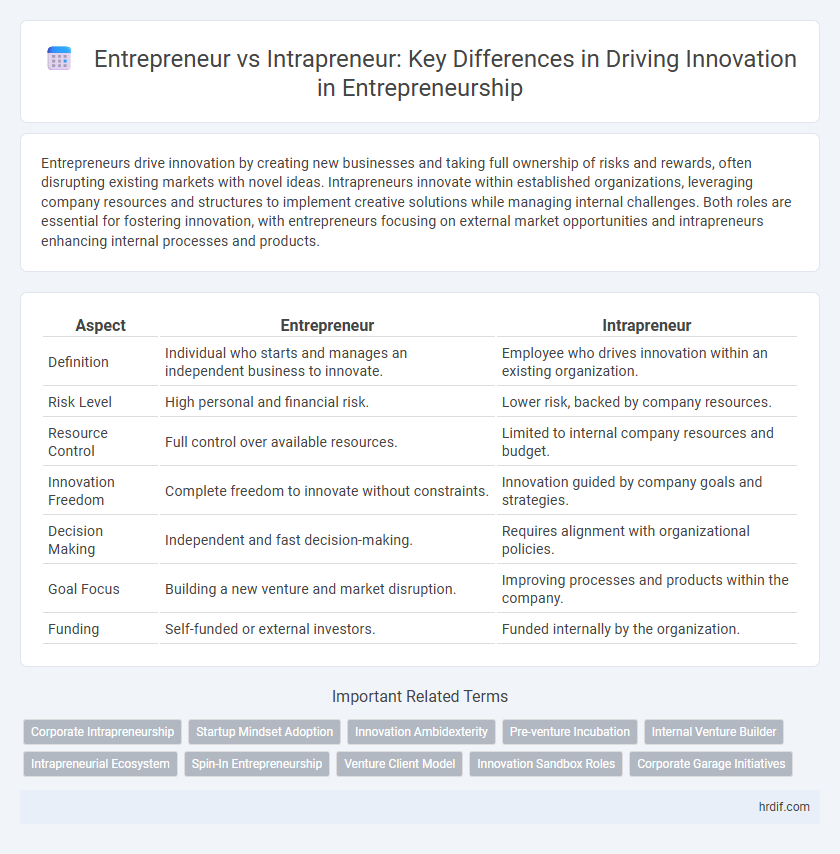
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and manages an independent business to innovate. | Employee who drives innovation within an existing organization. |
| Risk Level | High personal and financial risk. | Lower risk, backed by company resources. |
| Resource Control | Full control over available resources. | Limited to internal company resources and budget. |
| Innovation Freedom | Complete freedom to innovate without constraints. | Innovation guided by company goals and strategies. |
| Decision Making | Independent and fast decision-making. | Requires alignment with organizational policies. |
| Goal Focus | Building a new venture and market disruption. | Improving processes and products within the company. |
| Funding | Self-funded or external investors. | Funded internally by the organization. |
Defining Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs are individuals who establish and manage new businesses, taking on financial risks to bring innovative ideas to market and drive economic growth. Intrapreneurs operate within existing organizations, leveraging company resources to develop new products, services, or processes that foster internal innovation while minimizing external risk. Both roles are crucial for innovation, with entrepreneurs focusing on market disruption and intrapreneurs enhancing competitive advantage through internal development.
Key Differences: Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur
Entrepreneurs assume full ownership and financial risk while driving innovation through new ventures, often focusing on market disruption and scalability. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources and support to develop innovative projects without personal financial exposure. A crucial difference lies in decision-making autonomy; entrepreneurs make independent strategic decisions, whereas intrapreneurs navigate corporate hierarchies and align innovations with organizational goals.
Skills Required for Innovation Roles
Entrepreneurs excel in risk-taking, creativity, and resilience, driving innovation through visionary leadership and resource mobilization. Intrapreneurs leverage deep organizational knowledge, collaboration, and strategic thinking to innovate within established companies, balancing risk with corporate goals. Both roles demand adaptability, problem-solving skills, and a strong bias towards action to successfully implement innovative ideas.
Organizational Support and Resources
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by leveraging external resources and personal risk-taking to create new ventures, often facing limited organizational support but high autonomy. In contrast, intrapreneurs innovate within established companies, benefiting from structured organizational support, access to internal resources, and existing market channels that accelerate product development. Effective innovation roles require aligning entrepreneurial creativity with organizational backing to optimize resource utilization and reduce market-entry risks.
Risk Tolerance and Decision-Making
Entrepreneurs exhibit high risk tolerance, embracing uncertainty to drive innovation and seize new market opportunities, while intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, balancing risk with strategic alignment to existing goals. Decision-making for entrepreneurs tends to be swift and autonomous, enabling rapid pivots, whereas intrapreneurs rely on collaborative processes and organizational resources to implement innovative ideas. Both roles are critical for fostering innovation, but their approaches to risk and decision-making reflect distinct operational environments.
Innovation Impact: Startup vs Corporate
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating disruptive startups that scale rapidly through agile decision-making and risk-taking, often resulting in breakthrough technologies and new market creation. Intrapreneurs within corporate environments leverage established resources and market access to implement incremental innovations, enhancing existing products and processes with lower risk but slower impact. The innovation impact of startups tends to be radical and transformative, while corporate innovation through intrapreneurship delivers sustained improvements and competitive advantage within established industries.
Career Pathways: Growth and Opportunities
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating and scaling new ventures, offering diverse career pathways with high autonomy and potential for equity growth. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging company resources and networks to develop new products or processes, with steady career advancement and leadership opportunities. Both roles demand creativity and risk-taking but differ in stability and resource access, shaping distinct professional growth trajectories.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Entrepreneurs often face challenges such as securing funding, managing market risks, and building a customer base from scratch, which demand high levels of resilience and adaptability. Intrapreneurs encounter obstacles like navigating corporate bureaucracy, aligning innovation with existing company goals, and obtaining internal support, requiring strong negotiation and influence skills. Both roles must overcome uncertainty, but entrepreneurs operate with greater autonomy while intrapreneurs leverage established organizational resources.
Measuring Success and Failure
Entrepreneurs measure success by market disruption, revenue growth, and scalability, while intrapreneurs evaluate success through internal impact, process improvements, and alignment with corporate goals. Failure for entrepreneurs often results in financial loss or venture collapse, whereas intrapreneurs face setbacks in project adoption or resource allocation within the organization. Key performance indicators differ, with entrepreneurs tracking external market metrics and intrapreneurs focusing on internal efficiency and stakeholder engagement.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Ambitions
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by founding startups and taking full ownership of product development, often embracing risk and uncertainty to bring new ideas to market. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging company resources and networks to develop new products or processes while navigating corporate structures. Selecting the right role depends on your ambition for autonomy, risk tolerance, and desire to influence organizational strategy.
Related Important Terms
Corporate Intrapreneurship
Corporate intrapreneurship empowers employees to drive innovation within established organizations by leveraging internal resources and market insights, contrasting with entrepreneurs who independently launch ventures. Intrapreneurs accelerate corporate growth through risk-managed experimentation and cross-functional collaboration, fostering a culture of continuous innovation without the external challenges faced by entrepreneurs.
Startup Mindset Adoption
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by embracing risk and ownership to create new ventures, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations by leveraging resources and navigating internal structures; adopting a startup mindset enhances agility, creativity, and rapid experimentation in both roles. Cultivating this mindset accelerates value creation through proactive problem-solving and iterative development, crucial for sustaining competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Innovation Ambidexterity
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by leveraging risk-taking and autonomy to create new ventures, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations by balancing exploratory initiatives with existing operational efficiencies. Innovation ambidexterity requires organizations to integrate entrepreneurial creativity with intrapreneurial discipline to sustain competitive advantage and adapt to dynamic markets.
Pre-venture Incubation
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by initiating new ventures and taking full ownership of risks during the pre-venture incubation phase, leveraging creativity to develop market-disrupting solutions. Intrapreneurs, embedded within existing organizations, apply entrepreneurial principles to innovate internally, utilizing company resources and networks to accelerate idea validation and business model refinement.
Internal Venture Builder
Internal venture builders harness intrapreneurial talent to drive innovation within established companies, combining entrepreneurial agility with corporate resources. Entrepreneurs initiate ventures independently, but internal venture builders leverage structured innovation processes to scale ideas rapidly while mitigating external risks.
Intrapreneurial Ecosystem
Intrapreneurs drive innovation within established organizations by leveraging internal resources and navigating corporate structures, fostering a robust intrapreneurial ecosystem that accelerates product development and competitive advantage. This ecosystem emphasizes collaboration, risk-taking, and strategic alignment, contrasting with entrepreneurs who independently innovate by building startups outside existing corporate frameworks.
Spin-In Entrepreneurship
Spin-In entrepreneurship leverages intrapreneurs' deep organizational knowledge to drive innovation by integrating external startups and new technologies within established companies, accelerating growth and competitive advantage. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who build ventures independently, spin-in intrapreneurs focus on strategic partnerships and internalizing innovative solutions to transform existing business models.
Venture Client Model
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures with high risk and autonomy, while intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging existing resources and market access. The Venture Client Model enables companies to act as early customers of startup innovations, bridging the gap between entrepreneurial agility and corporate scale to accelerate product development and market validation.
Innovation Sandbox Roles
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures and embracing risk to disrupt markets, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations by leveraging company resources to develop new products or processes; both roles are critical in Innovation Sandbox environments where experimentation and agile development are prioritized. Innovation sandbox roles empower entrepreneurs to validate business models rapidly and enable intrapreneurs to pilot innovative solutions without the constraints of traditional corporate bureaucracy.
Corporate Garage Initiatives
Corporate garage initiatives thrive when intrapreneurs leverage internal resources to innovate within established companies, driving agile solutions and reducing risk compared to external entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs focus on disruptive market entry and scaling startups, while intrapreneurs accelerate innovation by aligning with corporate strategy and utilizing existing infrastructure.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for innovation roles. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com