Employers often prioritize stability and structured environments, favoring employees who excel in defined roles and long-term commitment. Portfolio careerists embrace flexibility, managing multiple projects or roles simultaneously to diversify skills and income streams. This contrast highlights how entrepreneurs must choose between consistency and adaptability when shaping their work style.
Table of Comparison
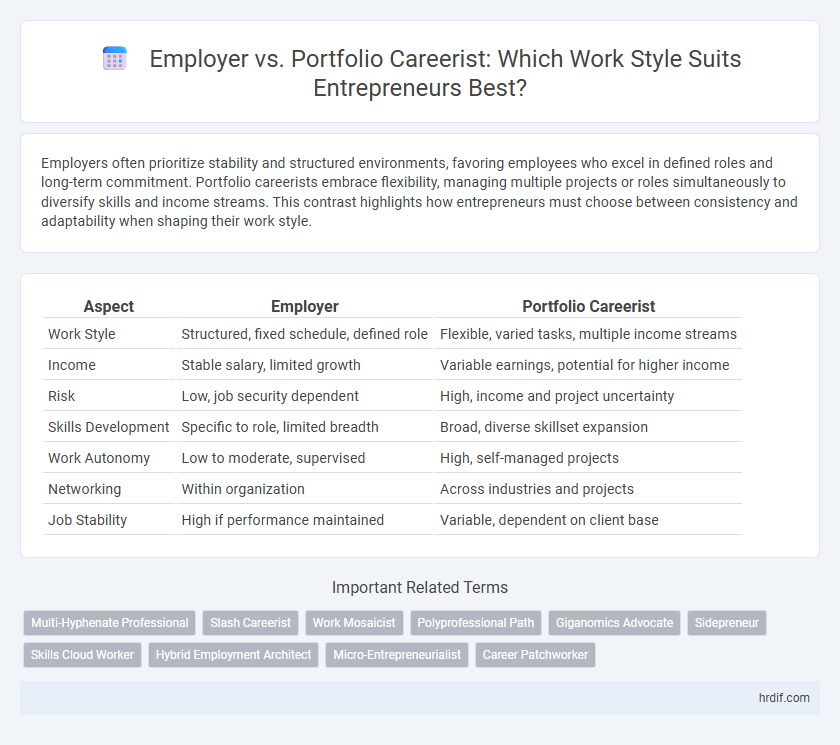
| Aspect | Employer | Portfolio Careerist |
|---|---|---|
| Work Style | Structured, fixed schedule, defined role | Flexible, varied tasks, multiple income streams |
| Income | Stable salary, limited growth | Variable earnings, potential for higher income |
| Risk | Low, job security dependent | High, income and project uncertainty |
| Skills Development | Specific to role, limited breadth | Broad, diverse skillset expansion |
| Work Autonomy | Low to moderate, supervised | High, self-managed projects |
| Networking | Within organization | Across industries and projects |
| Job Stability | High if performance maintained | Variable, dependent on client base |
Understanding Employer-Based Careers
Employer-based careers typically offer structured job roles, clear hierarchies, and steady income through long-term employment contracts with established organizations. This work style emphasizes specialization within a single company, providing benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and professional development opportunities. Understanding employer-based careers involves recognizing the stability and resource access they afford compared to the flexible and diverse income streams associated with portfolio careers.
Defining the Portfolio Careerist Approach
The portfolio careerist approach emphasizes diverse income streams by managing multiple part-time roles, freelance projects, or entrepreneurial ventures simultaneously, fostering adaptability and continuous skill development. Unlike traditional employers committed to a single organization, portfolio careerists prioritize autonomy, flexibility, and cross-industry experience to mitigate risks and maximize career satisfaction. This work style aligns with evolving labor market trends, supporting innovation and personal branding in entrepreneurial ecosystems.
Key Differences in Work Styles
Employer work styles prioritize structured schedules, clear hierarchies, and defined roles within a single organization, promoting stability and focused expertise. Portfolio careerists embrace flexibility, managing multiple income streams and projects simultaneously, fostering adaptability and diverse skill development. Key differences include risk tolerance, autonomy levels, and the scope of professional networks cultivated across varied industries versus concentrated organizational environments.
Flexibility: Portfolio Careerist vs Employer Model
Portfolio careerists enjoy greater flexibility by juggling multiple projects or roles simultaneously, tailoring their work hours and locations to fit personal preferences. Employers often require fixed schedules and defined job responsibilities, limiting adaptability but providing stability and structured growth paths. Flexibility in portfolio careers enhances work-life balance and skill diversification, contrasting with the more rigid but predictable employer model.
Stability and Security in Both Paths
Employers typically offer greater stability and security through consistent salaries, benefits, and structured career progression, which appeal to individuals valuing predictable income and job protection. Portfolio careerists, while embracing diverse projects and income streams, often face variable earnings and less formal security, requiring proactive financial management and adaptability to maintain stability. Both paths demand distinct approaches to managing career risks, with employers relying on organizational safeguards and portfolio careerists leveraging flexibility and diversification for long-term security.
Skills Development and Career Growth
Employer-based work styles often provide structured skill development programs and clear career advancement pathways within a single organization, fostering deep expertise in a specific industry. Portfolio careerists, managing multiple concurrent projects or roles, cultivate diverse skills across various sectors, enhancing adaptability and entrepreneurial thinking. This approach accelerates career growth by promoting cross-functional competencies and expanding professional networks beyond traditional corporate boundaries.
Income Diversification: Pros and Cons
Income diversification for employers typically involves stable revenue streams from consistent clients or products, offering predictable cash flow but limited flexibility in adjusting income sources. Portfolio careerists benefit from multiple income streams across varied projects or roles, which enhances financial resilience but may introduce complexity in managing fluctuating earnings and time commitments. Balancing stability with adaptability is critical for entrepreneurs deciding between traditional employment models and portfolio careers.
Work-Life Balance Comparison
Employer-based work often provides structured hours and predictable income, supporting a more stable work-life balance through clear boundaries between professional and personal time. Portfolio careerists, juggling multiple projects or roles, experience greater flexibility and autonomy, enabling them to tailor their schedules but often face challenges in maintaining consistent downtime. Comparing work-life balance, employer roles excel in routine and security, while portfolio careers offer adaptability at the cost of potential work encroachment on personal life.
Networking and Professional Opportunities
Employers often rely on established internal networks and hierarchical structures to foster professional opportunities, creating stable but sometimes limited pathways for career growth. Portfolio careerists leverage diverse external networks across multiple industries, maximizing access to varied projects and collaborative ventures that drive innovation and adaptability. This dynamic approach to networking enhances exposure to new markets and skill sets, offering a competitive advantage in an evolving entrepreneurial landscape.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Goals
Employer-based careers offer stability, structured growth, and clear advancement paths ideal for professionals seeking long-term security and defined roles. Portfolio careerists leverage diverse projects and multiple income streams to maximize flexibility, skill development, and entrepreneurial opportunities aligned with evolving market demands. Selecting the right path depends on individual priorities such as risk tolerance, desire for variety, and long-term career objectives in entrepreneurship.
Related Important Terms
Multi-Hyphenate Professional
Multi-hyphenate professionals blend diverse skill sets across multiple industries, differentiating themselves from traditional employers by embracing portfolio careers that fuel innovation and adaptability. This work style enhances entrepreneurial success by leveraging varied expertise, fostering continuous learning, and expanding professional networks.
Slash Careerist
Slash careerists embrace a hybrid work style by simultaneously managing multiple roles across various industries, blending entrepreneurship with traditional employment to diversify income streams and skills. This flexible approach contrasts with conventional employers focused on a singular career path, highlighting adaptability and personal brand development in the dynamic gig economy.
Work Mosaicist
Work Mosaicists blend elements of both Employer and Portfolio Careerist styles by integrating multiple roles and projects to create a personalized and dynamic career path, optimizing flexibility and skill diversification. This hybrid approach enables entrepreneurs to adapt swiftly to market changes while maintaining stability through varied income streams and professional growth opportunities.
Polyprofessional Path
Employer-driven careers typically emphasize stability and hierarchy, while portfolio careerists pursue a polyprofessional path, combining multiple roles across industries to maximize skills diversification and income streams. This work style leverages adaptability, continuous learning, and networking to create dynamic professional identities beyond traditional employment structures.
Giganomics Advocate
Giganomics advocates emphasize portfolio careerists who leverage diverse gigs to maximize income streams and flexibility, contrasting traditional employers focused on stable, long-term roles. This work style thrives on adaptability, digital platforms, and continuous skill development, aligning with emerging market demands and entrepreneurial innovation.
Sidepreneur
Sidepreneurs blend entrepreneurial drive with portfolio career flexibility, managing multiple income streams while retaining autonomy. This hybrid work style fosters innovation and risk diversification, contrasting traditional employers who prioritize stability and hierarchical structures.
Skills Cloud Worker
A Skills Cloud Worker thrives by leveraging diverse competencies across multiple projects, blending adaptability and specialized expertise beyond traditional employer roles. This approach contrasts with conventional Employment, emphasizing autonomy, dynamic learning, and strategic skill deployment to navigate the fluid gig economy and portfolio career landscapes.
Hybrid Employment Architect
Hybrid Employment Architects blend the stability of traditional employers with the flexibility of portfolio careers, leveraging multiple income streams from varied projects and part-time roles. This work style maximizes entrepreneurial agility while maintaining strategic alignment with long-term professional goals in dynamic economic environments.
Micro-Entrepreneurialist
Micro-entrepreneurialists prioritize flexibility and autonomy, often blending employer roles with portfolio career strategies to diversify income streams and mitigate risks. Emphasizing innovation and scalability, they leverage multiple projects or startups simultaneously, optimizing resource allocation and market responsiveness.
Career Patchworker
Career patchworkers blend multiple part-time roles or freelance projects to build diverse income streams, contrasting with traditional employers who offer stable, full-time positions. This flexible work style enhances adaptability and skill diversification, crucial for entrepreneurial success in dynamic markets.
Employer vs Portfolio Careerist for work style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com