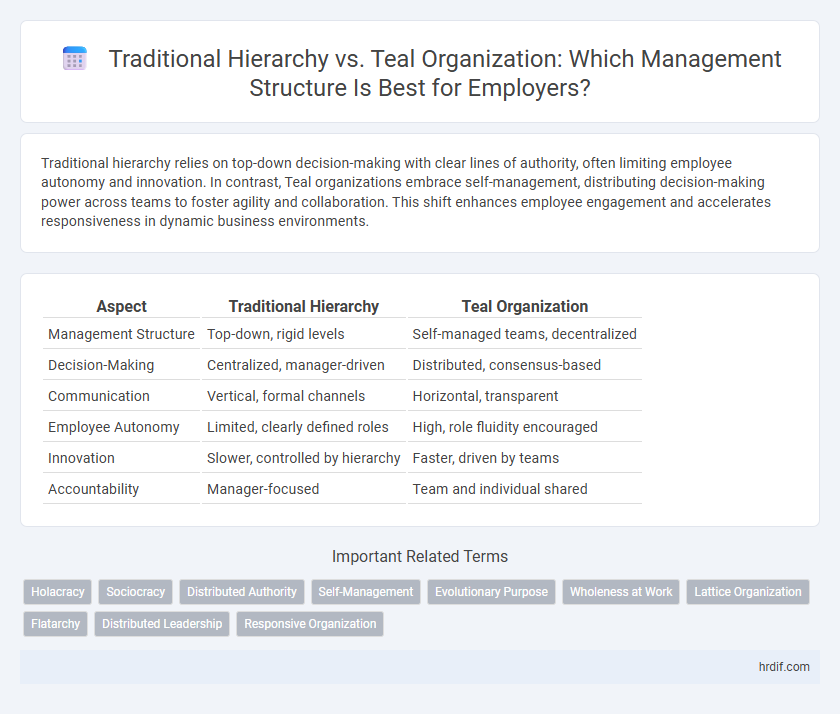
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down decision-making with clear lines of authority, often limiting employee autonomy and innovation. In contrast, Teal organizations embrace self-management, distributing decision-making power across teams to foster agility and collaboration. This shift enhances employee engagement and accelerates responsiveness in dynamic business environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Hierarchy | Teal Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Management Structure | Top-down, rigid levels | Self-managed teams, decentralized |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, manager-driven | Distributed, consensus-based |
| Communication | Vertical, formal channels | Horizontal, transparent |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited, clearly defined roles | High, role fluidity encouraged |
| Innovation | Slower, controlled by hierarchy | Faster, driven by teams |
| Accountability | Manager-focused | Team and individual shared |
Understanding Traditional Hierarchical Management
Traditional hierarchical management structures emphasize a clear chain of command with defined roles and responsibilities, ensuring top-down decision-making and control. This system prioritizes efficiency, accountability, and predictable workflows through tiered layers of authority. Understanding this model highlights its strengths in stability and clarity, but also exposes limitations in flexibility and employee empowerment compared to more decentralized approaches like Teal organizations.
Defining Teal Organizations in the Modern Workplace
Teal organizations emphasize self-management, decentralized decision-making, and a culture of trust, contrasting sharply with traditional hierarchical structures that rely on top-down control and rigid roles. In the modern workplace, Teal organizations prioritize employee autonomy, purpose-driven work, and adaptive structures that enhance innovation and engagement. This management style fosters resilience and aligns organizational purpose with individual values, driving sustainable performance.
Key Differences: Hierarchy vs Teal Management Structures
Traditional hierarchy in management structures features rigid layers of authority, top-down decision-making, and clearly defined roles that maintain control through supervision and formal processes. Teal organizations emphasize self-management, distributed authority, and evolutionary purpose, allowing employees to operate with greater autonomy and adapt dynamically to change. The key differences center on power distribution, decision-making processes, and organizational adaptability, with teal models fostering decentralized leadership and continuous innovation.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs Distributed Authority
Traditional hierarchy centralizes decision-making authority at the top levels of management, creating a clear chain of command where orders flow downward and employee input is limited. In contrast, Teal organizations embrace distributed authority by empowering teams and individuals to make decisions autonomously, fostering collaboration and quicker responses to change. This shift enhances organizational agility and promotes a culture of trust, accountability, and innovation.
Employee Engagement and Motivation in Both Systems
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down management, which can limit employee engagement due to rigid roles and limited autonomy. Teal organizations foster self-management and purpose-driven work, significantly boosting motivation by empowering employees to make decisions and contribute meaningfully. Studies reveal that employees in Teal structures report higher job satisfaction and commitment, directly enhancing productivity and innovation.
Flexibility and Innovation: Which Structure Wins?
Traditional hierarchy often limits flexibility and innovation due to rigid reporting lines and decision-making processes, resulting in slower response times to market changes. Teal organizations prioritize self-management and decentralized authority, fostering a culture where employees innovate freely and adapt swiftly to evolving challenges. Companies adopting Teal structures typically report higher employee engagement and accelerated innovation cycles, positioning them as leaders in dynamic industries.
Communication Flows: Hierarchical vs Self-Managed Teams
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down communication flows, where instructions and feedback travel through multiple management layers, often causing delays and information distortion. In contrast, Teal organizations emphasize self-managed teams with decentralized communication, enabling faster decision-making and more direct, transparent interactions among employees. This shift fosters agility, employee empowerment, and more responsive organizational dynamics.
Leadership Roles: From Bosses to Facilitators
Traditional hierarchy relies on authoritative bosses who issue directives and control decision-making, often limiting employee autonomy and innovation. Teal organizations emphasize leadership roles as facilitators who empower teams, promote self-management, and encourage collaborative problem-solving. This shift fosters a culture of trust and adaptability, enhancing overall organizational agility and employee engagement.
Organizational Culture: Stability vs Adaptability
Traditional hierarchies emphasize stability through rigid roles, clear authority lines, and standardized procedures that ensure consistent outcomes. In contrast, Teal organizations foster adaptability by promoting self-management, distributed decision-making, and a culture of continuous learning that responds swiftly to change. Employers aiming to enhance innovation and employee engagement may benefit from embracing the fluid, purpose-driven culture characteristic of Teal organizations.
Choosing the Right Management Structure for Your Business
Selecting the right management structure is crucial for aligning organizational goals with employee engagement and efficiency. Traditional hierarchy offers clear authority and streamlined decision-making, while Teal organizations emphasize self-management, transparency, and empowerment, fostering innovation and adaptability. Businesses must evaluate their size, culture, and strategic objectives to determine whether a rigid chain of command or a decentralized, purpose-driven model best supports sustainable growth.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down decision-making with clearly defined roles and ranks, while Teal organizations embrace self-management, decentralized authority, and adaptability. Holacracy, a key Teal practice, distributes authority through dynamic roles and governance processes, enhancing transparency and employee empowerment.
Sociocracy
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down decision-making with rigid authority levels, whereas Teal organizations embrace decentralized management, promoting autonomy and self-management through Sociocracy's circular governance and consent-based decisions. Sociocracy enhances collaboration by structuring teams into interconnected circles that enable transparent communication and continuous feedback, fostering adaptive and inclusive leadership.
Distributed Authority
Traditional hierarchy centralizes authority with top-level managers, creating rigid decision-making processes and limited autonomy for employees. Teal organizations embrace distributed authority, empowering teams with decentralized decision-making to foster agility, innovation, and greater ownership across all organizational levels.
Self-Management
Traditional hierarchy relies on top-down decision-making and rigid reporting lines, often limiting employee autonomy and slowing innovation. Teal organizations embrace self-management by distributing authority across teams, empowering employees to take initiative and collaborate more effectively without relying on centralized control.
Evolutionary Purpose
Traditional hierarchy emphasizes fixed roles and top-down decision-making, whereas a Teal organization embraces Evolutionary Purpose by empowering employees to self-manage and adapt dynamically to changing needs, fostering innovation and intrinsic motivation. This shift from rigid structures to purpose-driven autonomy aligns organizational goals with individual contributions, enhancing responsiveness and long-term sustainability.
Wholeness at Work
Traditional hierarchy structures emphasize clear authority lines and role specialization, often leading to compartmentalized employee experiences, whereas Teal organizations promote Wholeness at Work by encouraging individuals to bring their full selves, integrating emotional, intellectual, and spiritual dimensions into their roles. This shift fosters a more inclusive, adaptive work environment that values personal growth and collective responsibility over rigid control.
Lattice Organization
Lattice organizations replace traditional hierarchy with a flexible, network-based management structure that empowers employees to collaborate across departments without rigid chains of command. This approach fosters innovation and agility by promoting transparency, shared decision-making, and self-management, contrasting with the top-down control typical of traditional hierarchies and teal organizations.
Flatarchy
Flatarchy blends traditional hierarchy with Teal organization principles by reducing layers of management to foster open communication and faster decision-making. This hybrid structure promotes employee autonomy and innovation while maintaining clear accountability and organizational alignment.
Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership in Teal organizations decentralizes decision-making authority, empowering employees at all levels to take initiative and drive innovation, whereas traditional hierarchies concentrate power within top management, often slowing responsiveness and limiting employee autonomy. This shift enhances organizational agility, fosters collaboration, and aligns leadership roles with evolving project needs rather than rigid, fixed positions.
Responsive Organization
Traditional hierarchy relies on rigid, top-down decision-making processes that can slow responsiveness, while Teal organizations empower self-managing teams and decentralized authority to increase agility and adaptability. Employers adopting Teal structures benefit from faster innovation cycles and enhanced employee engagement, driving a more responsive organizational culture.
Traditional hierarchy vs Teal organization for management structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com