Employers in traditional management structures maintain hierarchical control with clear lines of authority and decision-making centralized at the top. In contrast, teal organizations adopt decentralized management, promoting self-management and distributed leadership to enhance employee autonomy and innovation. This shift redefines employer roles from supervisors to facilitators of collaborative work environments.
Table of Comparison
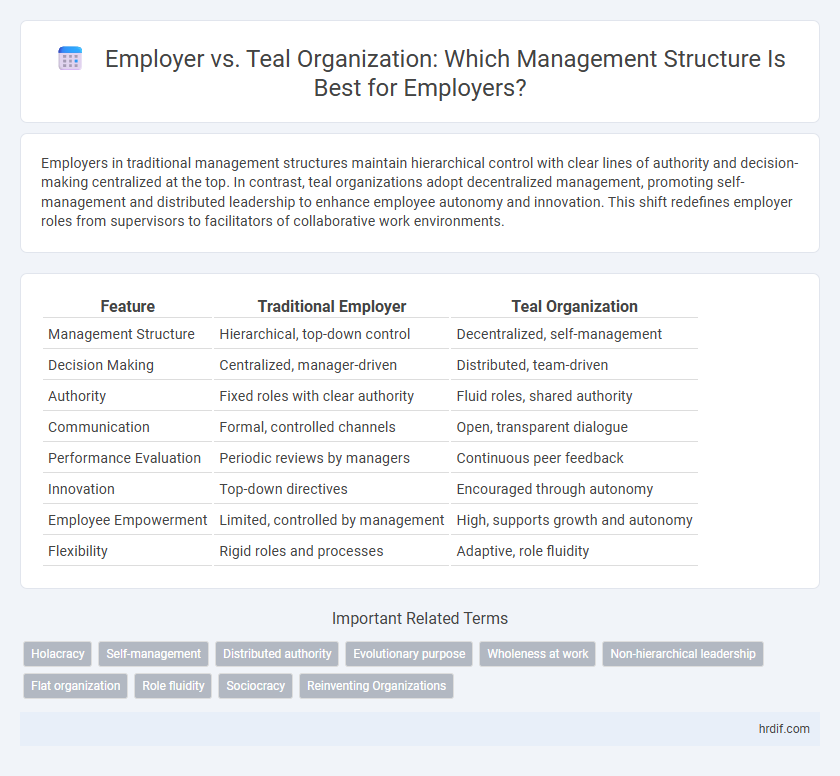
| Feature | Traditional Employer | Teal Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Management Structure | Hierarchical, top-down control | Decentralized, self-management |
| Decision Making | Centralized, manager-driven | Distributed, team-driven |
| Authority | Fixed roles with clear authority | Fluid roles, shared authority |
| Communication | Formal, controlled channels | Open, transparent dialogue |
| Performance Evaluation | Periodic reviews by managers | Continuous peer feedback |
| Innovation | Top-down directives | Encouraged through autonomy |
| Employee Empowerment | Limited, controlled by management | High, supports growth and autonomy |
| Flexibility | Rigid roles and processes | Adaptive, role fluidity |
Traditional Employer Management vs Teal Organization: A Comparative Overview
Traditional employer management relies on hierarchical structures with clear authority lines, centralized decision-making, and defined job roles to ensure accountability and control. In contrast, Teal organizations adopt self-management principles, decentralizing decision-making and empowering employees through autonomy, shared purpose, and adaptive processes. This shift promotes agility, innovation, and employee engagement by fostering trust and collaboration over rigid command-and-control systems.
Decision-Making Processes: Hierarchy vs Self-Management
Traditional employer management structures rely heavily on hierarchical decision-making processes where authority flows from top executives to lower-level employees, ensuring clear accountability and control. In contrast, teal organizations prioritize self-management, empowering employees at all levels to make decisions collaboratively, fostering agility and innovation. This shift from rigid hierarchy to decentralized authority transforms workplace dynamics, enhancing employee engagement and responsiveness to change.
Authority and Power Distribution in Employers and Teal Organizations
Employers in traditional organizations typically centralize authority and power within hierarchical management levels, enforcing top-down decision-making and clearly defined roles. In contrast, teal organizations promote decentralized authority by distributing power across self-managed teams, encouraging autonomy and collective responsibility. This shift from hierarchical control to distributed empowerment fosters innovation and employee engagement while reducing bureaucratic constraints.
Employee Autonomy and Empowerment: A Structural Perspective
Traditional employer management structures centralize decision-making authority, limiting employee autonomy and often resulting in hierarchical control mechanisms. In contrast, teal organizations emphasize decentralized management where employees are empowered to make decisions, fostering innovation and intrinsic motivation. This structural shift enhances responsiveness and adaptability, aligning organizational goals with individual autonomy and collective purpose.
Organizational Culture: Conventional Employers vs Teal Organizations
Conventional employers typically maintain hierarchical management structures with rigid roles and top-down decision-making processes that emphasize control and predictability. Teal organizations embrace decentralized management, promoting self-management and autonomy to foster innovation and adaptability. This shift cultivates an organizational culture centered on trust, employee empowerment, and holistic engagement.
Communication Flow: Top-Down vs Distributed Models
Employers in traditional management structures commonly use a top-down communication flow, where directives and information cascade from leaders to employees, ensuring clear accountability but often limiting feedback loops. In contrast, teal organizations embrace distributed communication models that foster decentralized decision-making and empower employees at all levels to share information freely, enhancing collaboration and innovation. This shift promotes transparency and agility in workplace dynamics, aligning communication flow with evolving organizational values and employee engagement.
Innovation and Agility Across Management Structures
Employers embracing teal organizations prioritize self-management and decentralized decision-making, fostering higher innovation and agility compared to traditional hierarchical structures. These organizations implement evolutionary purpose and encourage employee autonomy, resulting in faster adaptation to market changes and enhanced creative problem-solving. The shift towards teal management enables employers to attract talent seeking meaningful work environments, ultimately improving organizational resilience and long-term success.
Role Clarity and Job Descriptions: Differences in Approach
Employers in traditional organizations emphasize clear hierarchical role clarity and detailed job descriptions to define responsibilities and chain of command, ensuring accountability and operational consistency. In contrast, teal organizations adopt a more fluid management structure where roles evolve dynamically based on individual strengths and organizational needs, minimizing rigid job descriptions to foster autonomy and self-management. This shift reduces micromanagement and encourages employees to take initiative, aligning personal purpose with organizational goals.
Performance Evaluation and Accountability Mechanisms
Employers in traditional hierarchical organizations rely on top-down performance evaluation and accountability mechanisms to ensure employee compliance and goal achievement. Teal organizations implement decentralized management structures where self-management and peer evaluations replace conventional performance reviews, fostering transparency and intrinsic motivation. This shift enhances accountability by empowering teams to take ownership of outcomes rather than depending on managerial oversight.
Leadership Styles: Directive Leadership vs Inspirational Guidance
Employers with traditional management structures often rely on directive leadership, emphasizing clear authority lines and task-oriented supervision to maintain control and ensure productivity. In contrast, teal organizations prioritize inspirational guidance by fostering autonomy, encouraging collaborative decision-making, and promoting intrinsic motivation through shared purpose and trust. This shift from authoritative commands to empowering leadership styles enhances innovation and employee engagement within modern workplaces.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Employers adopting Holacracy in teal organizations implement decentralized management structures emphasizing distributed authority and self-management, contrasting traditional hierarchical employer models with centralized decision-making. This shift enhances organizational agility, employee autonomy, and role clarity by replacing rigid job descriptions with dynamic roles aligned to evolving business needs.
Self-management
Teal organizations prioritize self-management by eliminating hierarchical structures, empowering employees to make decisions autonomously and fostering a culture of trust and accountability. Employers adopting this model enhance adaptability and innovation by decentralizing authority and encouraging collaborative problem-solving.
Distributed authority
Employers adopting a traditional management structure maintain centralized authority with clear hierarchical levels, while teal organizations implement distributed authority that empowers employees at all levels to make decisions. This shift fosters increased autonomy, collaboration, and adaptability within teal organizational frameworks compared to conventional employer-driven models.
Evolutionary purpose
Employers in traditional management structures maintain hierarchical authority focused on predefined roles and profitability, whereas teal organizations adopt a decentralized approach aligned with an evolutionary purpose that emphasizes self-management and collective growth. This shift enables teal organizations to foster innovation and adaptability by empowering employees to contribute meaningfully to the organization's evolving mission.
Wholeness at work
Employers adopting traditional management structures emphasize hierarchical control and defined roles, whereas Teal organizations prioritize Wholeness by encouraging employees to bring their authentic selves to work and fostering self-management. This approach enhances collaboration, creativity, and employee engagement, leading to a more adaptive and resilient workplace culture.
Non-hierarchical leadership
Employers adopting teal organization principles implement non-hierarchical leadership structures that emphasize autonomy, self-management, and decentralized decision-making, contrasting traditional top-down management. This approach fosters employee empowerment, innovation, and agility by eliminating rigid hierarchies and promoting collaborative, purpose-driven work environments.
Flat organization
Flat organizations eliminate hierarchical layers, promoting direct communication between employers and employees to enhance agility and decision-making speed. Employers in flat organizations prioritize employee empowerment and collaborative management structures to increase innovation and responsiveness.
Role fluidity
Employers embracing teal organizations prioritize role fluidity, allowing employees to shift responsibilities based on expertise and project needs rather than fixed job descriptions, fostering adaptability and innovation. This management structure contrasts traditional hierarchical models by decentralizing authority and promoting self-management, enhancing employee autonomy and collaborative decision-making.
Sociocracy
Employers adopting teal organizational structures prioritize decentralized management with sociocracy principles, emphasizing distributed authority and collaborative decision-making to enhance agility and employee empowerment. Unlike traditional hierarchical employers, teal organizations utilize consent-based governance and dynamic roles, fostering transparency, accountability, and adaptive strategies within the workforce.
Reinventing Organizations
Employers transitioning from traditional hierarchical structures to teal organizations emphasize self-management, wholeness, and evolutionary purpose, fostering environments where employees take autonomous responsibility and align their work with the organization's deeper mission. Reinventing Organizations by Frederic Laloux highlights that teal organizations outperform conventional models by promoting decentralized decision-making and empowering teams, leading to enhanced innovation and employee engagement.
employer vs teal organization for management structure Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com