Employers choosing between traditional business models and B-Corp certification must weigh their commitment to social impact against operational goals. B-Corp organizations prioritize transparency, environmental responsibility, and community engagement, setting them apart from conventional employers focused primarily on profitability. Embracing B-Corp standards can enhance brand reputation and attract socially conscious talent, driving meaningful change within and beyond the workplace.
Table of Comparison
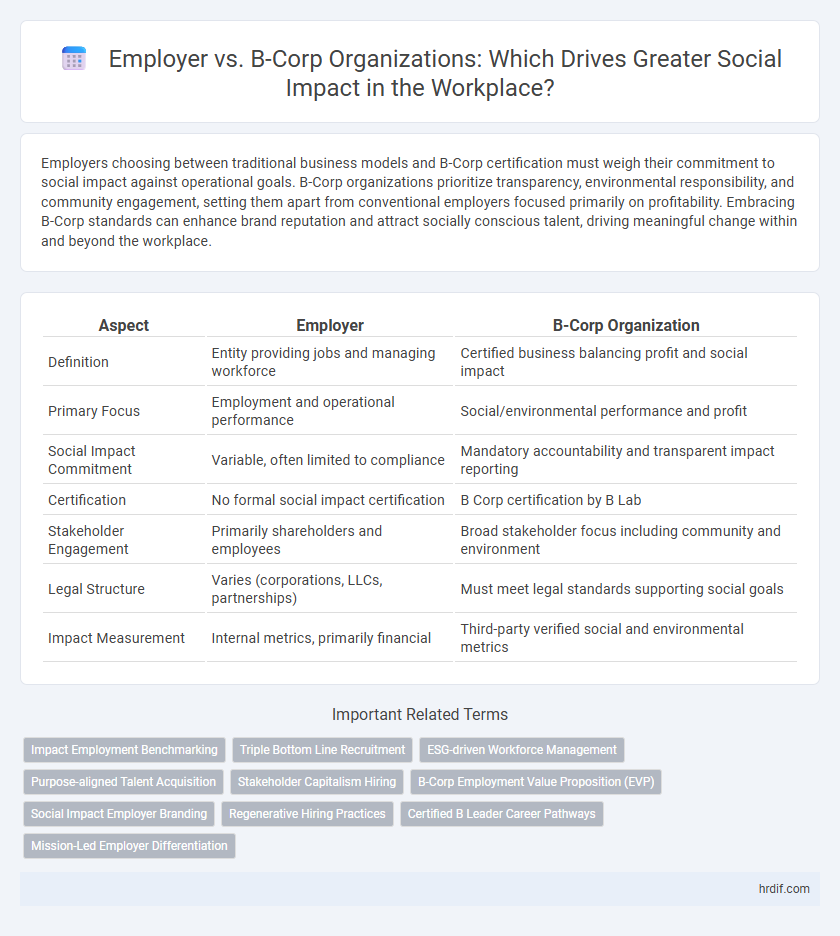
| Aspect | Employer | B-Corp Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entity providing jobs and managing workforce | Certified business balancing profit and social impact |
| Primary Focus | Employment and operational performance | Social/environmental performance and profit |
| Social Impact Commitment | Variable, often limited to compliance | Mandatory accountability and transparent impact reporting |
| Certification | No formal social impact certification | B Corp certification by B Lab |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Primarily shareholders and employees | Broad stakeholder focus including community and environment |
| Legal Structure | Varies (corporations, LLCs, partnerships) | Must meet legal standards supporting social goals |
| Impact Measurement | Internal metrics, primarily financial | Third-party verified social and environmental metrics |
Understanding Traditional Employers vs. B-Corps
Traditional employers prioritize profit maximization and shareholder value, often focusing on economic performance over social or environmental outcomes. B-Corp organizations integrate social impact and environmental responsibility into their core business models, meeting rigorous certification standards to balance purpose and profit. This distinction highlights how B-Corps embed accountability and transparency in governance, fostering sustainable practices that appeal to socially conscious employees and consumers.
Core Values: Profit-Driven vs. Purpose-Driven
Employers in traditional businesses prioritize profit-driven core values, emphasizing financial performance and shareholder returns as primary success metrics. B-Corp organizations operate with purpose-driven values, balancing profit goals with social and environmental impact commitments, integrating stakeholder interests into their business models. This fundamental difference influences decision-making, corporate culture, and long-term sustainability strategies within each entity.
Legal Structure and Accountability
Employers operating as traditional corporations prioritize shareholder profits, often structured as C-Corps or LLCs, limiting legal accountability primarily to financial performance and regulatory compliance. In contrast, B-Corp Organizations are certified to meet rigorous social and environmental performance standards, legally embedding accountability to stakeholders beyond shareholders, including employees, communities, and the environment. This legal structure requires B-Corps to balance profit and purpose, ensuring transparent impact reporting and higher social responsibility commitments.
Social and Environmental Impact Commitments
Employers prioritizing social and environmental impact commitments must evaluate the distinction between traditional corporate structures and B-Corp certification, which mandates rigorous standards for social responsibility, environmental performance, and transparency. B-Corp organizations integrate stakeholder interests, including employees, communities, and the environment, into their business models, driving measurable positive outcomes beyond profit. This comprehensive approach positions B-Corps as leaders in sustainable business practices and social impact, offering a benchmark for employers aiming to embed ethical values and sustainability into their operations.
Employee Experience and Workplace Culture
Employers prioritize competitive benefits and career growth opportunities to enhance employee experience, whereas B-Corp organizations emphasize social impact alongside profit, fostering a workplace culture rooted in sustainability and ethical practices. B-Corp certification signals a commitment to stakeholder balance, which improves employee engagement through shared values and purposeful work. This alignment between social mission and employee experience contributes to higher retention rates and stronger organizational commitment in B-Corp workplaces.
Recruitment and Talent Attraction
Employers branded as B-Corp organizations attract top talent by showcasing a genuine commitment to social and environmental responsibility, which resonates with purpose-driven candidates. Recruitment efforts in B-Corp companies often highlight ethical practices and community impact, differentiating them from traditional employers focused solely on profit. Talent attraction is enhanced through transparent sustainability initiatives and employee engagement in meaningful corporate missions, driving higher retention and job satisfaction.
Measuring Success: Profitability vs. Triple Bottom Line
Employers typically measure success through profitability metrics such as revenue growth, net income, and return on investment, reflecting traditional financial performance priorities. B-Corp organizations prioritize the triple bottom line, evaluating success based on social impact, environmental sustainability, and financial viability, integrating stakeholder value beyond profit. This comprehensive approach aligns business operations with ethical, environmental, and social goals, fostering long-term societal benefits alongside economic success.
Stakeholder Engagement and Transparency
Employer commitment to stakeholder engagement enhances workplace culture and fosters trust through transparent communication of social and environmental goals. B-Corp organizations prioritize rigorous third-party assessments to ensure accountability, embedding transparency in their legal frameworks to benefit all stakeholders. Both models emphasize social impact, but B-Corps provide structured metrics and public reporting that elevate stakeholder involvement beyond traditional employer practices.
Career Growth and Skill Building Opportunities
Employers who choose B-Corp certification demonstrate a strong commitment to social and environmental performance, which often translates into enhanced career growth and skill-building opportunities for employees. B-Corp organizations prioritize continuous learning, leadership development, and fostering innovative problem-solving aligned with sustainable business practices. Employees in B-Corps gain unique experience in navigating social impact challenges, positioning them for advanced roles in socially responsible industries.
Choosing the Right Fit: Employer or B-Corp for Your Career
Choosing between an employer and a B-Corp organization for your career depends on your values and impact goals. Employers offer diverse opportunities and stability, while B-Corps prioritize social and environmental performance verified through rigorous certification standards. Aligning with a B-Corp ensures your career directly contributes to measurable social impact alongside business success.
Related Important Terms
Impact Employment Benchmarking
Employers adopting B-Corp certification demonstrate measurable social impact by adhering to rigorous standards in impact employment benchmarking, which evaluates worker benefits, diversity, and community engagement. This benchmarking provides a transparent framework for comparing traditional employers with B-Corp organizations, highlighting superior practices in employee well-being, equitable pay, and sustainable workplace policies.
Triple Bottom Line Recruitment
Employers adopting Triple Bottom Line recruitment prioritize environmental responsibility, social equity, and economic viability, aligning hiring practices with sustainable development goals. B-Corp organizations exemplify this approach by certifying businesses that meet rigorous standards of social and environmental performance, transparency, and accountability to create positive social impact.
ESG-driven Workforce Management
Employers integrating ESG-driven workforce management prioritize sustainable labor practices, diverse hiring, and equitable employee benefits to enhance social impact. B-Corp organizations formalize these commitments by meeting rigorous environmental, social, and governance standards, fostering transparency and accountability in workforce operations.
Purpose-aligned Talent Acquisition
Employers committed to purpose-aligned talent acquisition increasingly prioritize B-Corp certification to attract socially conscious candidates who seek mission-driven workplaces. B-Corp organizations demonstrate verified social and environmental performance, appealing to employees motivated by impact beyond profit.
Stakeholder Capitalism Hiring
Employers embracing stakeholder capitalism hiring prioritize social impact by aligning recruitment strategies with B-Corp standards, ensuring fair wages, diversity, and environmental responsibility. These organizations integrate stakeholder interests--including employees, communities, and the planet--into their core operations to drive sustainable growth and positive social outcomes.
B-Corp Employment Value Proposition (EVP)
B-Corp organizations enhance their Employment Value Proposition (EVP) by integrating social impact and sustainability into their core business practices, attracting talent motivated by purpose-driven work. Employers adopting B-Corp standards demonstrate a commitment to environmental and social responsibility, resulting in improved employee engagement, retention, and brand reputation.
Social Impact Employer Branding
Employers adopting B-Corp certification demonstrate a heightened commitment to social impact, enhancing employer branding by showcasing accountability in environmental, social, and governance practices. This distinction attracts socially conscious talent and strengthens workplace culture through verified impact-driven initiatives.
Regenerative Hiring Practices
Employers adopting regenerative hiring practices prioritize long-term social impact by integrating B-Corp principles such as environmental stewardship, equity, and community engagement into recruitment and retention strategies. This approach enhances workforce resilience and promotes sustainable organizational growth, distinguishing progressive employers from traditional hiring models.
Certified B Leader Career Pathways
Certified B Leader Career Pathways provide employers with a structured approach to integrating social impact into business operations, aligning profit goals with sustainability and ethical practices. This framework empowers organizations to enhance corporate responsibility, attract mission-driven talent, and drive measurable social and environmental outcomes.
Mission-Led Employer Differentiation
Mission-led employers distinguish themselves by embedding social impact into their core business strategies, outperforming traditional employers in attracting and retaining talent committed to sustainable values. B-Corp organizations leverage certified social and environmental performance standards, providing a transparent and credible framework that amplifies employer differentiation through verified impact-driven operations.
Employer vs B-Corp Organization for social impact. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com