An employer traditionally manages organizational structure and policies, focusing on compliance and performance metrics. A culture designer prioritizes shaping the workplace environment to foster engagement, collaboration, and a sense of belonging among employees. This shift from authoritative management to intentional culture creation enhances overall employee experience and drives long-term retention.
Table of Comparison
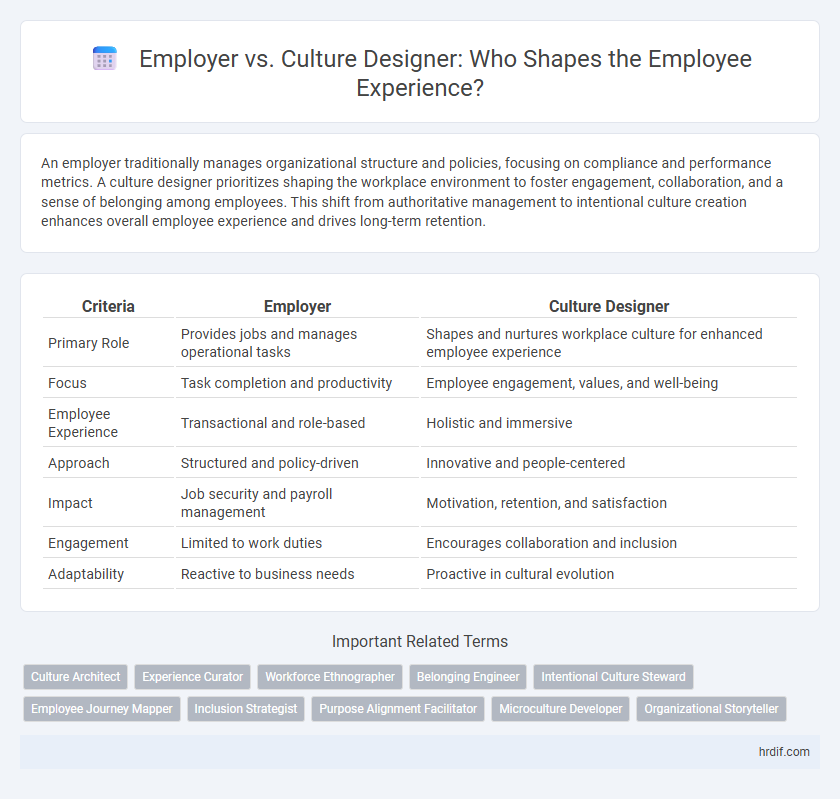
| Criteria | Employer | Culture Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Provides jobs and manages operational tasks | Shapes and nurtures workplace culture for enhanced employee experience |
| Focus | Task completion and productivity | Employee engagement, values, and well-being |
| Employee Experience | Transactional and role-based | Holistic and immersive |
| Approach | Structured and policy-driven | Innovative and people-centered |
| Impact | Job security and payroll management | Motivation, retention, and satisfaction |
| Engagement | Limited to work duties | Encourages collaboration and inclusion |
| Adaptability | Reactive to business needs | Proactive in cultural evolution |
Understanding the Role: Employer vs Culture Designer
Employers primarily manage organizational objectives, compliance, and resource allocation, ensuring operational efficiency and legal adherence. Culture designers focus on shaping employee experience through intentional values, behaviors, and workplace environment, fostering engagement, motivation, and a sense of belonging. Understanding the distinction clarifies how strategic leadership integrates structural management with cultural innovation to enhance overall workforce satisfaction and performance.
Defining Employee Experience: Who Shapes It?
Employers set the foundational framework and policies that influence the overall employee experience through organizational goals and resource allocation. Culture designers, often HR professionals or internal consultants, craft the day-to-day environment by curating values, behaviors, and rituals that directly affect employee engagement and satisfaction. Together, employers provide strategic direction while culture designers operationalize those insights into tangible experiences shaping workforce morale and productivity.
Leadership Styles: Traditional Employer vs Culture Designer
Traditional employers often rely on hierarchical leadership styles that emphasize authority, rules, and top-down decision-making, which can limit employee autonomy and engagement. In contrast, culture designers adopt transformational leadership approaches, fostering collaboration, innovation, and a shared vision that enhances motivation and retention. This shift from control to empowerment significantly improves overall employee experience and organizational culture.
Impact on Workplace Engagement
Employers shape workplace engagement through policies and leadership styles, directly influencing employee motivation and productivity. Culture Designers craft the organizational environment by embedding values and rituals that foster belonging and collaboration, enhancing long-term engagement. Effective collaboration between Employers and Culture Designers drives sustained employee satisfaction and performance.
Authority vs Collaboration in Employee Experience
Employers hold authoritative power to set policies and enforce standards that shape the employee experience, ensuring organizational goals are met with clear directives. Culture designers emphasize collaboration by engaging employees in creating values and workplace norms, fostering a sense of belonging and shared purpose. Balancing authority with collaborative culture design enhances employee motivation, retention, and overall workplace satisfaction.
Talent Acquisition: Employer Brand vs Culture Design
Talent acquisition thrives on a strong employer brand that clearly communicates company values and mission to attract top candidates. Culture design shapes the ongoing employee experience by fostering an environment aligned with those values, enhancing retention and engagement. Prioritizing employer brand builds initial interest, while culture design sustains workforce satisfaction and loyalty.
Measuring Success: Productivity vs Employee Fulfillment
Employers prioritize productivity metrics such as output volume and efficiency to evaluate success, while culture designers emphasize employee fulfillment indicators like engagement scores and workplace satisfaction. Measuring success through productivity alone can overlook critical factors impacting retention and innovation, which are better captured by assessing fulfillment-driven metrics. A balanced approach integrating quantitative productivity data with qualitative employee experience insights delivers a more comprehensive understanding of organizational health.
Navigating Change: Directive vs Adaptive Approaches
Employers implementing directive approaches enforce structured policies and clear expectations to manage employee experience during change, ensuring consistency and accountability. Culture designers adopt adaptive strategies that promote flexibility, innovation, and employee empowerment, fostering resilience in dynamic work environments. Balancing directive controls with adaptive cultural elements optimizes organizational agility and enhances overall employee engagement.
Long-Term Outcomes: Retention and Growth Strategies
Employers focused on long-term retention and growth prioritize creating a culture that aligns with employee values and career aspirations. Culture designers craft experiences that foster engagement, resilience, and innovation, directly impacting employee loyalty and performance. Integrating cultural strategy with talent management drives sustainable organizational success and reduced turnover rates.
The Future of Work: Evolving from Employer to Culture Designer
The future of work demands a shift from traditional employer roles to culture designers who actively shape employee experience through intentional values and environments. Culture designers foster innovation, engagement, and retention by embedding purpose and inclusivity into organizational DNA rather than relying solely on hierarchical management. This evolution enhances workforce agility and aligns company goals with employee well-being, driving sustainable business success.
Related Important Terms
Culture Architect
Culture Architects strategically design organizational values and behaviors to enhance employee experience, driving engagement and productivity beyond traditional employer roles. Their expertise in shaping workplace culture aligns with business goals, fostering innovation and long-term retention by creating a supportive, purpose-driven environment.
Experience Curator
Employers who act as Experience Curators actively shape workplace environments by integrating employee feedback and data-driven insights, enhancing overall engagement and productivity. Unlike traditional Culture Designers, Experience Curators prioritize continuous, personalized employee experiences to foster adaptability and sustained satisfaction.
Workforce Ethnographer
Employers leveraging Workforce Ethnographers gain deep insights into employee behavior and preferences, enabling the design of authentic workplace cultures that enhance engagement and retention. Unlike traditional culture designers, Workforce Ethnographers ground employee experience strategies in real-world observations and data-driven analysis, fostering environments that truly resonate with diverse workforce needs.
Belonging Engineer
Employers who prioritize Belonging Engineers foster inclusive workplaces that enhance employee engagement and retention by designing culture strategies centered on belonging and psychological safety. Unlike traditional culture designers, Belonging Engineers utilize data-driven approaches to systematically build connections and align organizational values with employee identities, resulting in a more cohesive and motivated workforce.
Intentional Culture Steward
An intentional culture steward actively shapes and maintains workplace values, aligning organizational goals with employee behaviors to enhance engagement and productivity. Unlike traditional employers who focus primarily on operational outcomes, culture designers prioritize strategic cultural initiatives that foster a supportive and innovative employee experience.
Employee Journey Mapper
Employer roles focus on organizational goals and resource allocation, whereas Culture Designers prioritize shaping workplace values and fostering engagement. An Employee Journey Mapper strategically analyzes touchpoints within the employee lifecycle to enhance satisfaction, retention, and productivity by tailoring experiences aligned with cultural objectives.
Inclusion Strategist
An Inclusion Strategist within an organization bridges the gap between Employer and Culture Designer roles by embedding diversity and belonging into every facet of the employee experience, fostering innovation and retention. Their expertise drives inclusive policies and practices that align with business objectives while cultivating a workplace culture where all employees feel valued and empowered.
Purpose Alignment Facilitator
Purpose Alignment Facilitators play a critical role in bridging the gap between Employer strategies and Culture Designer initiatives to enhance employee experience. By ensuring that organizational goals align with employee values, they foster a cohesive environment that drives engagement, productivity, and long-term retention.
Microculture Developer
Employers who act as Microculture Developers strategically shape subgroups within the organization to enhance employee experience, fostering collaboration, engagement, and innovation at a granular level. This targeted approach contrasts with broader Culture Designers by emphasizing tailored cultural elements that directly impact daily interactions and team dynamics.
Organizational Storyteller
An Employer shapes the framework of workplace policies and benefits, while a Culture Designer actively crafts the narratives and rituals that define employee engagement and identity. The Organizational Storyteller plays a pivotal role by weaving compelling stories that reinforce company values, foster connection, and enhance the overall employee experience.
Employer vs Culture Designer for employee experience. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com