Employees who work for a single employer often experience stability, consistent income, and clear career progression within one organization. Polyworkers, on the other hand, engage with multiple employers or projects, gaining diverse skills and flexible work schedules but facing challenges in income predictability and workload management. Choosing between single employment and polyworking depends on individual priorities such as job security, variety of work, and work-life balance.
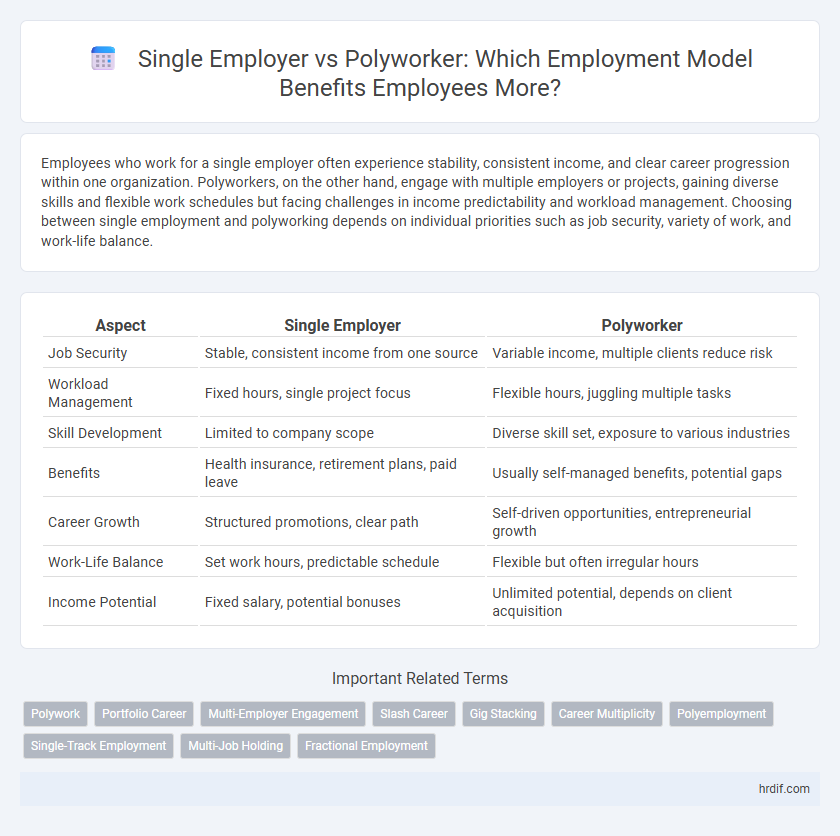
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single Employer | Polyworker |
|---|---|---|
| Job Security | Stable, consistent income from one source | Variable income, multiple clients reduce risk |
| Workload Management | Fixed hours, single project focus | Flexible hours, juggling multiple tasks |
| Skill Development | Limited to company scope | Diverse skill set, exposure to various industries |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | Usually self-managed benefits, potential gaps |
| Career Growth | Structured promotions, clear path | Self-driven opportunities, entrepreneurial growth |
| Work-Life Balance | Set work hours, predictable schedule | Flexible but often irregular hours |
| Income Potential | Fixed salary, potential bonuses | Unlimited potential, depends on client acquisition |
Understanding Single Employer vs Polyworker Models
The Single Employer model involves an employee working exclusively for one organization, fostering deep expertise and stable benefits within a focused corporate structure. In contrast, the Polyworker model allows employees to engage simultaneously in multiple roles across different companies or projects, promoting diverse skill development and flexible income streams. Understanding these models helps employees align career strategies with their goals, balancing job security against adaptability in the evolving workforce.
Advantages of Working for a Single Employer
Working for a single employer provides employees with job stability, consistent income, and clear career progression paths, fostering long-term professional growth. Employees benefit from comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, often unavailable to polyworkers. Additionally, a single-employer setting enhances workplace relationships, team collaboration, and access to specialized training programs.
Benefits of Embracing Polywork as an Employee
Embracing polywork allows employees to diversify their skill sets across multiple roles and industries, enhancing career resilience and increasing earning potential. Engaging in various projects fosters continuous learning and innovation, improving job satisfaction and professional growth. This dynamic approach helps employees build a versatile portfolio that appeals to future employers and creates opportunities beyond a single employer framework.
Job Stability: Single Employer vs Polyworker
Job stability is typically higher for employees with a single employer due to consistent income, established benefits, and clear career progression within one organization. Polyworkers, juggling multiple roles or gigs across different employers, may face income variability but benefit from diversified opportunities and reduced dependency on any single job. The trade-off between steady employment and flexible work arrangements affects long-term financial security and career development strategies.
Skill Development Opportunities in Both Models
Single employers often provide structured skill development programs tailored to specific job roles, enabling employees to deepen expertise within a focused career path. Polyworkers gain diverse skills rapidly by engaging in multiple projects or roles across different industries, fostering adaptability and broad knowledge. Both models offer unique growth opportunities: single employers emphasize specialized training, while polyworkers benefit from varied experiential learning.
Work-Life Balance: Comparing the Two Paths
Single employer roles often provide structured hours and consistent income that can enhance work-life balance through predictability and job stability. Polyworkers juggle multiple jobs or projects, offering variety and potential income growth but may face challenges in managing time and stress levels effectively. Balancing these demands requires strong organizational skills and clear boundaries to maintain personal well-being in either path.
Income Security and Financial Growth
Employees working for a single employer typically experience more stable income security due to consistent salary and benefits, which supports predictable financial planning. Polyworkers, managing multiple income streams from various employers or projects, often face income variability but gain enhanced financial growth potential through diversified earnings. Balancing steady paychecks with multiple revenue sources allows employees to optimize income security while pursuing greater financial advancement.
Career Progression: Traditional vs Polywork Approaches
Career progression in a single employer setting often follows a structured path with clear promotion ladders and defined roles, offering stability and predictable growth. Polyworkers experience accelerated skill development and diverse opportunities by balancing multiple roles across industries, fostering adaptability and broader professional networks. This approach challenges traditional linear career models by emphasizing versatility and continual learning over tenure.
Managing Workload and Burnout Risks
Managing workload effectively is crucial for employees whether they are single employers or polyworkers. Single employers often benefit from focused responsibilities, reducing task-switching and potential burnout, while polyworkers juggle multiple roles that can increase workload complexity but also provide diverse engagement that may buffer stress. Implementing time management strategies and setting clear boundaries helps mitigate burnout risks for both employment types.
Choosing the Best Fit for Your Career Goals
Evaluating single employer roles versus polyworker opportunities depends on your career goals, work-life balance preferences, and skill diversification ambitions. Single employer positions offer stability, clear advancement paths, and consistent benefits, while polyworker roles provide flexibility, varied experience, and potential multiple income streams. Align your choice with your long-term objectives, considering industry demands and personal growth priorities to optimize career satisfaction and financial rewards.
Related Important Terms
Polywork
Polyworkers engage in multiple roles or projects simultaneously, enhancing skills diversity and increasing income streams compared to single employers. This flexible work approach fosters adaptability, continuous learning, and broader professional networks, making it an attractive alternative to traditional single-employer employment.
Portfolio Career
A portfolio career allows employees to diversify their skills and income streams by working multiple roles or projects simultaneously, unlike a single employer arrangement that limits growth to one company's scope. Embracing a polyworker lifestyle fosters adaptability and resilience in rapidly changing job markets, leveraging varied experiences to enhance professional value and job security.
Multi-Employer Engagement
Multi-employer engagement allows employees to diversify income streams, enhancing job security and skill development across various industries. Single-employer models provide stable benefits and streamlined career progression but may limit exposure to diverse professional experiences.
Slash Career
A single employer employee benefits from job stability, consistent income, and focused career growth, while a polyworker in a slash career juggles multiple roles or gigs, enhancing skill diversity and income streams but facing challenges in time management and benefits access. The slash career model suits employees seeking flexibility and varied experiences, leveraging digital platforms to navigate multiple employment opportunities simultaneously.
Gig Stacking
Single employers offer stable income and consistent benefits, while polyworkers leveraging gig stacking diversify earnings by simultaneously managing multiple gig economy jobs, enhancing financial flexibility and skill development. Balancing gig stacking requires effective time management and adaptability to avoid burnout while maximizing income streams across various platforms.
Career Multiplicity
Career multiplicity empowers employees to diversify their skill sets and income streams by balancing roles as single employers or polyworkers, enhancing adaptability in dynamic job markets. Polyworkers leverage multiple part-time positions or freelance gigs, fostering innovation and continuous professional growth, while single employers benefit from focused expertise and stability in career development.
Polyemployment
Polyemployment enables employees to diversify income streams by working with multiple employers or clients, enhancing skill development and job security in a dynamic labor market. Unlike traditional single-employer arrangements, polyworkers benefit from increased flexibility, broader professional networks, and reduced dependency on a single source of income.
Single-Track Employment
Single-track employment offers stability and clear career progression within a single organization, enhancing expertise in a specialized role. In contrast, polyworking diversifies skills across multiple jobs but may dilute focus and long-term growth in a specific profession.
Multi-Job Holding
Multi-job holding can enhance an employee's skill set and income stability by allowing work for multiple employers or engaging in diverse roles within a single company. Balancing responsibilities between a single employer and polyworker status requires effective time management and clear communication to prevent conflicts and maintain productivity.
Fractional Employment
Fractional employment allows polyworkers to diversify income streams by engaging with multiple employers simultaneously, enhancing skills and flexibility compared to traditional single employer arrangements. Employers benefit from fractional employees through access to specialized expertise on a project basis without long-term commitments or full-time salary obligations.
Single Employer vs Polyworker for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com