Managers oversee overall team performance, resource allocation, and strategic goals, ensuring alignment with company objectives. Agile squad leads focus on facilitating Agile practices, removing obstacles, and fostering collaboration within the team to enhance iterative delivery. The distinct roles complement each other by balancing strategic oversight with hands-on team support.
Table of Comparison
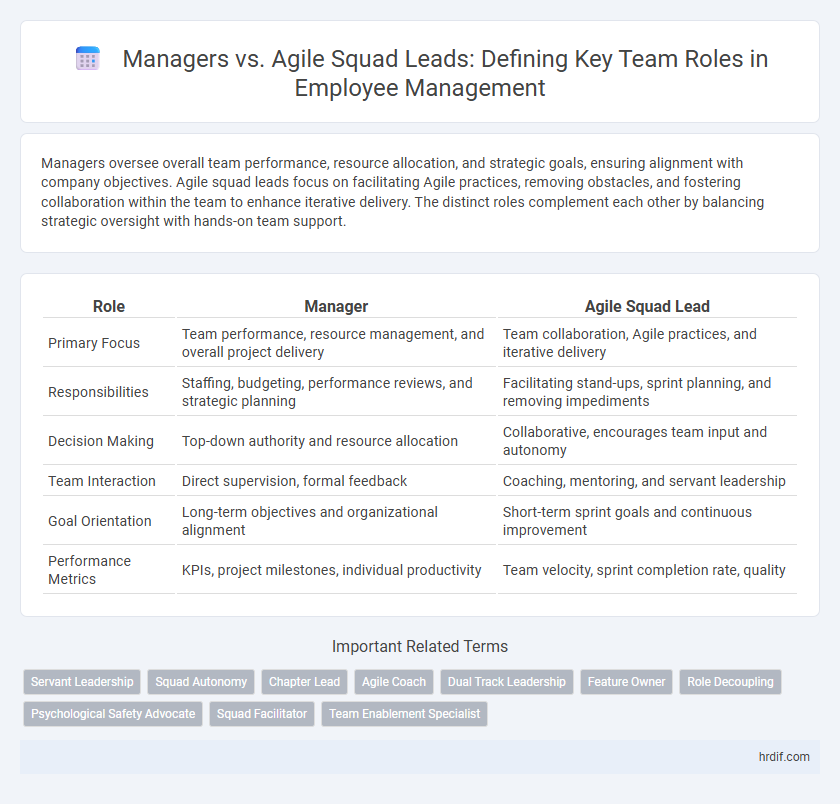
| Role | Manager | Agile Squad Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Team performance, resource management, and overall project delivery | Team collaboration, Agile practices, and iterative delivery |
| Responsibilities | Staffing, budgeting, performance reviews, and strategic planning | Facilitating stand-ups, sprint planning, and removing impediments |
| Decision Making | Top-down authority and resource allocation | Collaborative, encourages team input and autonomy |
| Team Interaction | Direct supervision, formal feedback | Coaching, mentoring, and servant leadership |
| Goal Orientation | Long-term objectives and organizational alignment | Short-term sprint goals and continuous improvement |
| Performance Metrics | KPIs, project milestones, individual productivity | Team velocity, sprint completion rate, quality |
Defining the Roles: Manager vs Agile Squad Lead
Managers oversee team performance, resource allocation, and strategic planning, focusing on organizational hierarchy and long-term objectives. Agile Squad Leads facilitate daily stand-ups, remove impediments, and foster collaboration, emphasizing team autonomy and iterative delivery. Clear role definition ensures efficient workflow and maximizes team productivity by aligning leadership style with project methodologies.
Core Responsibilities: Traditional Management vs Agile Leadership
Traditional managers focus on setting strategic goals, allocating resources, and overseeing performance metrics to ensure departmental alignment and efficiency. Agile squad leads prioritize facilitating collaboration, removing impediments, and enabling self-organizing teams to deliver iterative value continuously. The core responsibilities shift from command-and-control to servant leadership, emphasizing communication, adaptability, and empowerment within Agile frameworks.
Decision-Making Authority: Who Leads the Team?
Managers typically hold formal decision-making authority within an organizational hierarchy, overseeing team performance, resource allocation, and strategic direction. Agile squad leads, however, facilitate team collaboration and empower members to make decisions collectively, promoting autonomy and adaptability in project execution. The distinction lies in managers exercising top-down authority, while Agile leads guide decentralized, team-driven decision processes.
Communication Styles: Directive vs Collaborative Approaches
Managers typically employ a directive communication style, providing clear instructions and expecting adherence to established processes, which ensures accountability and structured decision-making. Agile squad leads favor a collaborative approach, encouraging open dialogue, feedback, and shared ownership to foster team empowerment and adaptability. Understanding these contrasting communication styles helps organizations balance control with flexibility, enhancing team performance and innovation.
Performance Evaluation: Metrics and Methods
Managers typically use traditional performance evaluation metrics such as goal achievement, productivity, and adherence to company policies, while Agile squad leads emphasize iterative feedback, team collaboration, and velocity metrics. Performance evaluation for managers often involves formal reviews and key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with organizational objectives, whereas Agile squad leads rely on continuous assessment techniques like sprint retrospectives and peer evaluations. Combining quantitative metrics with qualitative insights ensures a comprehensive performance evaluation tailored to each team role's unique responsibilities.
Employee Development: Coaching vs Supervising
Managers primarily focus on employee development through structured supervision, setting clear expectations, and performance evaluations to ensure accountability. Agile squad leads emphasize coaching by facilitating collaboration, fostering continuous learning, and empowering team members to take ownership of their growth within dynamic project environments. Both roles contribute to employee development, but coaching by Agile leads promotes adaptability and innovation, while managerial supervision ensures alignment with organizational goals.
Conflict Resolution: Approaches for Managers and Agile Leads
Managers typically use hierarchical authority and formal policies to resolve conflicts, emphasizing structure and accountability within teams. Agile squad leads prioritize collaborative problem-solving and open communication, encouraging consensus-building and adaptability to maintain team cohesion. Both roles require emotional intelligence but differ in leveraging power dynamics versus fostering self-organization to address disputes effectively.
Empowerment and Autonomy: Balancing Control and Flexibility
Managers traditionally provide structured oversight and strategic direction, ensuring alignment with organizational goals while maintaining control over team operations. Agile squad leads foster empowerment by promoting autonomy, encouraging self-organization, and enabling team members to make decisions that accelerate innovation and responsiveness. Balancing control and flexibility requires integrating managerial accountability with the adaptive, collaborative culture championed by Agile leadership, optimizing both performance and employee engagement.
Adapting to Change: Traditional Hierarchy vs Agile Mindset
Managers in traditional hierarchies often rely on structured decision-making and top-down communication to maintain control, which can slow adaptability during rapid change. Agile squad leads foster collaborative environments, empowering team members to quickly pivot and innovate in response to evolving project demands. The agile mindset prioritizes continuous feedback and flexibility, enabling teams to respond proactively rather than reactively to change.
Impact on Team Culture: Leadership Influence
Managers traditionally establish structure and enforce policies, shaping team culture through formal authority and performance management. Agile squad leads foster collaboration and adaptability by promoting servant leadership and empowering team members to self-organize. The leadership influence of managers often drives accountability and stability, while agile squad leads cultivate innovation and continuous improvement within the team culture.
Related Important Terms
Servant Leadership
Managers typically focus on hierarchical oversight and resource allocation, whereas Agile squad leads prioritize servant leadership by empowering teams, removing obstacles, and fostering collaboration to enhance productivity and innovation. The Agile squad lead cultivates a supportive environment that emphasizes team autonomy and continuous improvement, aligning leadership with Agile principles rather than traditional command-and-control structures.
Squad Autonomy
Agile squad leads empower teams by fostering squad autonomy, enabling self-organization and faster decision-making compared to traditional managers who often rely on hierarchical control and directive oversight. This shift enhances innovation, accountability, and team engagement by prioritizing collaborative leadership and minimizing dependency on centralized authority.
Chapter Lead
Chapter Leads act as managerial figures within Agile environments, focusing on fostering technical excellence and skill development across squads rather than directly managing daily tasks. Their primary role centers on mentoring team members and aligning individual growth with organizational goals, distinguishing them from traditional managers who oversee operational and administrative responsibilities.
Agile Coach
An Agile Coach guides Agile squad leads by fostering self-organizing teams and empowering managers to shift from directive roles to supportive facilitators. This dual approach enhances team collaboration, accelerates iterative delivery, and drives continuous improvement in Agile environments.
Dual Track Leadership
Managers provide strategic oversight, resource allocation, and performance management, while Agile squad leads focus on facilitating team collaboration, removing impediments, and driving iterative delivery. Dual Track Leadership combines these roles to enhance team alignment, accelerate decision-making, and foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
Feature Owner
Managers typically oversee broader organizational objectives and resource allocation, ensuring alignment with company goals, while Agile squad leads focus on enabling cross-functional teams to deliver specific features efficiently within iterations. As Feature Owners, Agile squad leads prioritize backlog grooming, stakeholder collaboration, and continuous value delivery, driving product increments that meet user needs and business requirements.
Role Decoupling
Managers primarily focus on strategic oversight, resource allocation, and performance evaluation, while Agile squad leads emphasize team facilitation, sprint planning, and continuous delivery within cross-functional teams. Decoupling these roles allows organizations to enhance agility by separating decision-making authority from day-to-day team support and process improvement.
Psychological Safety Advocate
Managers traditionally oversee performance and resource allocation, while Agile squad leads prioritize fostering psychological safety by encouraging open communication, risk-taking, and team trust. Emphasizing psychological safety helps Agile squads innovate effectively and maintain high engagement compared to conventional managerial approaches.
Squad Facilitator
Squad Facilitators prioritize servant leadership and team empowerment, focusing on removing obstacles and enabling Agile squads to deliver value efficiently, unlike traditional Managers who emphasize hierarchical control and direct supervision. By fostering collaboration and continuous improvement, Squad Facilitators drive adaptive workflows and enhance team autonomy within Agile frameworks.
Team Enablement Specialist
Managers oversee team performance and strategic alignment, focusing on resource management and organizational goals, while Agile squad leads act as Team Enablement Specialists by facilitating collaboration, removing obstacles, and nurturing continuous improvement within cross-functional teams. The Agile squad lead emphasizes empowering team members through coaching and fostering a culture of accountability and adaptability to drive high-performance delivery.
Managers vs Agile squad lead for team role. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com