Full-time employees commit to a standard workweek, offering consistent availability and deep integration within company culture, which supports long-term projects and team cohesion. Fractional employees work part-time or on specific projects, providing flexible expertise without the overhead of a full-time salary or benefits. Choosing between these roles depends on business needs for flexibility, budget constraints, and the scope of work requiring dedicated attention.
Table of Comparison
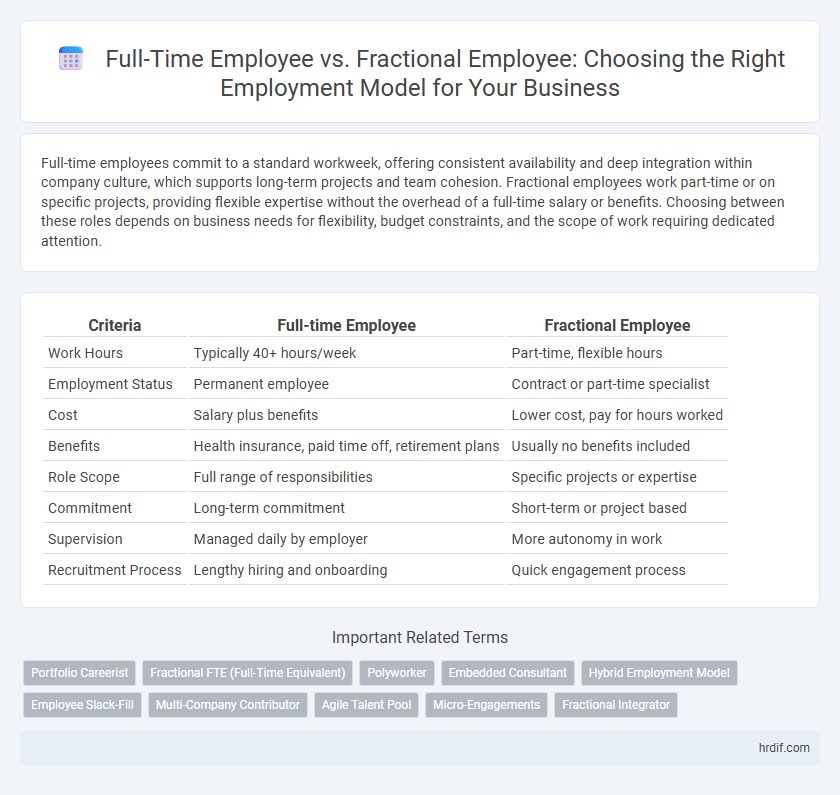
| Criteria | Full-time Employee | Fractional Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Work Hours | Typically 40+ hours/week | Part-time, flexible hours |
| Employment Status | Permanent employee | Contract or part-time specialist |
| Cost | Salary plus benefits | Lower cost, pay for hours worked |
| Benefits | Health insurance, paid time off, retirement plans | Usually no benefits included |
| Role Scope | Full range of responsibilities | Specific projects or expertise |
| Commitment | Long-term commitment | Short-term or project based |
| Supervision | Managed daily by employer | More autonomy in work |
| Recruitment Process | Lengthy hiring and onboarding | Quick engagement process |
Defining Full-Time and Fractional Employee Roles
Full-time employees typically hold a permanent position within an organization, working a standard 35-40 hour workweek with consistent responsibilities and access to full benefits. Fractional employees, also known as part-time or contract workers, engage in fewer hours or specific projects, offering flexibility and specialized skills without long-term commitments. Defining these roles clearly helps organizations optimize workforce allocation, cost management, and project delivery efficiency.
Key Differences: Full-Time vs Fractional Employment
Full-time employees typically work 35-40 hours per week with fixed salaries and comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Fractional employees engage on a part-time or project basis, providing specialized skills without the obligation of full-time hours or traditional benefits. The main differences lie in work hours, compensation structure, job security, and access to company benefits.
Benefits of Full-Time Employment for Employees
Full-time employees receive comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and job security, which are rarely available to fractional employees. They often have access to professional development opportunities and employee assistance programs that support long-term career growth. Consistent work hours and income stability provide financial security and enhance overall work-life balance for full-time employees.
Advantages of Fractional Employment for Workers
Fractional employees benefit from greater flexibility in work hours and project selection, allowing them to balance multiple roles or personal commitments effectively. They often gain diverse industry experience and skill enhancement by working with various organizations simultaneously. This employment model can lead to improved work-life balance and increased job satisfaction compared to traditional full-time roles.
Work-Life Balance: Full-Time vs Fractional Roles
Full-time employees typically experience structured work hours that may limit personal time, impacting work-life balance due to longer commitments and fixed schedules. Fractional employees benefit from flexible hours and project-based roles, allowing greater autonomy and improved work-life harmony. Organizations leveraging fractional roles can attract talent seeking balance, reducing burnout and increasing overall job satisfaction.
Job Security in Full-Time and Fractional Positions
Full-time employees typically enjoy greater job security due to stable contracts, consistent income, and access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Fractional employees, often engaged on a part-time or project basis, face less job security as their roles depend on fluctuating business needs and lack comprehensive benefits. Employers benefit from fractional employees' flexibility, while full-time employees gain protection through established organizational policies and labor laws.
Compensation: Comparing Salaries and Benefits
Full-time employees typically receive a fixed annual salary with comprehensive benefits packages including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, reflecting their ongoing commitment to the company. Fractional employees are compensated based on the hours worked or project scope, often receiving higher hourly rates but limited or no access to traditional benefits, making their total compensation more variable and project-dependent. Organizations balance cost efficiency and talent needs by leveraging fractional employees for specialized roles, while full-time employees provide consistent workforce stability and long-term value.
Career Growth Opportunities: Which Role Suits You?
Full-time employees often benefit from structured career growth opportunities, including promotions, training programs, and employee benefits that support long-term development. Fractional employees gain diverse experience by working across multiple companies or projects, enhancing their skills and networking potential but may face limited formal advancement within any single organization. Selecting the right role depends on your career goals: choose full-time employment for stability and internal progression or fractional roles for flexibility and broad skill acquisition.
Flexibility and Autonomy in Employee Roles
Full-time employees typically have fixed schedules with less flexibility, making their roles more structured and closely managed by employers. Fractional employees enjoy greater autonomy, allowing them to choose when and how to complete tasks within agreed-upon deadlines, boosting productivity for project-based or specialized work. This flexibility in fractional roles enhances adaptability while full-time roles provide consistent availability and integration within company culture.
Choosing the Right Role: Full-Time or Fractional?
Choosing between a full-time employee and a fractional employee depends on the organization's workload and budget flexibility. Full-time employees offer consistent availability, deeper company integration, and long-term commitment, ideal for roles requiring ongoing responsibilities and team collaboration. Fractional employees provide specialized expertise and cost-efficiency for project-based tasks or fluctuating demands, delivering targeted skills without the expenses of full-time employment.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Careerist
Full-time employees dedicate 40+ hours weekly to a single employer, offering stability and comprehensive benefits, while fractional employees balance multiple part-time roles, enabling portfolio careerists to diversify skills and income streams across various industries. This strategic approach allows portfolio careerists to enhance professional agility, maintain work-life balance, and reduce dependency on a single employer's economic fluctuations.
Fractional FTE (Full-Time Equivalent)
Fractional employees contribute a portion of a full-time equivalent (FTE), allowing organizations to optimize labor costs and access specialized skills without the commitment of a full-time role. Utilizing fractional FTEs enhances workforce flexibility and supports project-specific needs while maintaining proportional workload balance compared to traditional full-time employees.
Polyworker
Full-time employees typically engage exclusively in one company with consistent hours and full benefits, whereas fractional employees work part-time or project-based across multiple organizations, offering specialized skills and flexibility. Polyworkers embrace this fractional model, leveraging diverse roles to maximize productivity and innovation through varied expertise and networks.
Embedded Consultant
Full-time employees provide consistent, long-term engagement with embedded consultant roles, ensuring deep integration within the organization's teams and culture. Fractional employees offer specialized expertise on a part-time basis, allowing companies to access high-level consultancy without the commitment of a full-time salary or benefits.
Hybrid Employment Model
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and deep organizational integration, while fractional employees offer specialized expertise and cost efficiency for specific projects; the hybrid employment model combines these advantages by balancing steady operational roles with flexible, targeted skill deployment. This approach enhances workforce agility, optimizes resource allocation, and supports scalable growth by leveraging both committed full-time staff and on-demand fractional talent.
Employee Slack-Fill
Full-time employees offer consistent availability and full engagement in Slack communication channels, ensuring seamless collaboration and real-time problem-solving across projects. Fractional employees provide specialized skills on a part-time basis, optimizing resource allocation but potentially requiring clear protocols to maintain responsiveness and integration within Slack workflows.
Multi-Company Contributor
Full-time employees typically dedicate their full working hours to a single employer, ensuring consistent availability and deep integration within one company's culture and processes. Fractional employees, often engaged as multi-company contributors, allocate their specialized skills across multiple organizations, offering flexibility and diverse expertise but requiring effective time management and clear role delineation.
Agile Talent Pool
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and deep organizational knowledge, essential for long-term projects and maintaining core business functions within an Agile Talent Pool. Fractional employees offer specialized skills and flexible engagement, enabling rapid scaling and targeted expertise to adapt to dynamic project demands.
Micro-Engagements
Full-time employees provide consistent availability and deep organizational integration, ideal for sustained project demands and comprehensive role responsibilities in micro-engagements. Fractional employees offer flexible, specialized expertise for targeted tasks, enabling cost-effective resource allocation and adaptability in short-term or part-time micro-engagement roles.
Fractional Integrator
A Fractional Integrator offers specialized leadership by working part-time to align company operations and strategy, providing flexible, cost-effective expertise compared to a Full-time Employee. This model optimizes resource allocation while maintaining executive-level decision-making critical for scaling business functions efficiently.
Full-time Employee vs Fractional Employee for employee roles Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com