QA Engineers ensure software quality by designing test plans, executing manual tests, and identifying defects throughout the development cycle. Test Automation Specialists focus on creating and maintaining automated test scripts to increase testing efficiency and coverage, often integrating these automated tests into continuous integration pipelines. Both roles complement each other in development by combining thorough manual testing expertise with scalable automated testing solutions to deliver robust software.
Table of Comparison
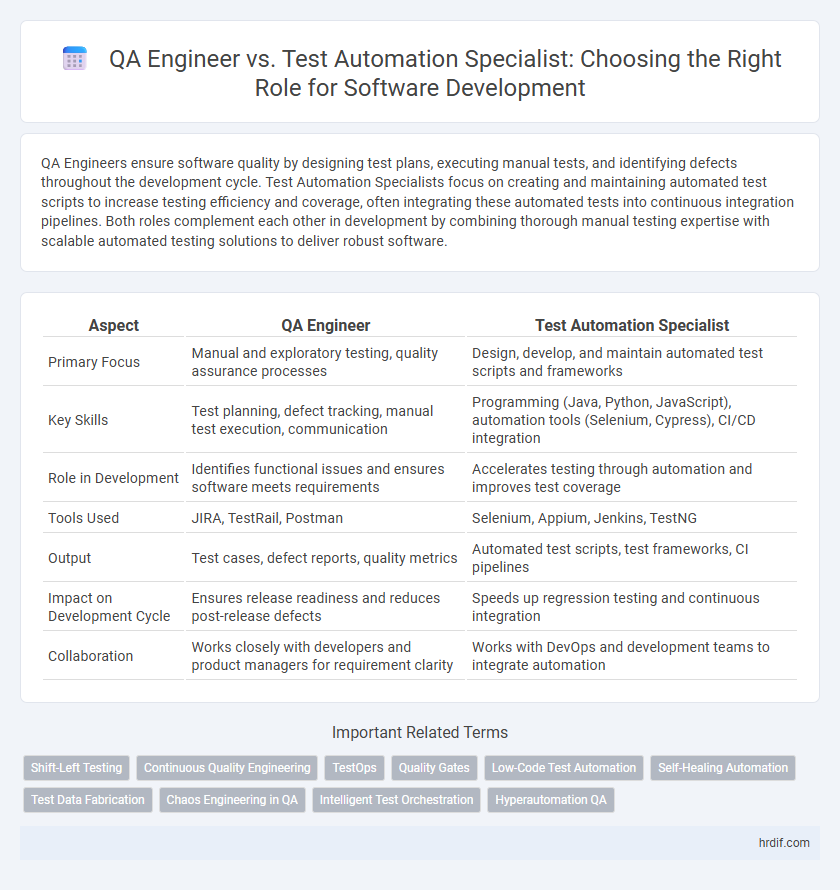
| Aspect | QA Engineer | Test Automation Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Manual and exploratory testing, quality assurance processes | Design, develop, and maintain automated test scripts and frameworks |
| Key Skills | Test planning, defect tracking, manual test execution, communication | Programming (Java, Python, JavaScript), automation tools (Selenium, Cypress), CI/CD integration |
| Role in Development | Identifies functional issues and ensures software meets requirements | Accelerates testing through automation and improves test coverage |
| Tools Used | JIRA, TestRail, Postman | Selenium, Appium, Jenkins, TestNG |
| Output | Test cases, defect reports, quality metrics | Automated test scripts, test frameworks, CI pipelines |
| Impact on Development Cycle | Ensures release readiness and reduces post-release defects | Speeds up regression testing and continuous integration |
| Collaboration | Works closely with developers and product managers for requirement clarity | Works with DevOps and development teams to integrate automation |
Overview: QA Engineer and Test Automation Specialist Roles
QA Engineers focus on designing and executing manual test cases to ensure software quality, identifying defects through exploratory and regression testing. Test Automation Specialists develop and maintain automated test scripts using tools like Selenium or Appium to increase testing efficiency and coverage. Both roles collaborate closely with development teams to improve product reliability and speed up release cycles.
Key Responsibilities Compared
QA Engineers focus on designing comprehensive test plans, executing manual and exploratory tests, and ensuring product quality through defect identification and reporting. Test Automation Specialists develop, maintain, and optimize automated test scripts and frameworks to increase testing efficiency and coverage within continuous integration pipelines. Both roles collaborate closely to improve software reliability, but QA Engineers emphasize test strategy and manual validation, while Test Automation Specialists prioritize automation tools and scripting expertise.
Required Skills and Technical Competencies
QA Engineers require strong analytical skills, proficiency in manual testing methodologies, and a deep understanding of software development life cycles to identify defects and ensure product quality. Test Automation Specialists must possess expertise in programming languages such as Python or Java, experience with automation tools like Selenium or Appium, and a solid grasp of continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to develop and maintain automated test scripts. Both roles demand knowledge of version control systems, debugging techniques, and effective communication skills for collaboration within agile development environments.
Educational Background and Certifications
QA Engineers typically hold a bachelor's degree in computer science, software engineering, or information technology, with certifications such as ISTQB Foundation Level emphasizing manual testing fundamentals. Test Automation Specialists often possess similar educational foundations but prioritize certifications in automation tools like Selenium, Certified Test Automation Engineer (CTAE), or advanced programming skills in languages such as Python or Java. Emphasizing specialized certifications in test automation frameworks reflects the evolving industry demand for efficient, scalable testing solutions in software development.
Daily Workflow Differences
QA Engineers focus on designing and executing manual test cases, analyzing requirements, and documenting defects to ensure software quality throughout development. Test Automation Specialists primarily develop, maintain, and optimize automated testing scripts using tools like Selenium or Appium to improve test efficiency and coverage. Daily workflows differ as QA Engineers emphasize exploratory testing and collaboration with developers, while Automation Specialists concentrate on scripting, framework development, and continuous integration pipeline integration.
Tools and Technologies Used
QA Engineers typically use manual testing tools such as JIRA, TestRail, and Selenium for test case management and defect tracking, emphasizing thorough exploratory testing. Test Automation Specialists focus on scripting and frameworks like Selenium WebDriver, Appium, Jenkins, and Cucumber to build automated test suites and integrate continuous testing into CI/CD pipelines. Both roles require proficiency in programming languages like Java, Python, or JavaScript, but automation specialists prioritize advanced coding skills and automation frameworks to enhance development efficiency and software quality.
Impact on Development Process
QA Engineers play a crucial role in the development process by thoroughly identifying defects and ensuring quality through manual and exploratory testing, which helps maintain software reliability. Test Automation Specialists significantly accelerate development cycles by designing and implementing automated test scripts, enabling continuous integration and faster feedback loops. Together, they optimize the development pipeline, reduce release times, and enhance overall product quality.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
QA Engineers gain broad experience in manual and automated testing, building expertise in test design, defect management, and quality assurance processes that prepare them for roles in test lead or quality manager positions. Test Automation Specialists develop advanced skills in scripting, automation frameworks, and CI/CD integration, positioning them for senior automation architect or DevOps engineer roles with higher technical demands. Career advancement for both roles benefits from continuous learning in emerging tools and methodologies, but Test Automation Specialists often experience faster growth due to the increasing demand for automation in development pipelines.
Salary Trends and Job Market Demand
QA Engineers and Test Automation Specialists show distinct salary trends influenced by growing demand for software quality assurance and automation skills. Test Automation Specialists typically command higher salaries, reflecting the premium on expertise in scripting, frameworks, and CI/CD integration within the development pipeline. Job market demand favors Test Automation Specialists due to increasing adoption of DevOps practices and the need for scalable, automated testing solutions.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career
QA Engineers focus on identifying bugs and ensuring software quality through manual and exploratory testing, emphasizing comprehensive understanding of application behavior. Test Automation Specialists design and implement automated test scripts to increase testing efficiency and coverage, leveraging programming skills and tools like Selenium and Jenkins. Choosing between these roles depends on your preference for hands-on manual testing versus coding-driven automation and your interest in continuous integration and deployment environments.
Related Important Terms
Shift-Left Testing
QA Engineers drive Shift-Left Testing by integrating early defect detection and quality assurance practices into the development lifecycle, enhancing collaboration with developers to prevent issues before code reaches later stages. Test Automation Specialists focus on designing and implementing automated test scripts that enable continuous integration pipelines to quickly identify regressions and maintain high code quality during rapid development cycles.
Continuous Quality Engineering
QA Engineers ensure continuous quality by designing and executing comprehensive manual and exploratory tests, identifying defects early in the development cycle to maintain software reliability. Test Automation Specialists accelerate Continuous Quality Engineering through scripting and maintaining automated test suites that integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling rapid and consistent validation of code changes.
TestOps
QA Engineers primarily focus on manual and exploratory testing to ensure software quality, while Test Automation Specialists design and maintain automated test frameworks to accelerate continuous integration and delivery. In the context of TestOps, Test Automation Specialists play a crucial role by integrating automated tests into DevOps pipelines, enabling faster feedback loops and more reliable release cycles.
Quality Gates
QA Engineers ensure quality gates are met by designing comprehensive test plans and performing manual testing to validate functionality, usability, and compliance. Test Automation Specialists optimize these quality gates by developing and maintaining automated test scripts that increase coverage and reduce regression testing time in continuous integration pipelines.
Low-Code Test Automation
QA Engineers ensure software quality through manual testing and process analysis, while Test Automation Specialists focus on creating automated test scripts to accelerate development cycles. Low-code test automation platforms empower both roles by enabling rapid, user-friendly creation of reusable tests, reducing maintenance efforts and improving testing efficiency across development teams.
Self-Healing Automation
QA Engineers ensure software quality through manual testing and validation, while Test Automation Specialists design and maintain automated test scripts with a focus on self-healing automation frameworks that adapt to code changes and reduce maintenance overhead. Self-healing automation enhances development efficiency by automatically detecting UI or API modifications and updating tests, minimizing downtime and improving continuous integration workflows.
Test Data Fabrication
QA Engineers ensure comprehensive test data fabrication by designing diverse datasets to validate software functionality and reliability, emphasizing manual and exploratory testing scenarios. Test Automation Specialists leverage advanced scripting and tools to automate the generation and management of large-scale test data, optimizing regression testing and continuous integration pipelines.
Chaos Engineering in QA
QA Engineers focus on manual and exploratory testing to ensure software quality, while Test Automation Specialists design and implement automated test scripts to accelerate regression testing cycles. Chaos Engineering in QA introduces controlled system failures and resilience testing, enabling both roles to validate system robustness and identify potential points of failure in development environments.
Intelligent Test Orchestration
QA Engineers specialize in designing comprehensive test strategies and performing manual testing to ensure software quality, while Test Automation Specialists focus on developing and maintaining automated test scripts to accelerate regression testing. Intelligent Test Orchestration optimizes both roles by dynamically prioritizing tests based on code changes and risk analysis, enhancing efficiency and reducing testing cycles in development pipelines.
Hyperautomation QA
QA Engineers ensure software quality through manual testing, defect tracking, and requirement analysis, while Test Automation Specialists design and implement automated test scripts to accelerate testing cycles. In Hyperautomation QA, Test Automation Specialists leverage AI-driven tools and robotic process automation to create scalable, intelligent testing frameworks that optimize continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
QA Engineer vs Test Automation Specialist for Development. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com