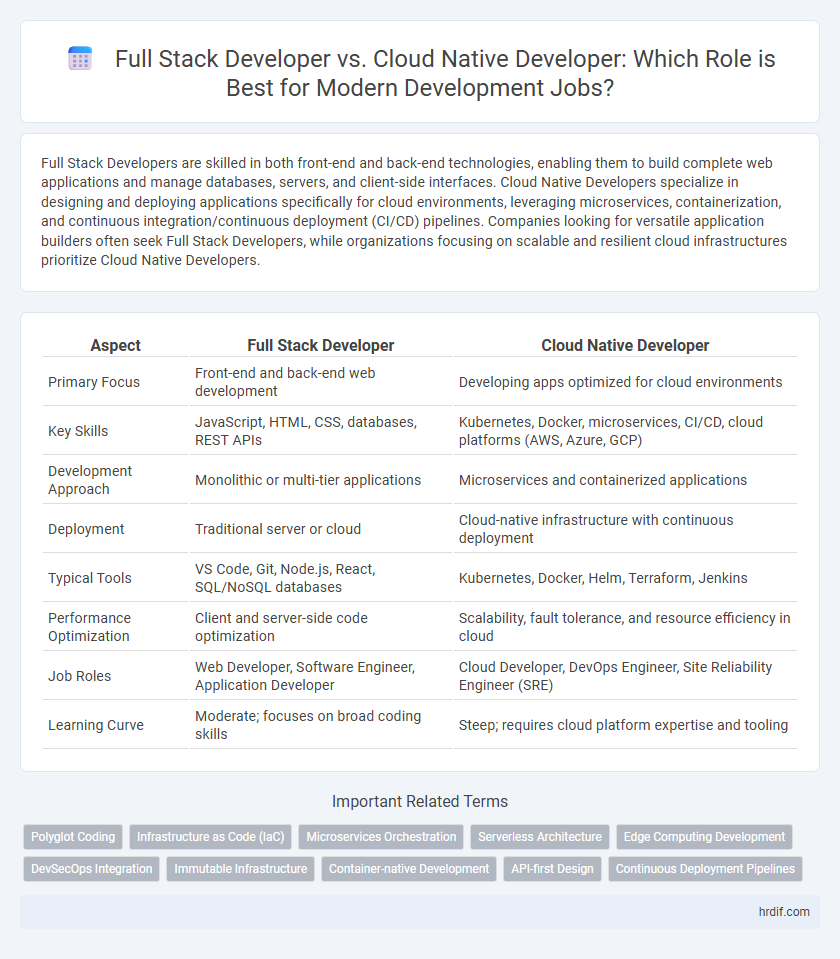
Full Stack Developers are skilled in both front-end and back-end technologies, enabling them to build complete web applications and manage databases, servers, and client-side interfaces. Cloud Native Developers specialize in designing and deploying applications specifically for cloud environments, leveraging microservices, containerization, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Companies looking for versatile application builders often seek Full Stack Developers, while organizations focusing on scalable and resilient cloud infrastructures prioritize Cloud Native Developers.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Full Stack Developer | Cloud Native Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Front-end and back-end web development | Developing apps optimized for cloud environments |
| Key Skills | JavaScript, HTML, CSS, databases, REST APIs | Kubernetes, Docker, microservices, CI/CD, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) |
| Development Approach | Monolithic or multi-tier applications | Microservices and containerized applications |
| Deployment | Traditional server or cloud | Cloud-native infrastructure with continuous deployment |
| Typical Tools | VS Code, Git, Node.js, React, SQL/NoSQL databases | Kubernetes, Docker, Helm, Terraform, Jenkins |
| Performance Optimization | Client and server-side code optimization | Scalability, fault tolerance, and resource efficiency in cloud |
| Job Roles | Web Developer, Software Engineer, Application Developer | Cloud Developer, DevOps Engineer, Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) |
| Learning Curve | Moderate; focuses on broad coding skills | Steep; requires cloud platform expertise and tooling |
Overview of Full Stack Developer and Cloud Native Developer Roles
Full Stack Developers specialize in creating and maintaining both client-side and server-side applications, working with front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and back-end frameworks such as Node.js, Django, or Ruby on Rails. Cloud Native Developers focus on building scalable, resilient applications designed specifically for cloud environments using containerization tools like Docker, orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, and microservices architecture. Both roles require strong programming skills, but Cloud Native Developers emphasize cloud infrastructure, automation, and deployment strategies to optimize application performance and scalability.
Core Responsibilities: Full Stack vs Cloud Native Developer
Full Stack Developers manage end-to-end development, handling both front-end interfaces and back-end server logic, ensuring seamless integration across the application stack. Cloud Native Developers specialize in creating scalable, resilient applications designed specifically for cloud environments, using microservices architecture, containerization, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes. While Full Stack roles emphasize broad programming skills across multiple layers, Cloud Native roles require expertise in cloud platforms, DevOps practices, and infrastructure automation.
Required Technical Skills and Tools
Full Stack Developers require expertise in front-end frameworks like React or Angular, back-end technologies such as Node.js or Django, and databases including MySQL or MongoDB, alongside proficiency in version control systems like Git. Cloud Native Developers focus on containerization tools like Docker, orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes, and are skilled in microservices architecture, serverless computing, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Both roles demand strong coding skills but differ in their emphasis on traditional application development versus scalable, cloud-first infrastructure management.
Typical Day-to-Day Tasks
Full Stack Developers typically handle both front-end and back-end development, managing databases, server logic, and user interface design within a single project framework, using technologies like JavaScript, React, Node.js, and SQL. Cloud Native Developers focus on building and deploying scalable applications using microservices architecture, container orchestration tools such as Kubernetes, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Both roles prioritize collaboration with DevOps teams and use version control systems like Git, but Cloud Native Developers emphasize cloud infrastructure management and automation more heavily in their daily tasks.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Full Stack Developers benefit from versatile skill sets across front-end and back-end technologies, enabling career growth in diverse projects and leadership roles in traditional and startup environments. Cloud Native Developers specialize in scalable, containerized applications using Kubernetes and microservices, positioning themselves at the forefront of modern infrastructure and DevOps integration for advanced career trajectories. Demand for Cloud Native expertise is growing rapidly, offering higher salary potential and opportunities in cutting-edge cloud computing sectors compared to more generalized full stack roles.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Full Stack Developers remain essential for versatile application development, with steady demand across startups and established businesses seeking broad programming expertise in JavaScript, Python, and Ruby. Cloud Native Developers experience rapid growth driven by enterprises adopting Kubernetes, Docker, and microservices architectures to optimize scalable, resilient systems in public and hybrid cloud environments. Market trends indicate a shift favoring Cloud Native expertise due to increased cloud migration, yet Full Stack skills ensure relevance for end-to-end web and mobile development projects.
Salary Comparison: Full Stack vs Cloud Native
Full Stack Developers typically earn an average salary ranging from $80,000 to $120,000 annually, depending on experience and location. Cloud Native Developers command higher salaries, often between $110,000 and $150,000, due to expertise in containerization, microservices, and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure. Demand for Cloud Native skills drives salary premiums in tech hubs such as San Francisco and Seattle, where cloud adoption is rapidly expanding.
Suitable Industries and Work Environments
Full Stack Developers excel in diverse industries such as e-commerce, fintech, and media, thriving in startups and agile development teams where versatility in front-end and back-end technologies is crucial. Cloud Native Developers are highly suited for sectors like cloud service providers, telecommunications, and large-scale SaaS companies, working primarily in DevOps-driven environments that emphasize containerization, microservices, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Both roles demand collaboration but differ in specialization, with Full Stack Developers focusing on comprehensive application development and Cloud Native Developers optimizing applications for cloud infrastructure.
Key Challenges and Learning Curves
Full Stack Developers face the challenge of mastering a wide range of technologies spanning front-end, back-end, databases, and APIs, requiring continuous learning to stay updated with evolving frameworks and programming languages. Cloud Native Developers must overcome the complexities of designing, deploying, and managing applications optimized for cloud environments, including containerization, microservices architecture, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes. The steep learning curve for Cloud Native Developers involves deep understanding of cloud infrastructure, DevOps practices, and scalability strategies, whereas Full Stack Developers focus more on integrating and maintaining full application stacks efficiently.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Role Fits You Best?
Full Stack Developers excel in building comprehensive applications by mastering both front-end and back-end technologies like JavaScript, React, Node.js, and databases, offering versatility in traditional and web development projects. Cloud Native Developers specialize in designing scalable, resilient applications using microservices, containers, Kubernetes, and cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, emphasizing automation and continuous delivery. Choosing the right path depends on your interest in end-to-end development versus cloud infrastructure and your willingness to engage with platform-specific tools and DevOps practices.
Related Important Terms
Polyglot Coding
Full Stack Developers excel in polyglot coding by integrating diverse programming languages across front-end and back-end systems to deliver cohesive applications, while Cloud Native Developers leverage polyglot coding to build scalable, containerized microservices that operate efficiently within cloud infrastructures. Mastery in multiple programming languages enables both roles to optimize performance and adaptability, with Full Stack Developers focusing on end-to-end application development and Cloud Native Developers emphasizing cloud-optimized architecture and deployment.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Full Stack Developers typically focus on building end-to-end applications with expertise in both frontend and backend technologies, while Cloud Native Developers specialize in designing scalable applications optimized for cloud environments using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Pulumi. Mastery of IaC is crucial for Cloud Native Developers to automate infrastructure deployment, enhance scalability, and ensure consistent environments, distinguishing their role from traditional Full Stack Developers.
Microservices Orchestration
Full Stack Developers typically manage frontend and backend development spanning multiple layers of the application, while Cloud Native Developers focus on building scalable, resilient applications using microservices orchestration tools like Kubernetes and Docker Swarm. Mastery in microservices orchestration is crucial for Cloud Native Developers to enable dynamic scaling, automated deployment, and seamless communication between distributed services within cloud environments.
Serverless Architecture
Full Stack Developers manage the entire application lifecycle with a broad skill set, while Cloud Native Developers specialize in building and deploying scalable applications using cloud services and serverless architecture, emphasizing microservices and event-driven models. Serverless architecture allows Cloud Native Developers to optimize resource utilization and reduce operational overhead by leveraging functions-as-a-service (FaaS) platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
Edge Computing Development
Full Stack Developers handle both frontend and backend web development, creating end-to-end applications with broad technology stacks, whereas Cloud Native Developers specialize in designing scalable, microservices-based applications optimized for cloud environments. In Edge Computing Development, Cloud Native Developers leverage containerization and orchestration tools like Kubernetes to deploy resilient services closer to data sources, enhancing latency and performance beyond traditional full stack roles.
DevSecOps Integration
Full Stack Developers often handle end-to-end application development, integrating DevSecOps practices by embedding security in both frontend and backend coding and deployment pipelines. Cloud Native Developers specialize in building scalable, containerized applications with a strong emphasis on DevSecOps automation, leveraging cloud infrastructure to enforce continuous security and compliance throughout the development lifecycle.
Immutable Infrastructure
Full Stack Developers typically manage end-to-end application development, including front-end interfaces and back-end services, while Cloud Native Developers specialize in building scalable, resilient applications optimized for cloud environments using immutable infrastructure to ensure consistency and rapid deployment. Emphasizing immutable infrastructure in Cloud Native roles enhances automation, reduces configuration drift, and boosts system reliability compared to traditional full stack development methods.
Container-native Development
Full Stack Developers manage both front-end and back-end development, often using traditional web frameworks, while Cloud Native Developers specialize in container-native development, leveraging Kubernetes and microservices to build scalable, resilient applications. Container-native development emphasizes automated deployment, orchestration, and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, critical for modern cloud infrastructure.
API-first Design
Full Stack Developers integrate API-first design principles to build seamless user interfaces and backend services, ensuring consistent data flow across multiple platforms. Cloud Native Developers prioritize API-first architectures to create scalable, microservices-based applications optimized for dynamic cloud environments and rapid deployment cycles.
Continuous Deployment Pipelines
Full Stack Developers integrate Continuous Deployment pipelines to streamline application updates across front-end and back-end environments, ensuring rapid feature delivery and bug fixes. Cloud Native Developers design and optimize these pipelines specifically for containerized microservices and cloud infrastructure, leveraging tools like Kubernetes and Jenkins to enable automated scaling and resilience.
Full Stack Developer vs Cloud Native Developer for job roles. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com