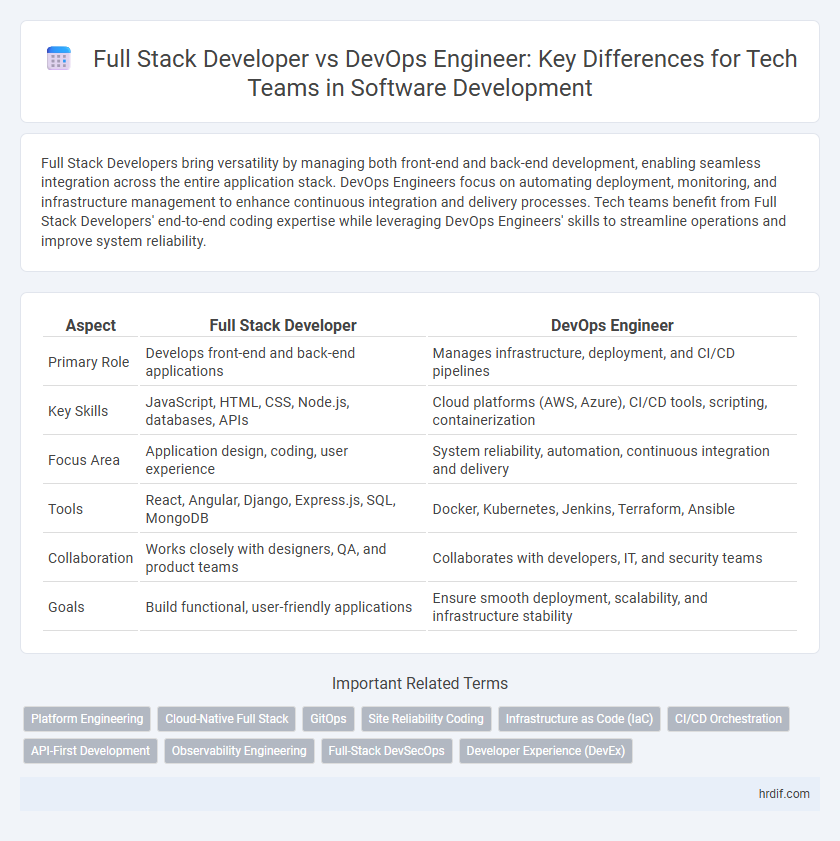
Full Stack Developers bring versatility by managing both front-end and back-end development, enabling seamless integration across the entire application stack. DevOps Engineers focus on automating deployment, monitoring, and infrastructure management to enhance continuous integration and delivery processes. Tech teams benefit from Full Stack Developers' end-to-end coding expertise while leveraging DevOps Engineers' skills to streamline operations and improve system reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Full Stack Developer | DevOps Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Develops front-end and back-end applications | Manages infrastructure, deployment, and CI/CD pipelines |
| Key Skills | JavaScript, HTML, CSS, Node.js, databases, APIs | Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure), CI/CD tools, scripting, containerization |
| Focus Area | Application design, coding, user experience | System reliability, automation, continuous integration and delivery |
| Tools | React, Angular, Django, Express.js, SQL, MongoDB | Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Terraform, Ansible |
| Collaboration | Works closely with designers, QA, and product teams | Collaborates with developers, IT, and security teams |
| Goals | Build functional, user-friendly applications | Ensure smooth deployment, scalability, and infrastructure stability |
Defining Roles: Full Stack Developer vs DevOps Engineer
Full Stack Developers design and build end-to-end web applications, managing both front-end and back-end development to ensure seamless user experiences and functional integration. DevOps Engineers specialize in automating deployment pipelines, maintaining infrastructure as code, and optimizing system reliability through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices. Clear role definitions help tech teams leverage Full Stack Developers' coding versatility alongside DevOps Engineers' operational expertise for efficient product development and stable delivery environments.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Full Stack Developers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining both frontend and backend components of applications, ensuring seamless user experiences and robust server-side logic. DevOps Engineers specialize in automating deployment pipelines, managing cloud infrastructure, and monitoring application performance to enable continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). Both roles collaborate to optimize development workflows, but Full Stack Developers concentrate on code creation while DevOps Engineers emphasize system reliability and scalability.
Required Skill Sets and Technical Expertise
Full Stack Developers require proficiency in front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript frameworks, and back-end languages such as Node.js, Python, or Ruby, along with database management and API integration skills. DevOps Engineers specialize in automation tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and cloud platforms including AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, emphasizing continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and infrastructure-as-code expertise. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities, but Full Stack Developers focus on software development and user experience, while DevOps Engineers prioritize system reliability, scalability, and deployment automation.
Collaboration within Tech Teams
Full Stack Developers and DevOps Engineers play complementary roles that enhance collaboration within tech teams by bridging development and operations. Full Stack Developers contribute versatile coding skills across multiple layers of the application, enabling seamless integration of front-end and back-end components. DevOps Engineers focus on automating deployment pipelines and monitoring, fostering a continuous feedback loop that aligns development with operational efficiency and reliability.
Toolsets and Technology Stacks Used
Full Stack Developers primarily utilize JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, and Node.js along with backend technologies like Python, Ruby on Rails, or Java to build comprehensive web applications. DevOps Engineers focus on infrastructure and automation tools including Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Terraform, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for continuous integration and deployment. Both roles require proficiency in version control systems like Git, but Full Stack Developers emphasize application development stacks whereas DevOps Engineers specialize in operational toolsets for scalable, reliable system delivery.
Impact on Product Development Lifecycle
Full Stack Developers accelerate product development lifecycle by enabling rapid feature implementation across both frontend and backend, ensuring seamless integration and iteration. DevOps Engineers optimize deployment frequency and system reliability through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, reducing downtime and enhancing scalability. Together, they drive faster releases, improve collaboration between development and operations, and increase overall product quality in tech teams.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Full Stack Developers benefit from versatile skill sets spanning both frontend and backend technologies, enabling rapid career advancement through roles like Technical Lead or Solutions Architect. DevOps Engineers capitalize on expertise in automation, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud infrastructure, positioning themselves for senior roles such as DevOps Manager or Site Reliability Engineer. Both career paths offer robust growth opportunities in tech teams, with Full Stack Developers aligning towards product innovation and DevOps Engineers focusing on operational excellence and scalability.
Salary Trends and Job Market Demand
Full Stack Developers command competitive salaries with an average range of $80,000 to $120,000 annually, driven by their versatility in both front-end and back-end development across industries. DevOps Engineers see slightly higher salary trends, averaging between $90,000 and $130,000, reflecting the increasing demand for automation, continuous integration, and deployment expertise in cloud-native environments. Job market demand for DevOps Engineers is rapidly growing due to the shift towards agile and scalable infrastructure, while Full Stack Developers remain essential for comprehensive product development cycles in evolving tech teams.
When to Hire: Full Stack Developer vs DevOps Engineer
Hire a Full Stack Developer when rapid product development and versatile coding skills across front-end and back-end technologies are essential for building and scaling applications quickly. Choose a DevOps Engineer to streamline continuous integration, automate deployment pipelines, and maintain infrastructure for reliable, scalable, and efficient operations. Timing depends on the project phase: early-stage startups benefit from Full Stack Developers, while growing teams require DevOps Engineers to optimize system performance and deployment workflows.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Project Needs
Full Stack Developers excel in building and maintaining comprehensive applications, handling both frontend and backend development to ensure seamless user experiences. DevOps Engineers specialize in automating deployment, managing infrastructure, and optimizing continuous integration and delivery pipelines for scalable, reliable operations. Selecting the right role depends on whether your project prioritizes rapid feature development and user interface design or infrastructure stability and efficient release management.
Related Important Terms
Platform Engineering
Full Stack Developers excel in building and maintaining comprehensive applications by integrating front-end and back-end technologies, enabling rapid feature development and user experience optimization. DevOps Engineers specialize in platform engineering by automating infrastructure, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and system monitoring to ensure scalable, reliable, and efficient software delivery.
Cloud-Native Full Stack
Cloud-native full stack developers specialize in designing and deploying scalable applications using microservices architectures and container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, enabling rapid iteration across frontend and backend environments. DevOps engineers focus on automating cloud infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring systems to ensure continuous integration, delivery, and operational reliability within agile tech teams.
GitOps
Full Stack Developers excel in building and managing complete applications from front-end to back-end, while DevOps Engineers specialize in automating deployment and infrastructure using GitOps practices that leverage Git repositories as the single source of truth for continuous delivery. Integrating GitOps enhances collaboration between Full Stack Developers and DevOps Engineers by streamlining version control, deployment automation, and rollback capabilities within tech teams.
Site Reliability Coding
Full Stack Developers bring expertise in both front-end and back-end coding, enabling rapid feature development and end-to-end application management crucial for scalable site reliability. DevOps Engineers specialize in automating infrastructure, continuous integration and deployment pipelines, and monitoring systems to enhance site stability and reliability through efficient coding practices and operational workflows.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Full Stack Developers primarily focus on building and maintaining application functionality across both front-end and back-end, while DevOps Engineers specialize in automating infrastructure deployment and management using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform and Ansible. Implementing IaC enhances collaboration between these roles by enabling consistent, version-controlled environments that streamline continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
CI/CD Orchestration
Full Stack Developers design and implement application features across the entire stack, while DevOps Engineers specialize in CI/CD orchestration, automating build, test, and deployment pipelines to ensure seamless integration and delivery. Effective tech teams leverage DevOps expertise to streamline workflows and Full Stack skills to develop robust, scalable applications.
API-First Development
Full Stack Developers excel in building comprehensive API-First applications by designing and implementing both front-end interfaces and back-end services, ensuring seamless integration and user experience. DevOps Engineers focus on automating deployment pipelines and infrastructure management, optimizing API delivery and scalability to support continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) in tech teams.
Observability Engineering
Full Stack Developers focus on building and maintaining comprehensive applications across front-end and back-end, emphasizing code efficiency and functionality, while DevOps Engineers specialize in infrastructure automation, continuous integration, and deployment pipelines with a critical emphasis on Observability Engineering to monitor system performance and ensure reliability. Observability tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Elastic Stack enable DevOps teams to proactively identify and resolve issues, enhancing system uptime and scalability compared to traditional development practices.
Full-Stack DevSecOps
Full-Stack DevSecOps professionals combine comprehensive skills in front-end and back-end development with integrated security practices and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, enabling tech teams to build secure, scalable, and efficient applications. Unlike traditional Full Stack Developers or DevOps Engineers, Full-Stack DevSecOps roles emphasize embedding security measures early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to reduce vulnerabilities and streamline collaborative workflows across development, operations, and security teams.
Developer Experience (DevEx)
Full Stack Developers enhance Developer Experience (DevEx) by integrating frontend and backend workflows, enabling seamless application development and reducing context switching. DevOps Engineers improve DevEx through automated deployment pipelines, infrastructure as code, and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD), accelerating feedback loops and minimizing downtime in tech teams.
Full Stack Developer vs DevOps Engineer for tech teams. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com