Teamwork fosters collaboration by encouraging clear roles, shared goals, and direct communication among team members, ensuring accountability and efficiency. Holacracy, on the other hand, distributes authority through self-organizing teams, promoting flexibility and innovation but requiring a cultural shift for effective implementation. Choosing between teamwork and holacracy depends on organizational needs for structure versus adaptability in driving collaboration success.
Table of Comparison
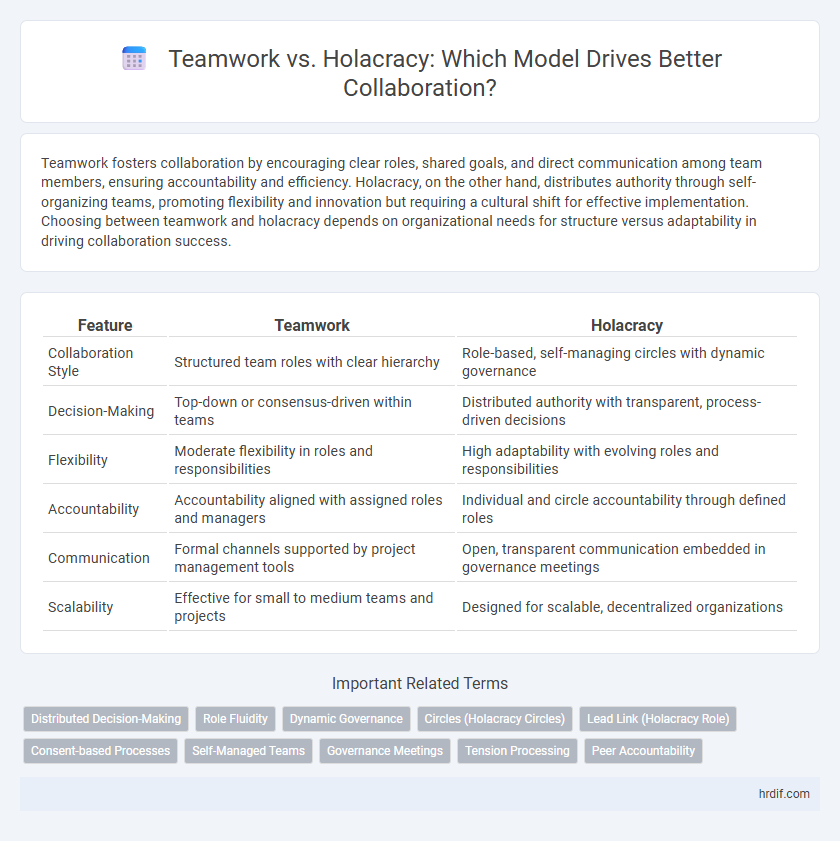
| Feature | Teamwork | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Collaboration Style | Structured team roles with clear hierarchy | Role-based, self-managing circles with dynamic governance |
| Decision-Making | Top-down or consensus-driven within teams | Distributed authority with transparent, process-driven decisions |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility in roles and responsibilities | High adaptability with evolving roles and responsibilities |
| Accountability | Accountability aligned with assigned roles and managers | Individual and circle accountability through defined roles |
| Communication | Formal channels supported by project management tools | Open, transparent communication embedded in governance meetings |
| Scalability | Effective for small to medium teams and projects | Designed for scalable, decentralized organizations |
Introduction: Defining Teamwork and Holacracy
Teamwork involves collaborative efforts where members share responsibilities and communicate openly to achieve common goals, emphasizing roles and hierarchical structures. Holacracy is a decentralized management system that replaces traditional hierarchies with self-organizing teams called circles, enabling dynamic role distribution and autonomous decision-making. Both approaches aim to enhance collaboration but differ fundamentally in structure and operational methods.
Core Principles of Teamwork
Teamwork centers on shared goals, open communication, and mutual accountability, fostering collaboration through clearly defined roles and trust among team members. Emphasizing interdependence and collective problem-solving, teamwork drives efficiency and innovation by leveraging diverse skills within a unified structure. These core principles create a cohesive environment where collaboration thrives through coordinated efforts and aligned objectives.
Foundations of Holacracy in the Workplace
Holacracy replaces traditional teamwork structures with a decentralized system that distributes authority through defined roles and circles, promoting dynamic collaboration and faster decision-making. The foundations of Holacracy include governance meetings, transparent role assignments, and explicit accountabilities, which empower employees to self-organize and adapt to changing work needs. This framework fosters agility and clarity, reducing hierarchical bottlenecks and enhancing organizational responsiveness.
Communication Styles: Teamwork vs Holacracy
Teamwork emphasizes direct, often hierarchical communication channels where information flows through designated roles, promoting clarity but potentially limiting input diversity. Holacracy fosters decentralized communication, encouraging transparent, real-time dialogue across roles to empower autonomous decision-making and rapid adaptability. Comparing these styles reveals teamwork's structured clarity contrasts with holacracy's fluid, inclusive exchange, each influencing collaboration efficiency and responsiveness.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Teamwork relies on hierarchical decision-making where team leads or managers direct outcomes, ensuring clarity and accountability but potentially limiting input diversity. Holacracy distributes decision-making authority across self-organizing roles, promoting agility and empowerment while requiring robust communication protocols to prevent confusion. Comparing these models, teams prioritizing fast, centralized decisions may favor traditional teamwork, whereas organizations valuing adaptability and shared responsibility benefit from holacracy's decentralized process.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Each Approach
Teamwork fosters flexibility through dynamic role-sharing and open communication channels, enabling quick adjustments to changing project demands. Holacracy enhances adaptability by distributing authority across self-managing teams, allowing rapid reconfiguration of roles based on evolving organizational needs. Both approaches prioritize responsiveness but differ in structural rigidity, with teamwork relying on interpersonal coordination and holacracy on formalized governance frameworks.
Empowerment and Role Distribution
Teamwork emphasizes empowerment through clearly defined roles and direct accountability, enabling efficient collaboration by leveraging individual strengths within a structured hierarchy. Holacracy distributes roles dynamically across self-organizing teams, fostering empowerment by allowing members to assume multiple roles and adapt responsibilities as projects evolve. This flexible role distribution in holacracy contrasts with teamwork's traditional role clarity, offering a more fluid approach to collaboration that encourages autonomy and shared leadership.
Potential Challenges and Pitfalls
Teamwork often faces challenges such as communication breakdowns, unclear roles, and reliance on hierarchical decision-making, which can hinder collaboration efficiency. Holacracy, while promoting decentralized authority and flexibility, may cause confusion due to ambiguous accountability and require extensive training to implement effectively. Both models risk reduced productivity if team members struggle to adapt to their respective structures and collaboration dynamics.
Impact on Productivity and Employee Engagement
Teamwork fosters collaboration through clear roles and hierarchical structures, which often enhance productivity by streamlining decision-making and accountability. Holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, boosting employee engagement by empowering individuals to take ownership and innovate. Organizations adopting holacracy frequently report increased creativity but may face initial productivity dips as employees adjust to decentralized workflows.
Choosing the Best Model for Organizational Collaboration
Teamwork thrives on clear roles and leadership, fostering efficient decision-making and accountability within structured hierarchies, which suits organizations needing stability and defined workflows. Holacracy offers a decentralized approach, empowering employees through self-management and flexible roles, ideal for innovative environments requiring adaptability and rapid response. Selecting the best collaboration model depends on organizational goals, culture, and the need for either control or autonomy to drive productivity and engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Decision-Making
Teamwork fosters distributed decision-making by leveraging collective input within structured roles, while holacracy emphasizes decentralized authority through autonomous circles enabling rapid adaptation; both approaches enhance collaboration but differ in control dynamics and decision fluidity. Effective use of distributed decision-making in teamwork ensures coordinated efforts, whereas holacracy's self-management drives innovation by eliminating hierarchical bottlenecks.
Role Fluidity
Teamwork emphasizes defined roles and responsibilities to ensure accountability and clear communication during collaboration, while holacracy promotes role fluidity by allowing individuals to shift roles dynamically based on project needs, fostering adaptability and innovation. Role fluidity in holacracy enhances collaboration by breaking down hierarchical barriers and enabling team members to contribute diverse skills where they are most impactful.
Dynamic Governance
Dynamic Governance, a key principle within Holacracy, enables decentralized decision-making by distributing authority throughout self-organizing teams, enhancing adaptability and responsiveness compared to traditional teamwork models. This approach fosters transparent communication and accountability, promoting agile collaboration that aligns with rapidly changing organizational needs.
Circles (Holacracy Circles)
Holacracy Circles empower teams by distributing authority within self-organizing units, enhancing collaboration through clear roles and transparent governance. Unlike traditional teamwork structures, Circles enable dynamic role assignments and seamless alignment with organizational purpose, fostering agility and accountability.
Lead Link (Holacracy Role)
Lead Link in Holacracy centralizes coordination by assigning clear accountabilities and linking circles, enhancing self-managed teams' agility without traditional hierarchy. Unlike conventional teamwork models reliant on managers, the Lead Link role empowers distributed authority and transparent governance, driving effective collaboration across autonomous units.
Consent-based Processes
Teamwork emphasizes hierarchical decision-making and predefined roles to streamline collaboration, whereas Holacracy uses consent-based processes that empower team members to propose and integrate changes unless there are well-reasoned objections. Consent-based governance in Holacracy fosters dynamic adaptation and distributed authority, enhancing responsiveness and engagement within collaborative environments.
Self-Managed Teams
Self-managed teams in holacracy enhance collaboration by distributing authority and enabling members to make decisions independently, fostering agility and innovation. In contrast, traditional teamwork relies on hierarchical roles, which can limit autonomy but provide clear structure and accountability.
Governance Meetings
Governance meetings in teamwork rely on hierarchical decision-making processes that streamline accountability and clarify roles, enhancing collaboration through structured communication. In contrast, holacracy governance meetings distribute authority across self-managed teams, fostering transparency and dynamic role allocation that adapt to evolving project needs.
Tension Processing
Teamwork relies on hierarchical structures to manage tension through clear roles and conflict resolution pathways, ensuring stability in collaboration. Holacracy processes tension dynamically by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, fostering adaptability and continuous organizational evolution.
Peer Accountability
Peer accountability in teamwork fosters direct responsibility among members through clear roles and mutual trust, enhancing collaboration efficiency. Holacracy promotes shared governance and dynamic role fluidity, which can empower peer accountability by distributing decision-making but may require adaptation for consistent accountability practices.
Teamwork vs Holacracy for collaboration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com