Group projects often involve dividing tasks among members to achieve a shared goal, fostering individual accountability within a structured framework. Co-creation emphasizes collective innovation through ongoing interaction and equal contribution, enhancing creativity and synergy among participants. Understanding these approaches can optimize collaboration strategies for improved team dynamics and project outcomes.
Table of Comparison
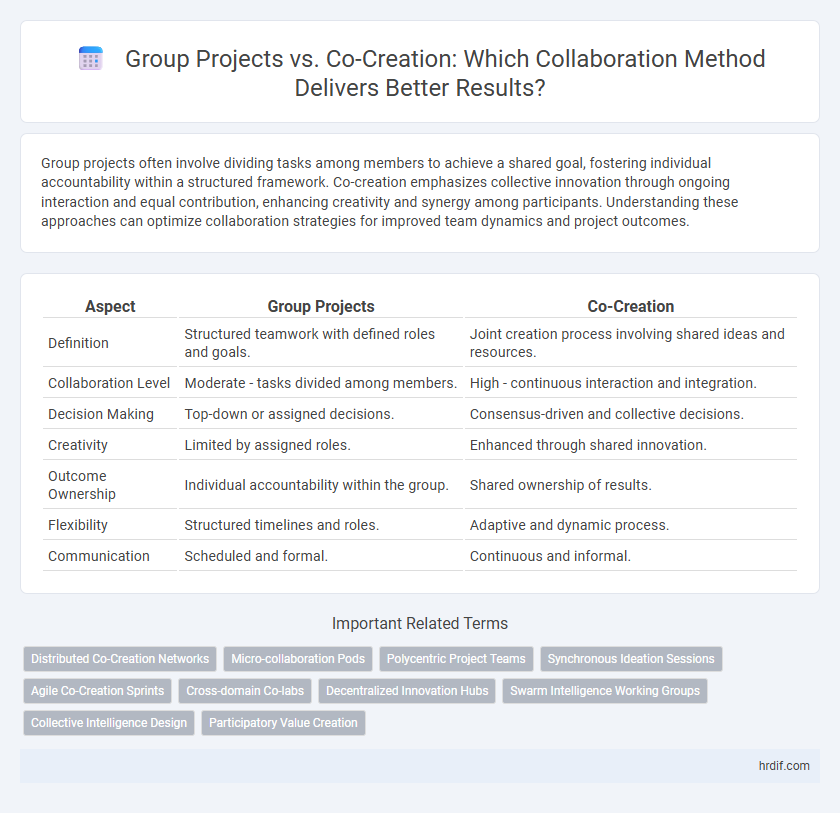
| Aspect | Group Projects | Co-Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured teamwork with defined roles and goals. | Joint creation process involving shared ideas and resources. |
| Collaboration Level | Moderate - tasks divided among members. | High - continuous interaction and integration. |
| Decision Making | Top-down or assigned decisions. | Consensus-driven and collective decisions. |
| Creativity | Limited by assigned roles. | Enhanced through shared innovation. |
| Outcome Ownership | Individual accountability within the group. | Shared ownership of results. |
| Flexibility | Structured timelines and roles. | Adaptive and dynamic process. |
| Communication | Scheduled and formal. | Continuous and informal. |
Defining Group Projects and Co-Creation in the Workplace
Group projects in the workplace involve a team working together towards a common goal, with tasks typically divided among members based on individual expertise. Co-creation emphasizes collaborative innovation, where all participants actively contribute ideas and solutions, blending diverse perspectives to achieve shared outcomes. Both methods foster teamwork but differ in the level of interaction and collective ownership during the collaborative process.
Key Differences Between Group Projects and Co-Creation
Group projects typically involve assigned roles with defined tasks aimed at completing a common goal, whereas co-creation emphasizes equal partnership and collective ideation throughout the process. In co-creation, stakeholders actively contribute and integrate diverse perspectives, fostering innovation and shared ownership, unlike traditional group projects which follow a linear execution model. The key difference lies in the level of interaction and mutual influence, with co-creation enabling dynamic collaboration and real-time feedback among participants.
Benefits of Traditional Group Projects for Teams
Traditional group projects foster clear role distribution and accountability, enhancing team organization and productivity. They provide structured timelines and milestones, which help in monitoring progress and meeting deadlines efficiently. This approach strengthens individual responsibility while promoting collective achievement within teams.
Advantages of Embracing Co-Creation at Work
Embracing co-creation at work fosters deeper engagement by integrating diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to innovative solutions that group projects often miss due to compartmentalized tasks. Co-creation enhances collective ownership and accountability, driving higher motivation and commitment among team members. This collaborative process accelerates knowledge sharing and adaptive problem-solving, resulting in more agile and effective outcomes for organizations.
Common Challenges in Group Projects
Group projects often face challenges such as unequal participation, miscommunication, and conflicting deadlines, which can hinder effective collaboration. These common issues reduce productivity and create frustration among team members, leading to suboptimal outcomes. Co-creation addresses these challenges by fostering shared ownership, continuous feedback, and aligned goals to enhance collaboration efficiency.
Overcoming Barriers to Effective Co-Creation
Overcoming barriers to effective co-creation involves fostering open communication and mutual trust among diverse stakeholders, unlike traditional group projects that often prioritize task division over shared innovation. Co-creation leverages collaborative technologies and real-time feedback loops to address misunderstandings and power imbalances that hinder synergy. Emphasizing collective ownership and adaptive problem-solving enhances creativity and accountability, driving superior collaborative outcomes.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Ownership
Group projects often assign specific roles, which can limit employee ownership and reduce overall engagement by focusing on task completion rather than personal contribution. Co-creation fosters a collaborative environment where employees actively contribute ideas and make decisions, significantly boosting engagement and ownership. This participative approach enhances motivation and accountability, ultimately driving innovation and stronger team cohesion.
Collaboration Tools: Supporting Group Projects vs Co-Creation
Collaboration tools for group projects typically focus on task assignment, progress tracking, and deadline management, enabling structured teamwork and clear role distribution. In contrast, tools designed for co-creation emphasize real-time interaction, idea sharing, and seamless integration of diverse inputs to foster innovation and collective creativity. Platforms like Trello or Asana excel in managing group project workflows, whereas Miro and Google Workspace enhance dynamic co-creative processes.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Group Projects and Co-Creation
Case studies reveal that group projects often excel in structured environments where roles and tasks are clearly defined, leading to measurable outcomes and efficient timelines. Co-creation thrives in dynamic settings by fostering innovation through active stakeholder engagement and shared decision-making, resulting in highly customized solutions. Success stories in both approaches highlight the importance of communication tools and adaptive collaboration frameworks to maximize productivity and creative input.
Choosing the Right Collaboration Model for Your Organization
Group projects often involve dividing tasks among members to achieve a common goal, promoting accountability and structured workflows, whereas co-creation emphasizes simultaneous ideation and shared ownership, fostering innovation and collective problem-solving. Selecting the right collaboration model depends on organizational goals, team dynamics, and project complexity, with group projects suited for clearly defined deliverables and co-creation ideal for creative product development. Evaluating factors such as communication styles, resource availability, and desired outcomes ensures alignment with the collaboration approach that maximizes productivity and engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Co-Creation Networks
Distributed co-creation networks enhance collaboration by leveraging diverse expertise across geographies, enabling real-time innovation and agile problem-solving beyond traditional group projects. These networks utilize digital platforms to facilitate seamless interaction, knowledge sharing, and collective value creation, optimizing project outcomes through distributed intelligence and collaborative synergy.
Micro-collaboration Pods
Micro-collaboration pods foster deeper engagement and innovation by enabling small, autonomous teams to co-create in real-time, contrasting with traditional group projects that often rely on segmented, individual task completion. This agile approach enhances knowledge sharing and accelerates decision-making, driving higher productivity and creative outcomes within collaborative environments.
Polycentric Project Teams
Polycentric project teams in group projects often face challenges in integrating diverse perspectives due to hierarchical task divisions, whereas co-creation promotes dynamic interaction and shared ownership, enhancing innovation and collective problem-solving. Leveraging geographic and cultural diversity in co-creation fosters adaptive strategies and more inclusive outcomes compared to traditional group project structures.
Synchronous Ideation Sessions
Group projects often emphasize task division and individual contributions, while co-creation prioritizes real-time, synchronous ideation sessions that enhance dynamic interaction and collective problem-solving. Synchronous ideation sessions in co-creation foster immediate feedback and iterative creativity, driving innovation through active engagement and shared ownership.
Agile Co-Creation Sprints
Agile Co-Creation Sprints foster dynamic collaboration by integrating diverse expertise in short, iterative cycles that enhance innovation and adaptability, unlike traditional group projects which often follow linear, segmented approaches. This method emphasizes real-time feedback and collective ownership, accelerating problem-solving and delivering more user-centric solutions.
Cross-domain Co-labs
Cross-domain co-labs enhance collaboration by integrating diverse expertise from multiple fields, fostering innovative solutions that transcend traditional group project boundaries. Unlike group projects that often operate within single domains, co-creation in cross-domain environments drives more dynamic interactions and synergistic results through shared knowledge and creative problem-solving.
Decentralized Innovation Hubs
Decentralized innovation hubs foster co-creation by enabling diverse stakeholders to collaboratively generate ideas and solutions, leveraging real-time communication and shared resources to accelerate creativity. Unlike traditional group projects, which often rely on hierarchical structures, co-creation in decentralized environments promotes inclusive participation and distributed decision-making, enhancing innovation outcomes.
Swarm Intelligence Working Groups
Swarm Intelligence working groups leverage decentralized decision-making and self-organization to enable co-creation, surpassing traditional group projects by maximizing collective intelligence and adaptive problem-solving. This approach enhances innovation and efficiency through dynamic interaction patterns and real-time collaboration without hierarchical constraints.
Collective Intelligence Design
Group projects rely on predefined roles and division of tasks, often limiting spontaneous idea exchange, whereas co-creation fosters dynamic interaction that harnesses collective intelligence through shared creativity and adaptive problem-solving. Designing collaborative frameworks that emphasize real-time feedback and iterative input optimizes knowledge integration and innovation outcomes within teams.
Participatory Value Creation
Group projects emphasize task distribution and individual accountability, often resulting in segmented outputs, whereas co-creation fosters integrative collaboration by engaging diverse stakeholders in shared ideation and decision-making processes, maximizing participatory value creation. This approach enhances innovation and collective ownership, leading to outcomes that reflect the collective intelligence and expertise of all contributors.
Group Projects vs Co-Creation for Collaboration Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com