Group projects foster shared responsibility and collective problem-solving by assigning specific roles and tasks to each member, promoting accountability and clear communication. Holacracy emphasizes decentralized authority and self-management, enabling teams to adapt quickly through defined roles that evolve based on project needs. Both methods enhance collaboration, with group projects providing structured teamwork and holacracy encouraging flexibility and autonomous decision-making.
Table of Comparison
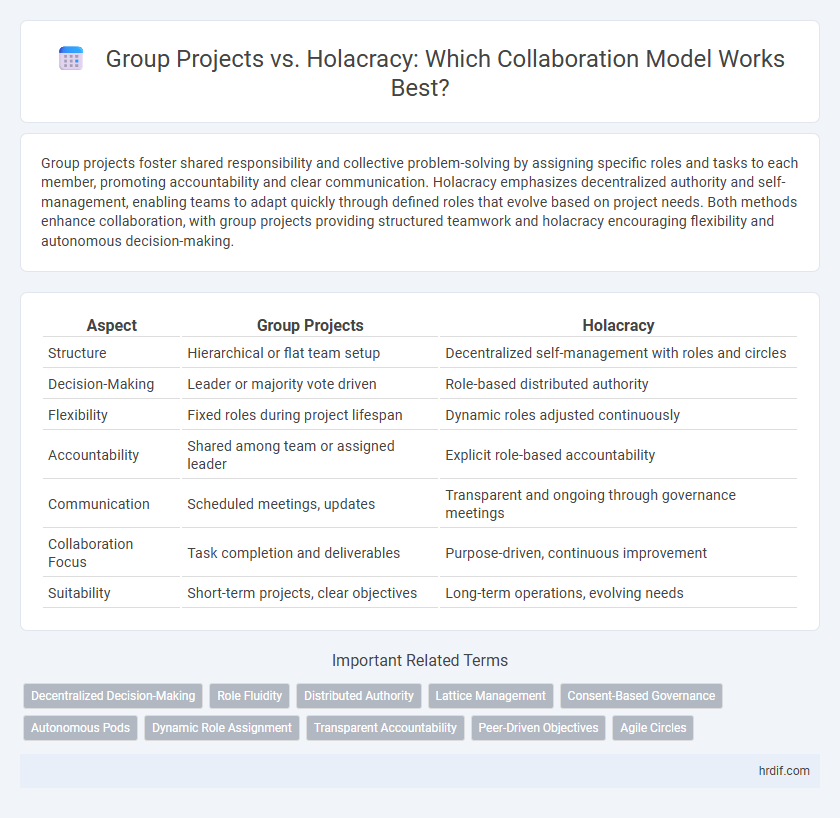
| Aspect | Group Projects | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical or flat team setup | Decentralized self-management with roles and circles |
| Decision-Making | Leader or majority vote driven | Role-based distributed authority |
| Flexibility | Fixed roles during project lifespan | Dynamic roles adjusted continuously |
| Accountability | Shared among team or assigned leader | Explicit role-based accountability |
| Communication | Scheduled meetings, updates | Transparent and ongoing through governance meetings |
| Collaboration Focus | Task completion and deliverables | Purpose-driven, continuous improvement |
| Suitability | Short-term projects, clear objectives | Long-term operations, evolving needs |
Defining Group Projects and Holacracy in the Workplace
Group projects involve a defined team working together on shared objectives, fostering collaboration through role assignments and collective accountability. Holacracy is a decentralized management practice that replaces traditional hierarchy with self-organizing teams, emphasizing distributed authority and dynamic roles. In the workplace, group projects prioritize structured collaboration, while holacracy encourages agile decision-making and individual autonomy within interconnected circles.
Key Differences in Structure and Authority
Group projects typically follow a hierarchical structure where authority is centralized and roles are clearly defined, enabling streamlined decision-making but potentially limiting individual autonomy. Holacracy, in contrast, employs a decentralized system with distributed authority across self-managing teams, fostering adaptability and empowering employees to take initiative within defined circles. This structural difference significantly impacts collaboration dynamics, with group projects emphasizing top-down coordination and holacracy promoting fluid, role-based accountability.
Communication Channels in Group Projects vs. Holacracy
Group projects typically rely on hierarchical communication channels where information flows through designated leaders or team members, which can create bottlenecks and limit transparency. In contrast, holacracy employs decentralized communication paths that enable direct, real-time interactions across all roles, enhancing collaboration and responsiveness. This distributed channel structure in holacracy fosters quicker decision-making and more effective knowledge sharing among participants.
Impact on Team Decision-Making
Group projects often centralize decision-making authority, which can streamline processes but may limit diverse input, potentially causing slower consensus-building and reduced team engagement. Holacracy distributes decision-making across roles and circles, fostering autonomy and rapid adaptability while enhancing transparency and accountability. This decentralized approach tends to improve innovation and responsiveness in complex, dynamic environments.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Collaborative Models
Group projects often rely on defined roles and hierarchical decision-making, which can limit flexibility and adaptability in fast-changing environments. Holacracy promotes a decentralized structure with dynamic roles and distributed authority, enabling teams to quickly adjust workflows and responsibilities to meet evolving needs. This model enhances agile collaboration by embracing continuous feedback and iterative improvements, fostering a resilient and responsive organizational culture.
Accountability and Role Clarity Comparison
Group projects often face challenges with accountability as responsibilities may overlap and role clarity can be ambiguous, leading to potential conflicts and inefficiencies. Holacracy enforces clear role definitions and distributed authority, enhancing individual accountability by assigning specific tasks and decision-making powers within a structured framework. This systematic approach in holacracy improves collaboration by ensuring each member's responsibilities are well-defined and measurable compared to traditional group projects.
Fostering Innovation: Which Model Works Better?
Group projects foster innovation through structured teamwork and clear roles, allowing diverse ideas to converge within set timelines, while holacracy promotes continuous innovation by distributing authority and empowering autonomy in real-time decision-making. Studies show holacratic organizations experience higher adaptability and creativity due to decentralized collaboration, whereas traditional group projects excel in goal-oriented environments with defined deliverables. The choice depends on organizational culture; holacracy suits dynamic innovation-driven firms, and group projects benefit contexts requiring coordinated output and accountability.
Challenges and Pitfalls of Group Projects and Holacracy
Group projects often face challenges such as uneven workload distribution, communication breakdowns, and conflicts arising from unclear roles, which impede effective collaboration. Holacracy can present pitfalls including complexity in governance, resistance to change, and difficulties in decision-making due to decentralized authority. Both methods require intentional effort to overcome these barriers to achieve cohesive and productive teamwork.
Case Studies: Collaboration Outcomes in Real Organizations
Case studies reveal that group projects often face challenges in decision-making speed and role clarity, impacting collaboration outcomes in real organizations. Holacracy, implemented by companies like Zappos, demonstrates enhanced agility and employee engagement through decentralized authority and transparent role definitions. Data from these organizations show improvements in innovation rates and internal communication efficiency compared to traditional group project structures.
Choosing the Right Collaboration Model for Your Team
Group projects excel in environments requiring clear roles and hierarchical decision-making, promoting efficiency through assigned tasks and structured timelines. Holacracy offers a decentralized collaboration model, empowering teams with distributed authority and dynamic roles to enhance adaptability and innovation. Choosing the right collaboration model depends on your team's size, organizational culture, and need for flexibility versus control in project execution.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Decision-Making
Group projects often rely on centralized decision-making with designated leaders guiding tasks, whereas holacracy promotes decentralized decision-making by distributing authority across self-organizing teams. This structure enhances agility and accountability, enabling faster responses to challenges and fostering collaborative innovation.
Role Fluidity
Group projects typically assign fixed roles to team members, limiting flexibility and adaptation during collaboration, whereas holacracy emphasizes role fluidity, allowing individuals to shift responsibilities based on real-time needs and expertise. This dynamic approach enhances responsiveness and innovation by enabling teams to reconfigure roles without hierarchical constraints.
Distributed Authority
Group projects often concentrate decision-making within designated leaders, creating bottlenecks and limiting distributed authority, whereas holacracy decentralizes power by distributing roles and responsibilities across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and collective ownership. This structure fosters dynamic collaboration by enabling members to make autonomous decisions aligned with evolving project needs.
Lattice Management
Group projects foster collaboration through defined roles and hierarchical task distribution, optimizing accountability and clarity in Lattice Management systems. Holacracy enhances collaboration by decentralizing authority and enabling dynamic role allocation, promoting agility and distributed decision-making within Lattice Management frameworks.
Consent-Based Governance
Group projects typically rely on hierarchical decision-making, whereas holacracy employs consent-based governance, enabling team members to consent to proposals rather than seeking consensus or majority vote. This approach fosters dynamic collaboration by distributing authority and empowering individuals within self-organizing teams.
Autonomous Pods
Group projects often struggle with inefficiencies and unclear accountability, whereas holacracy organizes collaboration into autonomous pods that empower team members with decentralized decision-making and agile workflows. Autonomous pods leverage self-management and role clarity, driving innovation and accelerating project outcomes through enhanced adaptability and peer accountability.
Dynamic Role Assignment
Dynamic role assignment in group projects often relies on predefined roles that can limit flexibility, whereas holacracy empowers teams by continuously redefining roles based on current needs and individual strengths. This fluid approach enhances collaboration by promoting adaptability, accountability, and real-time responsiveness within the organizational structure.
Transparent Accountability
Group projects often struggle with opaque accountability due to overlapping responsibilities and unclear individual contributions, whereas holacracy establishes transparent accountability through defined roles and distributed decision-making authority. This framework enables teams to track progress and ownership precisely, enhancing collaborative efficiency and trust.
Peer-Driven Objectives
Group projects rely on structured roles and predefined objectives, often leading to hierarchical decision-making that can limit peer-driven contributions. Holacracy empowers collaboration by distributing authority through self-organizing teams, enabling dynamic peer-driven objectives that adapt more fluidly to evolving project needs.
Agile Circles
Agile Circles facilitate collaboration by combining the structured flexibility of Holacracy with the shared responsibility of group projects, promoting decentralized decision-making and rapid adaptability. This approach enhances team autonomy and accountability, fostering continuous improvement and innovation within dynamic work environments.
Group Projects vs Holacracy for Collaboration Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com