Certificates provide formal recognition of skills and knowledge in a specific area, often requiring comprehensive coursework and assessments. Microcredentials focus on targeted competencies, offering flexible, bite-sized endorsements that can be quickly earned and easily combined with other qualifications. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their ability to demonstrate up-to-date, relevant expertise in dynamic job markets.
Table of Comparison
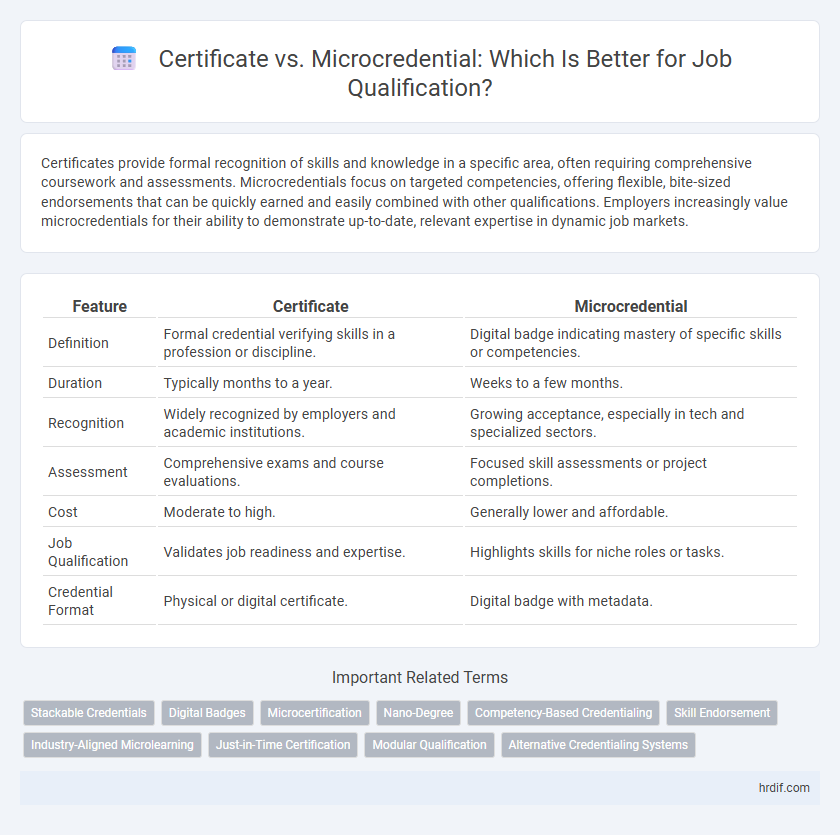
| Feature | Certificate | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal credential verifying skills in a profession or discipline. | Digital badge indicating mastery of specific skills or competencies. |
| Duration | Typically months to a year. | Weeks to a few months. |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and academic institutions. | Growing acceptance, especially in tech and specialized sectors. |
| Assessment | Comprehensive exams and course evaluations. | Focused skill assessments or project completions. |
| Cost | Moderate to high. | Generally lower and affordable. |
| Job Qualification | Validates job readiness and expertise. | Highlights skills for niche roles or tasks. |
| Credential Format | Physical or digital certificate. | Digital badge with metadata. |
Understanding Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates formally validate specific skills or knowledge acquired through comprehensive training programs recognized by educational institutions or industry bodies. Microcredentials represent granular, stackable learning achievements targeting niche competencies, often delivered through short-term, flexible online courses. Both enhance job qualifications, but certificates typically carry broader recognition, while microcredentials offer tailored skill endorsements aligned with current workforce demands.
Key Differences Between Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates typically involve a comprehensive program of study completed over weeks or months, demonstrating mastery of a broad skill set relevant to a professional field. Microcredentials focus on specific, targeted skills or competencies, offering flexible, shorter-term learning paths that can be stacked or combined to enhance job qualifications. Key differences include program length, depth of content, and recognition, with certificates often recognized by employers as formal qualifications, while microcredentials provide agile, skill-specific validation adaptable to evolving industry needs.
Industry Recognition: Certificate vs Microcredential
Certificates typically offer broad industry recognition due to established standards and accreditation processes, making them widely accepted by employers for job qualifications. Microcredentials provide targeted skills validation that aligns closely with specific industry demands, often gaining rapid recognition in niche sectors or emerging fields. Both serve as valuable credentials, but certificates emphasize comprehensive expertise while microcredentials highlight specialized competencies for job readiness.
Time Commitment and Flexibility
Certificates typically require a longer time commitment, often spanning several months to a year, and follow a fixed schedule with limited flexibility. Microcredentials offer a shorter, more flexible learning experience, allowing individuals to acquire targeted skills in weeks or even days, accommodating busy work schedules. For job qualifications, microcredentials provide a quicker path to skill validation, while certificates deliver comprehensive knowledge through structured learning.
Cost Comparison: Certificates vs Microcredentials
Certificate programs typically require higher tuition fees due to their comprehensive curriculum and longer duration, often ranging from $1,000 to $5,000 or more. Microcredentials offer a more affordable alternative, with costs usually between $100 and $1,000, reflecting their targeted, short-term learning approach. Employers increasingly recognize microcredentials as cost-effective ways to validate specific skills without the financial commitment of traditional certificates.
Relevance to Specific Job Roles
Certificates provide broad validation of skills often applicable across multiple industries, while microcredentials focus on specific competencies tailored to particular job roles, enhancing targeted employability. Employers prefer microcredentials when seeking evidence of proficiency in niche areas or emerging technologies directly linked to job requirements. The precision of microcredentials ensures alignment with industry standards and immediate relevance, making them highly valuable for career advancement in specialized fields.
Employer Preferences and Trends
Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their targeted skill validation and shorter completion times, aligning with dynamic industry needs. Certificates often signal broader knowledge but may lack the specificity that microcredentials provide, influencing hiring decisions. Trends show a shift toward microcredentials as they enable continuous learning and adaptability in fast-evolving job markets.
Return on Investment for Career Growth
Certificates often provide a broad foundation of skills recognized by employers, making them valuable for career advancement in established industries. Microcredentials offer targeted expertise and flexible learning paths, delivering quicker ROI by addressing specific job requirements and emerging market trends. Investing in microcredentials can lead to faster job promotions and salary increases due to their precise alignment with in-demand skills.
Stackability and Continuing Education
Certificates provide formal recognition of skill mastery and are often required for job qualifications, while microcredentials offer flexible, stackable learning units that enable professionals to build competencies over time. Microcredentials support continuing education by allowing individuals to accumulate specific skills that can be combined to meet evolving industry standards and career goals. Employers increasingly value stackable microcredentials for their adaptability and relevance in fast-changing job markets.
How to Choose the Right Credential for Your Career
Selecting the right credential depends on your career goals, industry standards, and the depth of knowledge required. Certificates often represent comprehensive mastery suitable for traditional qualifications, while microcredentials target specific skills or competencies valued for agile, evolving professions. Evaluate employer preferences, the credential's recognition, and its alignment with your professional growth to make an informed choice.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials, combining certificates and microcredentials, enable workers to build modular skills tailored to job qualification requirements across industries, enhancing employability and career advancement. Certificates typically signify comprehensive knowledge in a subject area, while microcredentials offer targeted, skill-specific validation, allowing individuals to accumulate diverse qualifications that align with evolving workplace demands.
Digital Badges
Digital badges represent a modern form of microcredentials that provide verifiable proof of specific skills and competencies, making them increasingly valuable for job qualification. Unlike traditional certificates, digital badges offer portability, instant validation, and the ability to showcase achievements across professional networks and online profiles.
Microcertification
Microcredentials offer targeted skill validation that aligns closely with specific job requirements, often recognized by employers for their relevance and flexibility. These digital badges provide verified evidence of expertise that can be easily updated and shared, making them a dynamic alternative to traditional certificates in workforce qualification.
Nano-Degree
Nano-Degrees offer targeted, skill-specific training recognized by industry leaders, making them a preferred microcredential for job qualification over traditional certificates, which often provide broader, less specialized knowledge. Employers increasingly favor Nano-Degrees for their practical, project-based learning approach that demonstrates immediate job readiness and up-to-date expertise in emerging technologies.
Competency-Based Credentialing
Competency-based credentialing emphasizes demonstrating specific skills and knowledge through targeted assessments, making microcredentials more flexible and focused than traditional certificates for job qualification. Unlike certificates, microcredentials often validate precise competencies aligned with industry standards, enhancing employability and career advancement.
Skill Endorsement
Certificates typically validate comprehensive skill mastery through formal assessments, establishing recognized job qualifications, while microcredentials offer flexible, targeted skill endorsements that highlight specific competencies valued by employers for immediate application. Employers increasingly favor microcredentials for their ability to swiftly demonstrate relevant expertise tailored to evolving industry requirements.
Industry-Aligned Microlearning
Industry-aligned microlearning delivers focused, skill-specific microcredentials that demonstrate real-time competency, offering greater agility and relevance for job qualification compared to traditional certificates. These microcredentials are rapidly updated to match evolving industry standards, ensuring professionals showcase the most current expertise demanded by employers.
Just-in-Time Certification
Just-in-time certification emphasizes rapid skill validation through microcredentials, enabling professionals to meet specific job requirements efficiently without the extensive time commitment of traditional certificates. Microcredentials offer targeted, stackable learning units that align closely with evolving industry needs, providing greater flexibility and immediate applicability in various job qualifications.
Modular Qualification
Modular qualification frameworks emphasize microcredentials as flexible, skill-specific credentials that complement comprehensive certificates by validating discrete competencies within a job role. Employers increasingly favor microcredentials for their precision in demonstrating targeted expertise and adaptability in rapidly evolving industries.
Alternative Credentialing Systems
Alternative credentialing systems like microcredentials offer targeted skill validation through short, flexible courses, contrasting with traditional certificates that typically represent comprehensive program completion. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their specificity and adaptability, enabling quicker assessment of job-relevant competencies in dynamic industries.
Certificate vs Microcredential for job qualification Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com