Certificates provide formal recognition of expertise in a specific field and often require completing a comprehensive course, enhancing a professional's credentials for career advancement. Microcredentials offer targeted, flexible learning units that validate specific skills and can be stacked to build broader qualifications, appealing to employers seeking specialized competencies. Both options support career growth, but microcredentials allow faster adaptation to evolving industry demands.
Table of Comparison
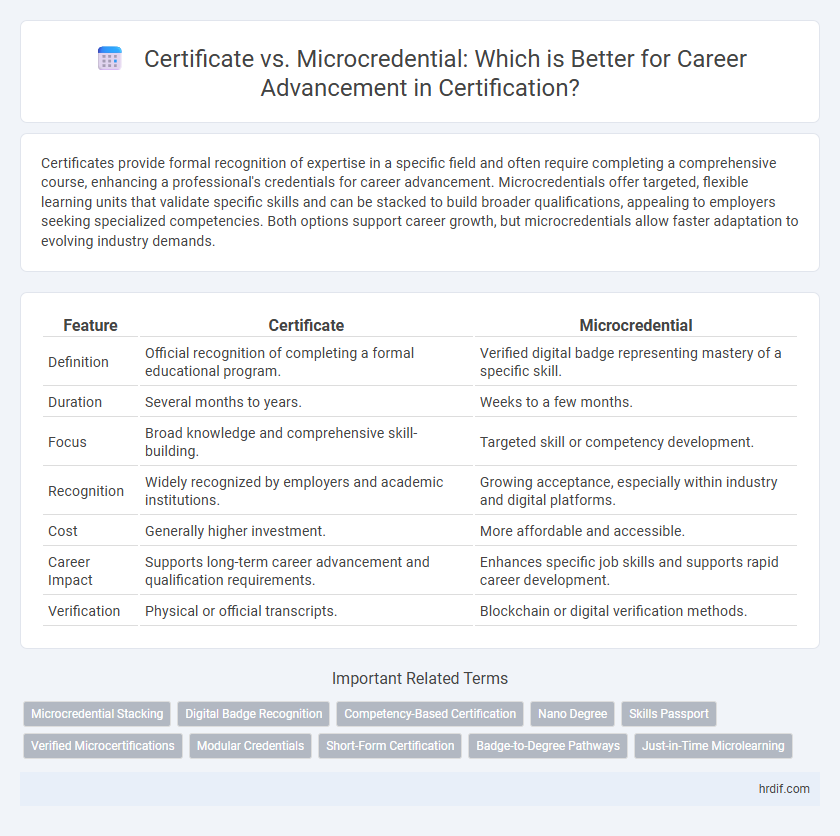
| Feature | Certificate | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official recognition of completing a formal educational program. | Verified digital badge representing mastery of a specific skill. |
| Duration | Several months to years. | Weeks to a few months. |
| Focus | Broad knowledge and comprehensive skill-building. | Targeted skill or competency development. |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and academic institutions. | Growing acceptance, especially within industry and digital platforms. |
| Cost | Generally higher investment. | More affordable and accessible. |
| Career Impact | Supports long-term career advancement and qualification requirements. | Enhances specific job skills and supports rapid career development. |
| Verification | Physical or official transcripts. | Blockchain or digital verification methods. |
Understanding Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates represent formal recognition of expertise completed through comprehensive programs, often requiring a set amount of coursework and assessments. Microcredentials offer targeted, skill-specific validation that can be earned faster and are designed to complement existing qualifications. Both play strategic roles in career advancement by enhancing professional credibility and meeting industry demands.
Key Differences Between Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates typically represent the successful completion of a comprehensive course or program, often covering a broad subject area with standardized criteria recognized by educational institutions or industries. Microcredentials validate specific skills or competencies through shorter, focused learning experiences, providing flexible, stackable credentials tailored to niche career advancements. Key differences include the scope, duration, and specificity, with certificates offering formal recognition for extended study and microcredentials enabling rapid, targeted skill validation aligned with evolving job market demands.
Industry Recognition: Certificates vs Microcredentials
Certificates often carry formal industry recognition and are typically issued by accredited institutions, making them valuable for traditional career advancement paths. Microcredentials, while emerging as flexible alternatives, are gaining traction in industries prioritizing specific skills and up-to-date expertise, often endorsed by professional organizations or employers. Both offer credibility, but certificates generally have broader acceptance, whereas microcredentials emphasize niche competencies and rapid acknowledgment in evolving job markets.
Duration and Commitment: What to Expect
Certificates typically require a longer duration of study, often spanning several months to a year, demanding a significant commitment of time and effort. Microcredentials usually involve shorter, focused learning experiences lasting a few weeks to a couple of months, allowing professionals to quickly acquire targeted skills. Choosing between the two depends on the desired depth of knowledge and available time for career advancement.
Cost Comparison: Which Is More Affordable?
Certificates typically require higher tuition fees and longer time commitments, making them a more substantial financial investment for career advancement. Microcredentials offer a cost-effective alternative by targeting specific skills with shorter durations and lower fees, providing flexibility for budget-conscious learners. Employers increasingly recognize microcredentials as valuable, balancing affordability with relevant skill validation.
Skill Relevance and Curriculum Depth
Certificates often provide comprehensive curriculum depth, covering broad knowledge areas essential for foundational career advancement, while microcredentials focus on specific, skill-relevant competencies suited for rapid skill acquisition in niche fields. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their targeted applicability and up-to-date relevance in fast-evolving industries, enhancing immediate job performance. Choosing between certificates and microcredentials depends on whether deep, structured learning or focused skill validation aligns better with career goals and industry demands.
Flexibility and Learning Formats
Certificates offer structured, often longer programs with fixed schedules, which work well for professionals seeking comprehensive knowledge and formal recognition. Microcredentials provide flexibility through shorter, modular courses that can be completed online or in hybrid formats, catering to busy individuals aiming to quickly upskill or reskill. The adaptability of microcredentials supports continuous learning and immediate application in dynamic career paths, while certificates emphasize in-depth mastery within traditional educational settings.
Impact on Employment Opportunities
Certificates demonstrate validated skills and knowledge in specific professional areas, often recognized by employers and industry standards, leading to enhanced job prospects and potential salary increases. Microcredentials, being shorter and more focused, provide targeted expertise in niche skills, making candidates more attractive for specialized roles and rapid upskilling. Both credentials contribute to career advancement, but certificates tend to carry more weight for traditional employment due to their comprehensive curriculum and formal recognition.
Choosing the Right Credential for Your Career Goals
Certificates typically involve comprehensive training programs that demonstrate mastery in a specific field, making them ideal for professionals seeking deep expertise and industry recognition. Microcredentials offer targeted, stackable learning experiences that validate specific skills or competencies, enabling quick skill acquisition and flexibility for career pivoting. Selecting the right credential depends on your career goals, whether you need broad knowledge for advancement or focused skills for immediate application.
Future Trends in Professional Certification and Microcredentialing
Certificates and microcredentials are evolving rapidly to meet the demands of dynamic job markets and technological advancements. Future trends emphasize stackable, competency-based credentials that offer personalized learning pathways and real-time skill validation through blockchain technology. Employers increasingly prioritize microcredentials for their agility in addressing specific skill gaps, enabling continuous career advancement and lifelong learning.
Related Important Terms
Microcredential Stacking
Microcredential stacking enables professionals to accumulate targeted skills through short, specialized courses, offering greater flexibility and relevance compared to traditional certificates. This approach accelerates career advancement by allowing learners to build a personalized portfolio of competencies recognized by employers.
Digital Badge Recognition
Digital badge recognition enhances career advancement by providing verifiable, stackable credentials that represent specific skills more flexibly than traditional certificates. Unlike certificates, microcredentials with digital badges enable employers to quickly assess up-to-date competencies and continuous learning in dynamic professional environments.
Competency-Based Certification
Competency-based certification validates specific skills and knowledge aligned with industry standards, making it more targeted for career advancement compared to traditional certificates that may cover broader topics. Microcredentials offer focused, stackable credentials that demonstrate mastery in niche areas, complementing competency-based certifications for a comprehensive skill portfolio.
Nano Degree
Nano degrees offer targeted skill development through microcredentialing, providing industry-relevant expertise that enhances career advancement more flexibly than traditional certificates. These microcredentials validate specialized competencies in shorter timeframes, aligning with evolving job market demands and increasing employability.
Skills Passport
Certificates typically represent completion of a comprehensive course or program, offering formal recognition of expertise, while microcredentials validate specific, job-relevant skills with greater flexibility and speed. Skills Passports integrate both certificates and microcredentials, providing a verified, digital record of an individual's competencies to enhance career advancement and employer trust.
Verified Microcertifications
Verified microcredentials offer targeted skill validation preferred by employers for rapid career advancement, providing precise evidence of competencies compared to traditional certificates. Their digital verification enhances credibility and accessibility, making them a valuable alternative in professional development and workforce upskilling.
Modular Credentials
Modular credentials like microcredentials offer targeted skill validation that complements traditional certificates by providing flexible, stackable learning units aligned with industry demands. These modular credentials enhance career advancement opportunities by allowing professionals to build specific competencies quickly and demonstrate continuous professional development.
Short-Form Certification
Short-form certifications provide targeted skill validation in specific areas, offering quicker, more accessible pathways for career advancement compared to traditional certificates. Microcredentials emphasize practical competencies and digital badges, enhancing employability through verifiable, stackable qualifications in dynamic industries.
Badge-to-Degree Pathways
Certificate programs offer focused skill development recognized by industry standards, while microcredentials provide modular, stackable achievements that can lead to advanced qualifications through badge-to-degree pathways, enhancing career mobility. Emphasizing badge-to-degree pathways allows professionals to accumulate verifiable digital credentials that seamlessly transfer into academic credits, accelerating lifelong learning and career advancement.
Just-in-Time Microlearning
Certificates provide comprehensive validation of skills over a broader period, while microcredentials deliver focused expertise through just-in-time microlearning, enabling rapid upskilling tailored to immediate job demands. Microcredentials enhance career advancement by offering flexible, targeted learning opportunities that align directly with evolving industry requirements.
Certificate vs Microcredential for career advancement Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com