Certification provides formal recognition of specific competencies through standardized assessments, ensuring verified expertise in a particular field. Skill passports offer a comprehensive record of practical skills and experiences, often linked to real-world job performance and continuous learning. Employers may prefer certification for its formal validation, while skill passports highlight ongoing development and adaptable abilities.
Table of Comparison
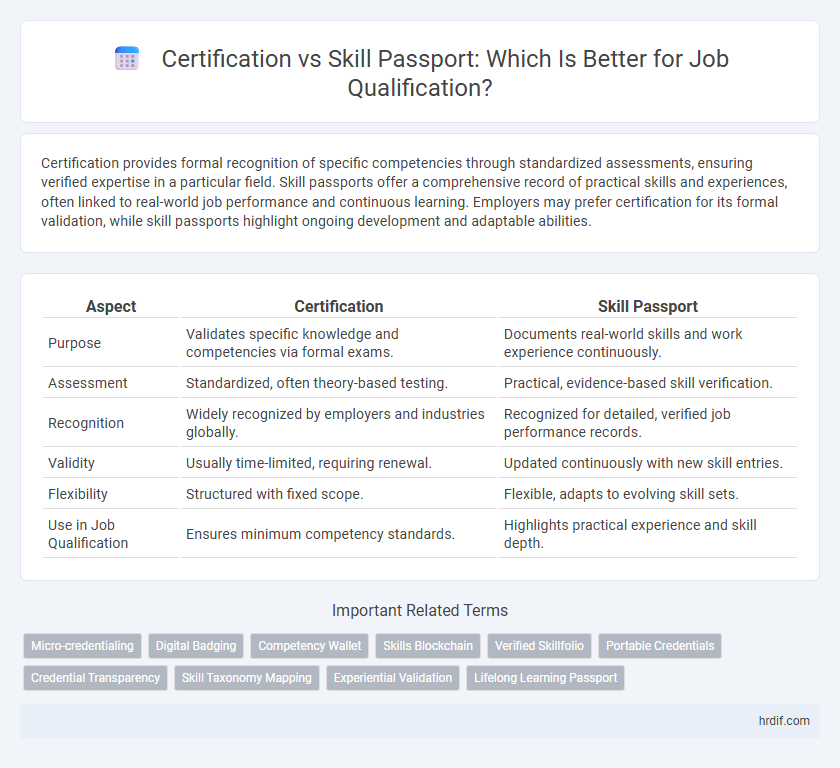
| Aspect | Certification | Skill Passport |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validates specific knowledge and competencies via formal exams. | Documents real-world skills and work experience continuously. |
| Assessment | Standardized, often theory-based testing. | Practical, evidence-based skill verification. |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and industries globally. | Recognized for detailed, verified job performance records. |
| Validity | Usually time-limited, requiring renewal. | Updated continuously with new skill entries. |
| Flexibility | Structured with fixed scope. | Flexible, adapts to evolving skill sets. |
| Use in Job Qualification | Ensures minimum competency standards. | Highlights practical experience and skill depth. |
Understanding Certification and Skill Passports
Certification validates an individual's competency through standardized testing and official recognition by industry authorities, ensuring measurable job qualifications. Skill passports document practical experience and verified skills, offering a comprehensive portfolio that highlights real-world capabilities. Employers use certification to confirm theoretical knowledge, while skill passports emphasize demonstrated expertise and job readiness.
Key Differences Between Certification and Skill Passports
Certifications are formal, standardized credentials issued by recognized institutions that validate a candidate's expertise in a specific field through rigorous testing and assessment. Skill passports, conversely, provide a personalized record of practical skills and experiences, often verified by employers or training organizations, emphasizing hands-on abilities rather than standardized benchmarks. The key differences lie in certification's broad acceptance and formal recognition versus the skill passport's focus on detailed, individualized skill documentation tailored to job-specific competencies.
The Role of Certifications in Job Qualification
Certifications provide standardized validation of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring employers can trust a candidate's expertise in a particular field. Unlike skill passports, which offer a broader, personalized record of competencies, certifications often carry industry recognition and regulatory approval, enhancing credibility in job qualification processes. These formal credentials play a crucial role in advancing career opportunities by meeting employer requirements and professional standards.
How Skill Passports Validate Competencies
Skill passports validate competencies by providing detailed, verifiable records of an individual's specific skills and practical experiences, offering employers precise evidence of job readiness beyond traditional certifications. Unlike certifications that often certify theoretical knowledge through standardized exams, skill passports capture real-world performance through continuous assessments, portfolios, and endorsements from supervisors or clients. This competency-based documentation enhances transparency in recruitment by aligning documented skills closely with job requirements, improving employer confidence in candidate qualifications.
Industry Preferences: Certification or Skill Passport?
Industry preferences for job qualifications vary, with certifications offering standardized validation of specific technical skills recognized across organizations. Skill passports provide a comprehensive portfolio showcasing practical experience and competencies, appealing to employers prioritizing demonstrable abilities over formal credentials. Companies in technology and healthcare sectors often favor certifications for regulatory compliance, while creative and project-based industries lean toward skill passports for their flexibility and real-world relevance.
Advantages of Traditional Certification
Traditional certification provides a standardized validation of professional skills recognized across industries and regions, enhancing employability and career advancement. It offers rigorous assessment methods ensuring credibility and consistency, which are often trusted more by employers compared to skill passports. Furthermore, certification programs frequently include ongoing education requirements, supporting continuous professional development and up-to-date expertise.
Benefits of Skill Passports for Modern Careers
Skill passports provide a dynamic, verifiable record of an individual's competencies, allowing employers to assess qualifications beyond traditional certifications. They facilitate continuous learning documentation and adaptability, essential for rapidly changing job markets in modern careers. By integrating real-time updates and third-party validations, skill passports enhance transparency and trust in workforce capabilities.
Recognizability and Portability Across Borders
Certification provides recognized and standardized validation of professional competencies, widely accepted by employers and regulatory bodies across multiple countries. Skill passports offer a detailed, personalized record of skills and experiences but may lack universal recognition, limiting their portability for international job qualification. Emphasizing globally accredited certifications enhances job mobility and trustworthiness in cross-border employment markets.
The Future of Job Qualification Standards
Certification remains a widely recognized benchmark for verifying professional expertise, while skill passports offer a dynamic and portable record of competencies aligned with evolving industry standards. Emerging job qualification frameworks emphasize the integration of both formal certifications and real-time skill validations to enhance workforce adaptability. The future of job qualification standards hinges on seamless interoperability between credentialing systems and digital skill portfolios, enabling employers to assess capabilities with greater precision.
Choosing the Right Path: Certification vs Skill Passport
Certification demonstrates validated expertise through formal assessments recognized by industry standards, ensuring credibility and often required by employers. Skill passports offer a flexible, comprehensive record of practical skills and experiences, highlighting real-world abilities beyond standardized tests. Selecting between certification and a skill passport depends on job requirements, industry expectations, and the individual's career goals for optimal qualification representation.
Related Important Terms
Micro-credentialing
Micro-credentialing offers targeted, verifiable proof of specific competencies, making it more adaptable for modern job qualifications compared to traditional certification which often covers broader skill sets. Skill passports aggregate these micro-credentials, providing a dynamic, digital portfolio that employers trust for assessing precise skills and experience.
Digital Badging
Digital badging offers a verifiable and portable way to showcase specific skills and competencies compared to traditional certification, which often emphasizes formal education or long-term qualifications. Skill passports leverage digital badges to provide employers with real-time, granular insights into a candidate's practical abilities and continuous learning achievements.
Competency Wallet
Competency Wallet consolidates verified certifications and skill passports into a unified digital profile, enabling employers to assess job qualifications with precise, standardized competency metrics. Unlike traditional certification that focuses on formal credentialing, Competency Wallet emphasizes real-time skill validation and continuous professional development tracking.
Skills Blockchain
Certification provides a verified and standardized proof of expertise recognized by employers, while a Skill Passport offers a portable, blockchain-secured record of specific competencies and achievements that enhance transparency and trust in job qualifications. Skills Blockchain technology ensures tamper-proof validation of both certifications and skill passports, facilitating seamless verification and boosting employer confidence in candidate qualifications.
Verified Skillfolio
Verified Skillfolio enhances job qualification by offering a dynamic Skill Passport that showcases verified skills and real-world achievements, unlike traditional certifications that merely confirm course completion or exam passing. This platform provides employers with transparent, up-to-date evidence of a candidate's capabilities, increasing hiring accuracy and workforce efficiency.
Portable Credentials
Portable credentials like skill passports offer dynamic, verifiable proof of job qualifications adaptable across different industries and regions, enhancing workforce mobility. Certifications provide formal recognition of expertise but often lack the flexibility and real-time update capabilities inherent in digital skill passports.
Credential Transparency
Certification provides a standardized validation of specific skills and knowledge assessed through formal examinations, ensuring clear and widely recognized credential transparency for employers. Skill passports offer a dynamic, portfolio-based record of competencies and experiences, promoting comprehensive but less standardized credential transparency in job qualification processes.
Skill Taxonomy Mapping
Certification validates specific industry standards and expertise, providing recognized proof of competency, while Skill Passport offers a dynamic, personalized record aligned with skill taxonomy mapping for precise job qualification assessment. Skill taxonomy mapping enhances the Skill Passport's effectiveness by categorizing skills into structured frameworks, enabling employers to match candidate qualifications with job requirements more accurately than traditional certification alone.
Experiential Validation
Certification provides formal recognition based on standardized assessments, whereas a Skill Passport emphasizes experiential validation by documenting practical competencies and real-world achievements. Employers value Skill Passports for showcasing verified hands-on experience that often surpasses traditional certification in demonstrating job readiness.
Lifelong Learning Passport
The Lifelong Learning Passport serves as a dynamic skill passport, capturing ongoing competencies and practical experiences beyond static certifications, which often validate knowledge at a specific point in time. This evolving record supports job qualification by demonstrating continuous professional development and adaptability in rapidly changing industries.
Certification vs Skill passport for job qualification. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com