Adaptability is crucial in navigating future jobs, enabling individuals to quickly learn new skills and adjust to changing environments. Unlike a portfolio career, which involves managing multiple job roles or projects simultaneously, adaptability prioritizes flexibility and continuous growth within varied or evolving roles. Employers increasingly value adaptability as it ensures resilience and long-term success amid unpredictable job markets.
Table of Comparison
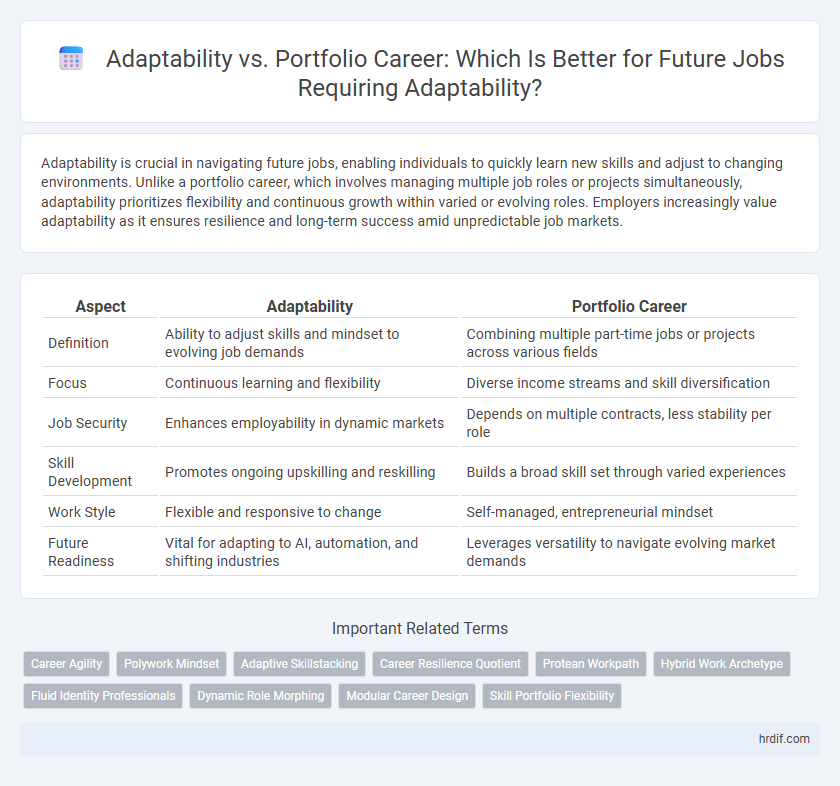
| Aspect | Adaptability | Portfolio Career |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust skills and mindset to evolving job demands | Combining multiple part-time jobs or projects across various fields |
| Focus | Continuous learning and flexibility | Diverse income streams and skill diversification |
| Job Security | Enhances employability in dynamic markets | Depends on multiple contracts, less stability per role |
| Skill Development | Promotes ongoing upskilling and reskilling | Builds a broad skill set through varied experiences |
| Work Style | Flexible and responsive to change | Self-managed, entrepreneurial mindset |
| Future Readiness | Vital for adapting to AI, automation, and shifting industries | Leverages versatility to navigate evolving market demands |
Understanding Adaptability in the Modern Workplace
Understanding adaptability in the modern workplace involves recognizing its role as a key driver of career resilience and growth amidst rapid industry changes. Adaptability enables professionals to swiftly learn new skills, pivot between roles, and embrace evolving technologies, which contrasts with the portfolio career approach that emphasizes juggling multiple specialized roles simultaneously. Emphasizing adaptability fosters continuous personal development and agile problem-solving, essential for thriving in dynamic job markets shaped by automation and globalization.
Defining a Portfolio Career
A portfolio career involves managing multiple part-time roles or freelance projects simultaneously, offering diverse skill development and income streams. Unlike traditional employment, it requires adaptability to navigate varying industries, clients, and work environments efficiently. This flexible career model aligns with future job trends emphasizing continuous learning and resilience in dynamic markets.
Key Differences: Adaptability vs Portfolio Career
Adaptability involves flexibility and continuous learning to thrive in changing job markets, while a portfolio career emphasizes managing multiple job roles or projects simultaneously. Adaptability centers on developing transferable skills that apply across various industries, whereas a portfolio career requires strategic balancing of diverse income streams and professional identities. Understanding these distinctions can guide future job seekers in choosing between fluid skill enhancement and diversified career structures.
Benefits of Being Adaptable in Future Jobs
Being adaptable enhances resilience and agility in an evolving job market, enabling professionals to quickly acquire new skills and pivot across industries. This flexibility supports sustained employability by allowing individuals to respond effectively to technological advancements and shifting economic demands. Embracing adaptability fosters continuous learning and innovation, critical for thriving in diverse and dynamic career landscapes.
Advantages of Building a Portfolio Career
Building a portfolio career enhances adaptability by diversifying skill sets across multiple industries, increasing resilience against job market fluctuations. This approach enables continuous learning and flexibility, allowing professionals to pivot roles or sectors with ease. A varied portfolio also expands networking opportunities, leading to greater job security and career satisfaction.
Challenges of Adapting vs Maintaining Multiple Careers
Adapting to future job markets requires continuous skill development and flexibility to navigate shifting industry demands, posing significant challenges in mastering new competencies rapidly. Maintaining a portfolio career involves juggling multiple roles simultaneously, which demands exceptional time management and the ability to balance diverse professional identities without compromising performance. Both strategies face the challenge of sustaining relevance, but adaptability prioritizes deep specialization in evolving fields, while portfolio careers emphasize breadth and resilience across sectors.
Skills Required for Adaptability and Portfolio Careers
Adaptability demands strong problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and continuous learning skills to navigate evolving job markets and unexpected challenges effectively. Portfolio careers require versatility in technical skills, time management, and self-marketing to successfully juggle multiple roles and industries. Both pathways prioritize digital literacy and resilience, but portfolio careers emphasize entrepreneurial skills and networking for sustained career growth.
Impact on Job Security: Adaptability vs Portfolio Career
Adaptability enhances job security by enabling professionals to quickly learn new skills and adjust to evolving industry demands, ensuring continuous relevance in the workforce. In contrast, a portfolio career, characterized by multiple concurrent roles or projects, can diversify income streams but may also introduce variability in job stability due to fluctuating demand across different engagements. Emphasizing adaptability fosters resilience against market disruptions, while portfolio careers require proactive management of diverse opportunities to maintain consistent employment.
How Employers Value Adaptability and Portfolio Experience
Employers increasingly prioritize adaptability for future jobs, valuing the ability to quickly learn new skills and navigate changing work environments. Portfolio career experience demonstrates a candidate's versatility and capacity to manage diverse projects, showcasing practical adaptability in varied professional contexts. This combination enhances employability by signaling resilience and a proactive approach to evolving job demands.
Choosing the Right Path: Adaptability or Portfolio Career
Choosing the right path between adaptability and a portfolio career depends on aligning skills with future job market demands, where adaptability emphasizes continuous learning and flexibility across roles, while a portfolio career involves managing multiple income streams from diverse projects. Adaptability suits dynamic industries requiring quick skill evolution, whereas a portfolio career benefits those seeking autonomy and varied professional experiences. Evaluating personal strengths, market trends, and long-term goals ensures a strategic choice for sustainable career growth.
Related Important Terms
Career Agility
Career agility enhances long-term success by cultivating adaptability, enabling professionals to pivot seamlessly across evolving roles and industries, unlike a static portfolio career that may limit flexibility. Emphasizing skill diversification and continuous learning fosters resilience in dynamic job markets, making adaptability a critical asset for future-proof careers.
Polywork Mindset
The Polywork Mindset emphasizes adaptability by encouraging professionals to diversify skills and embrace multifaceted roles, contrasting with traditional portfolio careers that segment expertise into distinct paths. This approach fosters continuous learning and flexibility, essential for navigating the evolving future job market shaped by cross-disciplinary collaboration and technological innovation.
Adaptive Skillstacking
Adaptive Skillstacking enhances career resilience by combining diverse, transferable skills tailored to evolving job markets, outperforming traditional portfolio careers limited to fixed roles. Emphasizing continuous skill adaptation prepares individuals for future job demands, fostering agility in navigating dynamic career landscapes.
Career Resilience Quotient
Adaptability enhances Career Resilience Quotient by enabling professionals to pivot skills and embrace continuous learning, ensuring stability amid job market fluctuations. In contrast, a Portfolio Career diversifies income streams but relies heavily on managing varied roles, which may challenge consistent career resilience without adaptable mindsets.
Protean Workpath
Adaptability in the Protean Workpath emphasizes continuous self-directed learning and flexibility, enabling professionals to navigate diverse roles and industries effectively. Unlike the portfolio career model, which involves juggling multiple simultaneous jobs, the Protean approach prioritizes internal growth and values alignment, fostering resilience in rapidly changing job markets.
Hybrid Work Archetype
Adaptability in the Hybrid Work Archetype enhances a professional's ability to navigate fluctuating job roles and remote-on-site dynamics, making them more resilient to changes in the future job market. While a portfolio career offers diversified skills, adaptability specifically empowers seamless transitions across hybrid work environments, optimizing productivity and collaboration.
Fluid Identity Professionals
Fluid identity professionals excel in adaptability by continuously evolving skills and roles, contrasting with the traditional portfolio career that emphasizes diverse but discrete job experiences. Embracing adaptability allows these professionals to navigate future job markets through seamless identity shifts and skill integrations, optimizing career resilience and growth.
Dynamic Role Morphing
Dynamic Role Morphing enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to seamlessly transition between diverse roles, fostering continuous skill acquisition and resilience in rapidly evolving job markets. Embracing a portfolio career further amplifies this flexibility, allowing individuals to curate varied work experiences that align with future job demands and economic uncertainties.
Modular Career Design
Modular career design enhances adaptability by allowing professionals to assemble diverse skill sets and experiences tailored to evolving job markets, outperforming traditional portfolio careers with fixed roles. Emphasizing flexibility and continuous learning, modular approaches enable seamless transitions across industries and projects, future-proofing careers against economic and technological shifts.
Skill Portfolio Flexibility
Skill portfolio flexibility enables professionals to navigate the evolving job market more effectively than a traditional portfolio career by continuously updating and diversifying competencies across multiple domains. This adaptability ensures resilience to industry disruptions and enhances employability by aligning skills with emerging opportunities.
Adaptability vs Portfolio Career for future jobs Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com