Adaptability emphasizes developing versatile skills and willingness to learn new roles, making employees resilient in changing job markets. Portfolioism focuses on building diverse income streams and projects, reducing reliance on a single employer or position. Balancing adaptability with a portfolio approach enhances career security and growth opportunities in unpredictable employment landscapes.
Table of Comparison
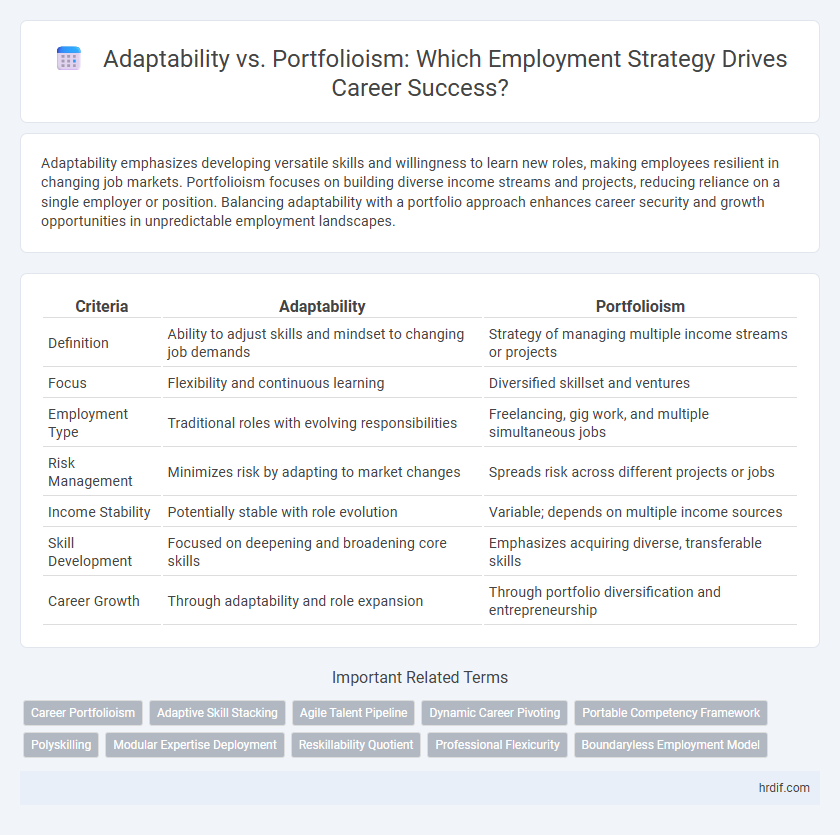
| Criteria | Adaptability | Portfolioism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust skills and mindset to changing job demands | Strategy of managing multiple income streams or projects |
| Focus | Flexibility and continuous learning | Diversified skillset and ventures |
| Employment Type | Traditional roles with evolving responsibilities | Freelancing, gig work, and multiple simultaneous jobs |
| Risk Management | Minimizes risk by adapting to market changes | Spreads risk across different projects or jobs |
| Income Stability | Potentially stable with role evolution | Variable; depends on multiple income sources |
| Skill Development | Focused on deepening and broadening core skills | Emphasizes acquiring diverse, transferable skills |
| Career Growth | Through adaptability and role expansion | Through portfolio diversification and entrepreneurship |
Defining Adaptability and Portfolioism in Modern Careers
Adaptability in modern careers refers to the ability to swiftly adjust skills and approaches in response to evolving job demands and market conditions, ensuring long-term employability. Portfolioism, by contrast, emphasizes cultivating multiple simultaneous income streams and diverse skill sets across different projects or roles to mitigate employment risks. Defining these concepts highlights adaptability as dynamic personal growth, while portfolioism represents strategic diversification in career management.
The Evolving Job Market: Why Strategy Matters
Adaptability in the evolving job market enables individuals to navigate shifting demands and emerging industries more effectively than relying solely on portfolioism, which often emphasizes collection over flexibility. Emphasizing adaptability cultivates skills like continuous learning, problem-solving, and resilience, making workers more agile amidst rapid technological changes and economic fluctuations. Strategic adaptability aligns employment approaches with future trends, enhancing long-term career sustainability in dynamic labor markets.
Core Traits of an Adaptable Professional
An adaptable professional demonstrates resilience, continuous learning, and flexibility in navigating career transitions, which contrasts with portfolioism's emphasis on accumulating diverse roles without deep skill integration. Core traits include cognitive agility, emotional intelligence, and proactive problem-solving, enabling quick adjustment to evolving job market demands. These attributes foster sustained employability by prioritizing skill mastery and situational awareness over merely expanding a job portfolio.
Portfolioism: Building a Diverse Skillset for Employment
Portfolioism emphasizes cultivating a diverse skillset across multiple disciplines to enhance employability in a dynamic job market. This strategy enables professionals to showcase versatility, making them attractive to a broader range of employers and industries. By continuously developing varied competencies, Portfolioism supports career resilience and long-term growth.
Pros and Cons: Adaptability versus Portfolio Careers
Adaptability in employment strategy emphasizes developing versatile skills that enable seamless transitions across roles and industries, fostering long-term career resilience. Portfolio careers offer diverse income streams and professional experiences but may lead to fragmented focus and less stability. Balancing adaptability and portfolioism requires weighing flexibility against depth of expertise and consistent income.
Career Resilience: Which Strategy Offers More Security?
Adaptability emphasizes continuous skill development and flexibility to navigate changing job markets, enhancing career resilience by enabling professionals to pivot across roles and industries seamlessly. Portfolioism, relying on multiple income streams or gigs, diversifies employment but can risk stability due to fluctuating demand and inconsistent benefits. Career resilience is generally stronger with adaptability, as it fosters long-term security through ongoing learning and the ability to meet evolving employer needs.
Skill Development: Depth Versus Breadth
Adaptability in employment strategy emphasizes deep skill development within a specialized area, fostering expertise that enhances problem-solving and innovation. In contrast, portfolioism promotes a broad skill set across multiple domains, enabling flexibility but potentially diluting mastery. Prioritizing depth over breadth in skill development drives higher value in competitive job markets and supports sustained career growth through focused adaptability.
Navigating Uncertainty: Adaptability and Portfolioism in Practice
Navigating uncertainty in employment strategy requires balancing adaptability and portfolioism to maximize career resilience. Adaptability emphasizes continuous learning and flexibility to respond swiftly to changing job markets, while portfolioism diversifies income streams through multiple concurrent projects or roles. Combining these approaches allows professionals to stay relevant and financially secure amid volatile economic conditions.
Employer Perspectives: What Do Hiring Managers Value?
Hiring managers prioritize adaptability as a critical skill, valuing candidates who demonstrate flexibility and the ability to thrive in dynamic work environments. While portfolioism showcases specific projects and skills, employers emphasize adaptability for its role in problem-solving, collaboration, and responding to evolving business needs. This preference highlights the importance of candidates who can quickly learn new tools and adjust to shifting priorities over static portfolios.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Career Goals
Adaptability enables professionals to effectively respond to changing job markets by continuously acquiring new skills and embracing diverse roles, while portfolioism focuses on showcasing a broad range of projects and experiences to attract varied opportunities. Selecting the right employment strategy depends on career goals: adaptability suits those seeking long-term growth within evolving industries, whereas portfolioism benefits freelancers and creatives aiming to highlight versatility. Aligning your approach with industry demands and personal strengths maximizes career success and resilience.
Related Important Terms
Career Portfolioism
Career Portfolioism emphasizes building a diversified skill set and multiple professional experiences to enhance employability across various industries, contrasting with Adaptability's focus on adjusting within a single role or sector. Employers increasingly value Career Portfolioism as it demonstrates proactive career management and resilience in dynamic job markets.
Adaptive Skill Stacking
Adaptive skill stacking cultivates a versatile employment strategy by combining complementary competencies that enhance responsiveness to evolving job market demands, contrasting with portfolioism's focus on diverse but unrelated skills. This approach optimizes career resilience and growth by integrating adaptive proficiencies tailored to dynamic industry trends and technological advancements.
Agile Talent Pipeline
An Agile Talent Pipeline leverages adaptability by continuously developing diverse skills and swiftly redeploying talent to meet evolving business needs, contrasting with portfolioism's fragmented focus on accumulating multiple job roles without strategic alignment. Emphasizing adaptability ensures sustained workforce agility and resilience, optimizing employment strategies beyond the episodic gains of portfolio approaches.
Dynamic Career Pivoting
Dynamic career pivoting emphasizes adaptability by enabling professionals to respond swiftly to evolving job markets and industry trends, contrasting portfolioism's approach of maintaining multiple concurrent roles. This strategy enhances long-term employability by fostering transferable skills and continuous learning, positioning individuals to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Portable Competency Framework
The Portable Competency Framework enhances adaptability by emphasizing transferable skills and continuous learning, enabling workers to navigate diverse job markets more effectively than traditional portfolioism, which relies heavily on accumulating varied experiences without cohesive skill integration. This framework supports employment strategies focused on dynamic skill application across industries, fostering resilience amid shifting economic demands and technological advancements.
Polyskilling
Polyskilling enhances adaptability by equipping individuals with versatile skills across multiple domains, offering a more dynamic and resilient employment strategy compared to traditional portfolioism. This approach fosters continuous learning and flexibility, enabling workers to seamlessly transition between roles and industries amid evolving job market demands.
Modular Expertise Deployment
Modular Expertise Deployment enhances adaptability by allowing professionals to apply discrete, transferable skills across diverse projects, contrasting with Portfolioism's fragmented job-hopping approach that may lack strategic coherence. This method maximizes employment stability and career growth by aligning specialized competencies with evolving market demands.
Reskillability Quotient
Adaptability in employment strategy centers on continuously enhancing one's Reskillability Quotient, reflecting the ability to learn new skills efficiently in response to evolving job demands. Portfolioism, by contrast, emphasizes maintaining a diverse set of skills and projects, but may neglect the depth of reskillability crucial for long-term career resilience.
Professional Flexicurity
Adaptability emphasizes continuous skill development and flexibility to meet evolving job demands, enabling professionals to navigate uncertain labor markets effectively. Portfolioism, while diversifying income sources, may lack the stability of professional flexicurity, which balances adaptable employment contracts with social security protections to foster long-term career resilience.
Boundaryless Employment Model
The Boundaryless Employment Model emphasizes adaptability by encouraging continuous skill development and cross-industry mobility, contrasting with portfolioism's reliance on managing multiple concurrent projects or gigs. Adaptability within this model enables workers to navigate evolving job markets and organizational shifts more effectively than portfolioism's segmented approach.
Adaptability vs Portfolioism for employment strategy. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com