Adaptability in remote work emphasizes an employee's ability to adjust to changing environments, tools, and workflows independently, ensuring consistent productivity and engagement. Hybridity combines in-office and remote work, requiring employees to navigate both settings seamlessly while managing communication and collaboration challenges. Prioritizing adaptability fosters resilience and a proactive mindset, crucial for success in hybrid models where flexibility is key.
Table of Comparison
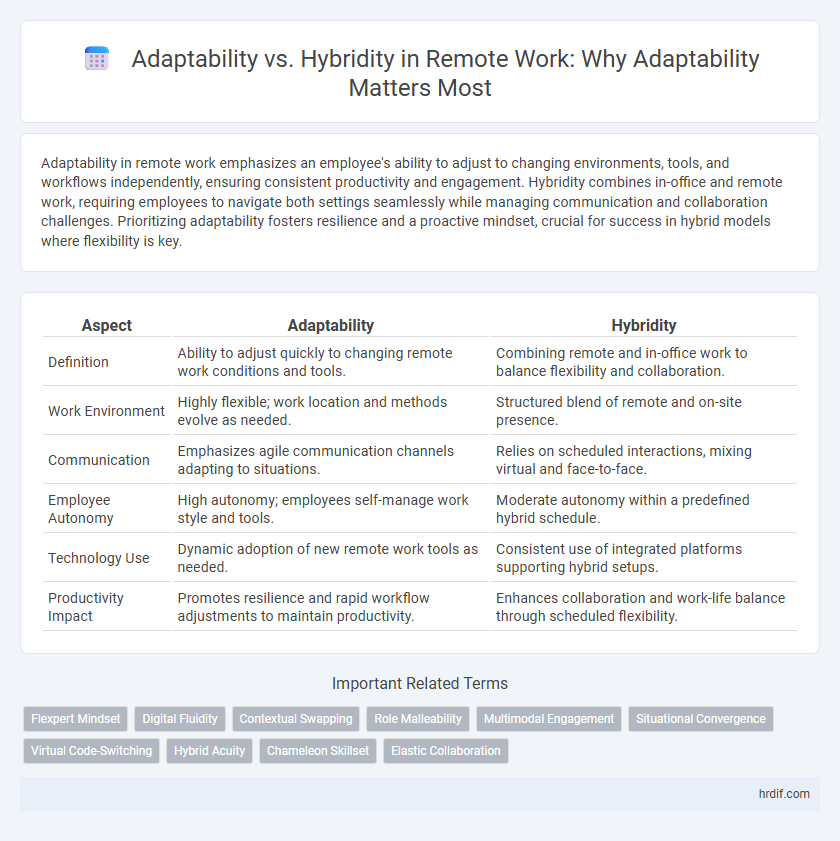
| Aspect | Adaptability | Hybridity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust quickly to changing remote work conditions and tools. | Combining remote and in-office work to balance flexibility and collaboration. |
| Work Environment | Highly flexible; work location and methods evolve as needed. | Structured blend of remote and on-site presence. |
| Communication | Emphasizes agile communication channels adapting to situations. | Relies on scheduled interactions, mixing virtual and face-to-face. |
| Employee Autonomy | High autonomy; employees self-manage work style and tools. | Moderate autonomy within a predefined hybrid schedule. |
| Technology Use | Dynamic adoption of new remote work tools as needed. | Consistent use of integrated platforms supporting hybrid setups. |
| Productivity Impact | Promotes resilience and rapid workflow adjustments to maintain productivity. | Enhances collaboration and work-life balance through scheduled flexibility. |
Understanding Adaptability in Remote Work
Adaptability in remote work involves the continuous adjustment to evolving technologies, communication styles, and work environments to maintain productivity and collaboration. Unlike hybridity, which blends remote and in-person work settings, adaptability emphasizes individual and organizational flexibility in real-time problem-solving and workflow optimization. Mastering adaptability enables remote workers to navigate uncertainties and sustain efficient performance despite shifting circumstances.
Defining Hybridity in Modern Work Environments
Hybridity in modern work environments refers to a flexible structure combining remote and on-site work, allowing employees to choose where and how they work based on role requirements and personal preferences. This model emphasizes the integration of digital tools and physical office spaces to optimize productivity and collaboration. Defining hybridity involves understanding its role in balancing employee autonomy with organizational goals in a dynamic post-pandemic landscape.
Key Differences: Adaptability vs Hybridity
Adaptability in remote work emphasizes the ability of individuals and organizations to swiftly adjust to changing environments, workflows, and technologies, ensuring productivity and resilience. Hybridity involves integrating both in-office and remote work models, balancing flexibility with structured collaboration to optimize team dynamics and resource allocation. Key differences lie in adaptability's focus on continuous, flexible change versus hybridity's emphasis on blending physical and virtual workspaces to create a cohesive work experience.
The Importance of Adaptability for Remote Teams
Adaptability in remote teams enhances flexibility in responding to dynamic work environments, promoting seamless communication across diverse time zones and technological platforms. Emphasizing adaptability over hybridity streamlines workflows by enabling team members to quickly adjust to evolving project requirements and remote collaboration tools. This responsive approach boosts productivity and fosters resilience, crucial for sustaining performance in remote work settings.
Hybrid Work Models: Benefits and Challenges
Hybrid work models combine remote and in-office work, offering flexibility that enhances employee adaptability by accommodating diverse work styles and improving work-life balance. These models boost productivity through tailored environments but challenge organizations with coordination complexities and potential communication gaps. Effective hybrid systems require robust digital tools and clear policies to maintain collaboration and organizational culture while leveraging adaptability benefits.
Building Adaptable Skillsets for Future Careers
Building adaptable skillsets for future careers in remote work emphasizes continuous learning, digital literacy, and emotional intelligence to navigate evolving job demands. Adaptability focuses on flexible problem-solving and resilience, enabling professionals to manage changing technologies and workflows efficiently. Unlike hybridity, which combines remote and in-office work models, adaptability equips individuals to thrive regardless of the environment by developing versatile capabilities essential for long-term career success.
Hybridity’s Impact on Workplace Collaboration
Hybridity in remote work fosters dynamic workplace collaboration by blending in-person and virtual interactions, enhancing communication channels and team cohesion. This model leverages diverse technological tools and flexible work environments to accommodate varying employee needs, boosting productivity and engagement. Effective hybridity strategies promote seamless knowledge sharing and innovation, driving organizational resilience and adaptability.
Adaptability and Employee Well-being in Remote Settings
Adaptability in remote work environments enhances employee well-being by promoting flexible responses to changing demands and fostering resilience against stressors. Unlike hybridity, which combines remote and in-office work, adaptability emphasizes individual capacity to adjust work patterns, improving mental health and productivity. Organizations prioritizing adaptability support personalized workflows, leading to increased job satisfaction and reduced burnout among remote employees.
Choosing Between Adaptability and Hybridity for Career Growth
Choosing adaptability over hybridity in remote work environments enables professionals to swiftly adjust to evolving technologies and workflows, fostering continuous skill development crucial for career growth. Emphasizing adaptability enhances resilience and problem-solving abilities, which are highly valued by employers in dynamic industries. While hybridity combines remote and in-office work, prioritizing adaptability ensures sustained relevance and competitiveness in increasingly fluid job markets.
Strategies to Foster Adaptability and Hybridity in Remote Work
Effective strategies to foster adaptability and hybridity in remote work include implementing flexible communication tools that support diverse collaboration styles and encouraging continuous learning through virtual training programs. Organizations can leverage hybrid work models by blending synchronous and asynchronous workflows, ensuring employees adjust seamlessly to varying schedules and environments. Promoting psychological safety and regular feedback loops further enhances employees' ability to navigate and thrive in dynamic remote settings.
Related Important Terms
Flexpert Mindset
The Flexpert Mindset enhances adaptability in remote work by seamlessly integrating expert knowledge with flexible working styles, surpassing traditional hybridity models that merely combine in-office and remote setups. This mindset fosters dynamic collaboration and continuous learning, driving higher productivity and employee engagement in distributed teams.
Digital Fluidity
Digital fluidity enhances adaptability by enabling seamless transitions between diverse remote work tools and environments, whereas hybridity integrates fixed remote and in-office patterns that may limit rapid flexibility. Emphasizing digital fluidity fosters continuous skill evolution and dynamic collaboration essential for thriving in ever-changing remote work landscapes.
Contextual Swapping
Contextual swapping in remote work highlights adaptability by enabling employees to shift fluidly between diverse virtual environments, optimizing productivity across various platforms. Unlike hybridity, which combines physical and remote settings, adaptability through contextual swapping emphasizes flexible cognitive and behavioral adjustments tailored to dynamic digital contexts.
Role Malleability
Role malleability in remote work emphasizes adaptability by allowing employees to modify their responsibilities and workflows based on dynamic virtual environments, enhancing productivity and engagement. Unlike hybridity, which blends in-office and remote settings, adaptability through role malleability prioritizes flexible skill application and task redefinition to meet evolving organizational demands.
Multimodal Engagement
Adaptability in remote work emphasizes flexible responses to changing environments, enabling seamless multimodal engagement across video, audio, and text platforms. Hybridity integrates multiple work models but often demands more structured coordination, whereas adaptability fosters spontaneous collaboration through diverse communication channels.
Situational Convergence
Situational convergence in remote work highlights adaptability as the ability to seamlessly align skills and behaviors with changing environments, rather than mere hybridity, which blends in-person and remote modalities without deep contextual integration. This adaptability-driven convergence fosters enhanced productivity and collaboration by continuously tuning workflows to specific situational demands.
Virtual Code-Switching
Adaptability in remote work hinges on effective virtual code-switching, which involves seamlessly shifting communication styles and digital tools to match diverse virtual environments and team cultures. Hybridity integrates multiple work modes but relies heavily on adaptability to navigate complex interactions and maintain productivity across in-person and remote settings.
Hybrid Acuity
Hybrid Acuity enhances remote work by combining adaptability with the strategic integration of hybrid models, enabling seamless transitions between in-office and virtual environments. This approach optimizes productivity and collaboration by leveraging flexible workflows tailored to diverse work settings.
Chameleon Skillset
Chameleon skillset exemplifies adaptability by enabling remote workers to seamlessly adjust behaviors and communication styles across diverse virtual environments, unlike hybridity which blends physical and digital workspaces. This dynamic flexibility enhances collaboration and productivity in remote settings by fostering resilience and cultural agility.
Elastic Collaboration
Elastic Collaboration enhances adaptability in remote work by allowing seamless scalability and dynamic team configurations, unlike hybridity which blends fixed in-office and remote setups. This approach optimizes productivity by enabling teams to fluidly adjust workflows and communication based on project needs and individual availability.
Adaptability vs Hybridity for remote work. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com