Adaptability in the workplace ensures employees can quickly respond to changing demands, making them valuable assets in any industry. Career cushioning involves building a safety net of skills and networks to protect against job loss but may not guarantee long-term job security. Prioritizing adaptability fosters continuous growth and resilience, creating a more sustainable path for career stability than relying solely on career cushioning strategies.
Table of Comparison
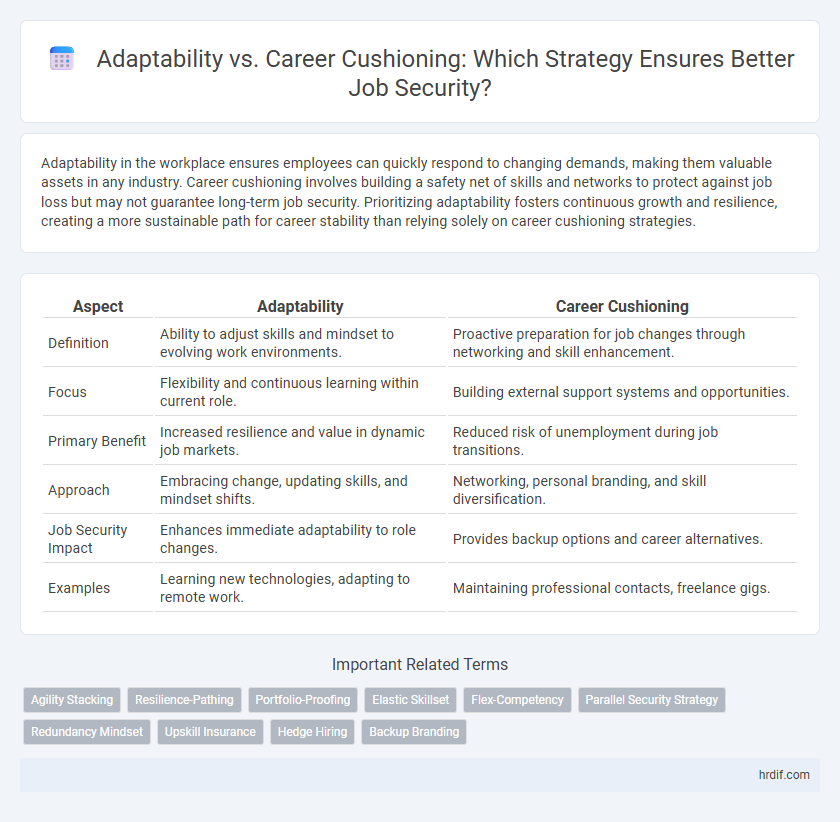
| Aspect | Adaptability | Career Cushioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust skills and mindset to evolving work environments. | Proactive preparation for job changes through networking and skill enhancement. |
| Focus | Flexibility and continuous learning within current role. | Building external support systems and opportunities. |
| Primary Benefit | Increased resilience and value in dynamic job markets. | Reduced risk of unemployment during job transitions. |
| Approach | Embracing change, updating skills, and mindset shifts. | Networking, personal branding, and skill diversification. |
| Job Security Impact | Enhances immediate adaptability to role changes. | Provides backup options and career alternatives. |
| Examples | Learning new technologies, adapting to remote work. | Maintaining professional contacts, freelance gigs. |
Defining Adaptability in the Modern Workplace
Adaptability in the modern workplace refers to the ability to quickly adjust to new technologies, shifting market demands, and evolving organizational structures. It involves continuous learning, flexibility in problem-solving, and openness to change, which are critical for sustaining long-term career growth. Unlike career cushioning, which focuses on building backup plans, adaptability emphasizes proactive skill development and resilience to navigate uncertainty effectively.
What Is Career Cushioning?
Career cushioning involves building alternative skills, networks, and income streams to maintain financial stability and job security during workforce disruptions. Unlike adaptability, which emphasizes flexibility and learning within current roles, career cushioning proactively prepares individuals for potential job loss or industry shifts. This strategy includes taking courses, freelancing, and expanding professional connections to create safety nets beyond one's primary employment.
Key Differences: Adaptability vs Career Cushioning
Adaptability involves continuously developing new skills and embracing change to thrive in evolving job markets, enhancing long-term career resilience. Career cushioning focuses on creating immediate fallback options such as part-time jobs or side gigs to mitigate the risk of job loss. While adaptability fosters sustainable growth and flexibility, career cushioning provides short-term security without necessarily improving professional competence.
The Role of Adaptability in Securing Your Job
Adaptability enhances job security by enabling employees to respond effectively to changing industry demands, technological advances, and organizational restructuring. Unlike career cushioning, which focuses on creating backup options, adaptability ensures long-term relevance by fostering continuous skill development and a proactive mindset. Employers increasingly prioritize adaptable workers who can seamlessly navigate uncertainty and contribute to sustained business success.
How Career Cushioning Influences Job Security
Career cushioning enhances job security by building a financial safety net and developing transferable skills, allowing professionals to manage employment risks more effectively. This proactive approach reduces dependency on a single job, enabling smoother transitions during layoffs or industry shifts. Employers recognize candidates who engage in career cushioning as resilient and versatile, increasing their long-term employability in competitive job markets.
Pros and Cons: Adaptability Compared to Career Cushioning
Adaptability enhances long-term job security by fostering continuous learning and flexibility in changing work environments, allowing individuals to seize emerging opportunities and remain relevant. Career cushioning provides immediate financial protection and reduces stress by building savings or side income but may limit professional growth if over-relied upon without skill development. Balancing adaptability with career cushioning strategies offers robust security by combining proactive skill enhancement with practical financial safeguards.
Building Adaptability Skills for Career Growth
Building adaptability skills enhances career growth by enabling professionals to embrace change, learn new technologies, and respond effectively to shifting industry demands. Unlike career cushioning, which focuses on safety nets like multiple income streams or side jobs, adaptability fosters long-term job security through continuous personal development and resilience. Investing in adaptability drives innovation, improves problem-solving, and aligns talents with evolving market needs, ensuring sustained career advancement.
Strategies for Effective Career Cushioning
Effective career cushioning involves continuous skill development, expanding professional networks, and diversifying income streams to safeguard against job market volatility. Emphasizing adaptability through acquiring transferable skills and staying informed about industry trends enhances resilience and ensures long-term career stability. Proactively managing career transitions and financial planning are crucial strategies for cushioning employment risks in an evolving workforce.
When to Prioritize Adaptability Over Career Cushioning
Prioritize adaptability over career cushioning when facing rapidly changing industries or technological disruptions, as flexibility enables individuals to acquire new skills and pivot effectively. Adaptability fosters resilience by allowing professionals to respond swiftly to market shifts, enhancing long-term job security beyond the temporary protections offered by career cushioning strategies like side gigs or emergency funds. Emphasizing continuous learning and skill diversification prepares workers to thrive in volatile job markets rather than solely relying on safety nets.
Integrating Adaptability and Career Cushioning for Long-Term Security
Integrating adaptability and career cushioning enhances long-term job security by combining continuous skill development with strategic risk management. Adaptability allows professionals to respond effectively to evolving market demands, while career cushioning provides a safety net through diversified income streams or upskilling. This dual approach ensures resilience against economic fluctuations and industry disruptions.
Related Important Terms
Agility Stacking
Agility stacking enhances job security by continuously building diverse, adaptable skills that align with evolving market demands, surpassing the static approach of career cushioning which relies on fallback plans. This dynamic skill accumulation fosters resilience and proactive career management, enabling professionals to thrive amid industry disruptions and rapid change.
Resilience-Pathing
Developing resilience-pathing enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to proactively navigate career shifts and uncertainties, outperforming career cushioning tactics that merely provide temporary job security. Emphasizing skill diversification and strategic mindset fosters long-term employment stability through continuous growth rather than reliance on fallback options.
Portfolio-Proofing
Portfolio-proofing enhances job security by continuously updating skills and experiences to match evolving industry demands, making adaptability a proactive strategy against job market fluctuations. Unlike career cushioning, which centers on fallback options, portfolio-proofing prioritizes growth and resilience through diversified competencies and tangible achievements.
Elastic Skillset
An elastic skillset enhances job security by enabling professionals to adapt quickly to evolving industry demands, whereas career cushioning relies on building buffers like savings or side gigs without directly improving adaptability. Investing in developing versatile, transferable skills positions individuals to navigate career shifts proactively, outperforming traditional cushioning strategies for long-term stability.
Flex-Competency
Flex-Competency enhances adaptability by equipping professionals with versatile skills that enable seamless transitions across roles, outperforming career cushioning strategies focused solely on job security. Emphasizing continuous learning and agility, Flex-Competency prepares individuals to thrive amidst evolving market demands and technological advancements.
Parallel Security Strategy
Adopting a parallel security strategy by balancing adaptability and career cushioning enhances job security, allowing professionals to pivot roles swiftly while maintaining financial stability through side projects or upskilling. This dual approach mitigates risks of job displacement and prepares individuals for evolving market demands without relying solely on one security method.
Redundancy Mindset
Adaptability enhances job security by fostering continuous skill development and embracing change, whereas a redundancy mindset fixates on career cushioning through fallback options that may limit growth. Emphasizing flexibility over precautionary measures enables professionals to navigate industry shifts effectively and reduce vulnerability to layoffs.
Upskill Insurance
Upskill insurance enhances adaptability by continuously expanding an employee's skill set, providing a proactive strategy for job security amid evolving industry demands. Unlike career cushioning, which prepares for transition, upskill insurance ensures ongoing relevance and competitiveness within the current role.
Hedge Hiring
Hedge hiring leverages adaptability as a strategic approach by recruiting versatile talent capable of navigating market fluctuations, contrasting career cushioning which focuses on individual job security through passive skill accumulation. Organizations emphasizing hedge hiring enhance long-term resilience by continuously aligning workforce capabilities with evolving industry demands.
Backup Branding
Backup branding enhances job security by showcasing a versatile personal brand that adapts to evolving industry demands, whereas traditional career cushioning relies on static fallback options. Emphasizing adaptability through continuous skill development and strategic personal branding ensures resilience and relevance in a competitive job market.
Adaptability vs Career cushioning for job security. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com