Adaptability in the job market involves embracing change and developing a flexible mindset, enabling individuals to navigate shifting roles and industries effectively. Reskilling focuses on acquiring specific new skills to meet evolving job requirements, often in response to technological advancements or market demands. Balancing adaptability with targeted reskilling ensures professionals remain competitive and resilient amid workforce transformations.
Table of Comparison
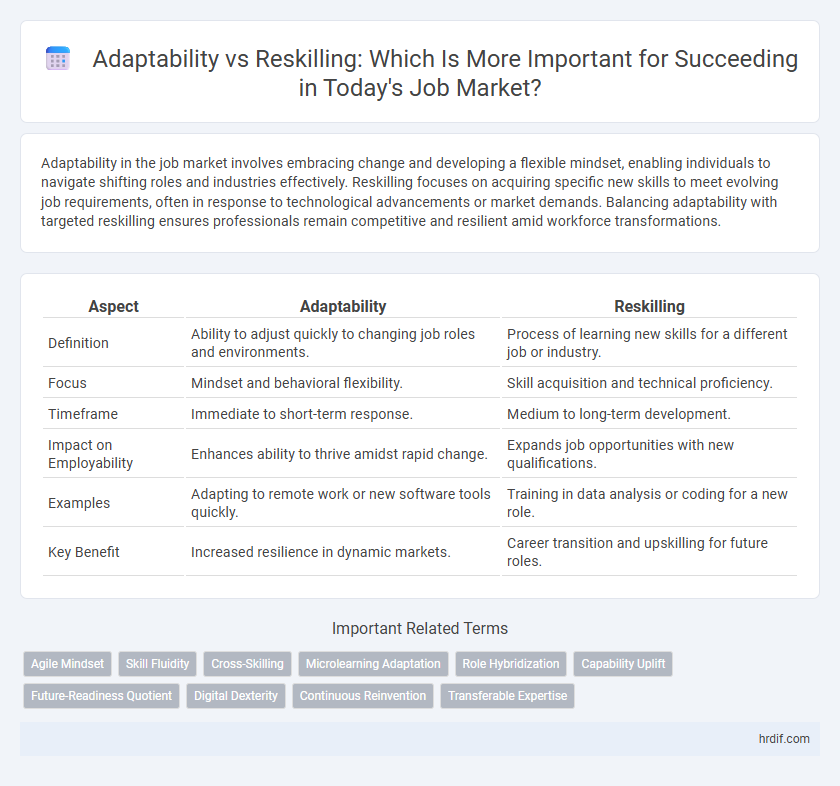
| Aspect | Adaptability | Reskilling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust quickly to changing job roles and environments. | Process of learning new skills for a different job or industry. |
| Focus | Mindset and behavioral flexibility. | Skill acquisition and technical proficiency. |
| Timeframe | Immediate to short-term response. | Medium to long-term development. |
| Impact on Employability | Enhances ability to thrive amidst rapid change. | Expands job opportunities with new qualifications. |
| Examples | Adapting to remote work or new software tools quickly. | Training in data analysis or coding for a new role. |
| Key Benefit | Increased resilience in dynamic markets. | Career transition and upskilling for future roles. |
Understanding Adaptability in the Modern Workforce
Understanding adaptability in the modern workforce involves recognizing the ability to rapidly adjust to changing job requirements and work environments. Unlike reskilling, which focuses on acquiring specific new skills, adaptability emphasizes flexibility, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence to navigate uncertainty and evolving roles. Employers increasingly value adaptability as a critical competency that drives long-term career resilience and organizational success.
The Importance of Reskilling for Career Longevity
Reskilling plays a crucial role in career longevity by equipping professionals with updated skills that align with evolving job market demands, ensuring sustained employability. Unlike general adaptability, which involves flexibility to changing conditions, reskilling entails deliberate learning of new competencies to remain relevant in specific industries. Investing in reskilling programs, such as digital literacy and advanced technical training, enables workers to navigate technological disruptions and continuously advance their careers.
Adaptability vs Reskilling: Key Differences
Adaptability involves the ability to quickly adjust to changing job roles and work environments, while reskilling focuses on acquiring new skills to transition into different positions or industries. Adaptability emphasizes mindset flexibility and continuous learning, enabling employees to respond effectively to unexpected challenges. Reskilling requires targeted training programs and time investment to develop specific competencies aligned with evolving market demands.
When Should You Focus on Adaptability?
Focus on adaptability when the job market faces rapid technological advancements or frequent industry shifts, requiring employees to adjust to new roles and environments swiftly. Cultivating adaptability enhances resilience and problem-solving skills, enabling professionals to navigate unpredictable changes without constant retraining. Prioritizing adaptability is crucial in dynamic sectors like technology, healthcare, and finance, where job functions evolve continuously.
Identifying the Right Time to Reskill
Recognizing the optimal moment to reskill hinges on labor market trends and emerging industry demands, where adaptability serves as a proactive mindset to anticipate shifts rather than merely react. Monitoring skill gaps through labor statistics and employer surveys can signal when current competencies risk obsolescence, prompting timely reskilling. Strategic alignment of reskilling efforts with forecasted job growth sectors maximizes employability and career longevity.
Industry Demands: Adaptability or Reskilling?
Industry demands increasingly favor adaptability over reskilling, as rapid technological advancements require employees to adjust quickly to evolving roles rather than acquiring entirely new skill sets. Employers prioritize workers who demonstrate agility in learning and applying new processes within existing frameworks to meet shifting market needs. Emphasizing adaptability enables organizations to maintain competitive advantage by swiftly responding to changes without the time and resource investment of comprehensive reskilling programs.
Adaptability as a Soft Skill: Its Impact on Job Security
Adaptability as a soft skill enhances job security by enabling employees to navigate rapid changes and evolving workplace demands more effectively than reskilling alone. Employers increasingly value adaptable individuals who demonstrate flexibility, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence, which contribute to long-term career resilience amidst technological advancements and market shifts. Unlike technical reskilling, adaptability fosters a mindset that supports continuous learning, collaboration, and proactive response to unforeseen challenges.
Reskilling Strategies for Ongoing Market Relevance
Reskilling strategies center on acquiring new skills that align with evolving industry demands, ensuring continuous employability and career growth. Emphasizing targeted training programs, online courses, and practical experience helps workers stay competitive amidst technological advancements and market shifts. Prioritizing reskilling initiatives enables professionals to navigate disruptions effectively, maintaining sustained relevance in the dynamic job market.
Balancing Adaptability and Reskilling for Career Growth
Balancing adaptability and reskilling is crucial for sustained career growth in today's dynamic job market, where technological advancements rapidly redefine skill requirements. Professionals who cultivate adaptability alongside targeted reskilling can navigate shifting industry demands effectively, ensuring they remain competitive and relevant. Companies that invest in both fostering adaptability and providing reskilling opportunities enhance workforce resilience and drive long-term business success.
Future-Proofing Your Career: Which Approach Wins?
Adaptability enhances your ability to navigate shifting job market demands by fostering a mindset open to continuous learning and change. Reskilling offers targeted skills development to meet specific emerging industry needs, but adaptability ensures long-term career resilience beyond individual skill sets. Prioritizing adaptability future-proofs your career by equipping you to pivot efficiently amid evolving technologies and market trends.
Related Important Terms
Agile Mindset
An Agile Mindset emphasizes continuous learning and flexibility, making adaptability crucial for navigating the evolving job market where reskilling alone may fall short. Employers increasingly value professionals who demonstrate resilience and the ability to pivot quickly in response to shifting industry demands and technological advancements.
Skill Fluidity
Skill fluidity enhances adaptability in the job market by enabling employees to seamlessly transfer and apply their competencies across diverse roles, reducing the need for constant reskilling. Emphasizing skill fluidity fosters a dynamic workforce that can quickly respond to industry shifts without extensive retraining, ensuring sustained employability and organizational agility.
Cross-Skilling
Cross-skilling enhances adaptability in the job market by enabling employees to acquire complementary skills across different roles, increasing their versatility and value within an organization. Unlike reskilling, which focuses on learning entirely new skills for a different job, cross-skilling leverages existing expertise to broaden capabilities and improve career resilience in dynamic industries.
Microlearning Adaptation
Microlearning adaptation enhances adaptability in the job market by delivering targeted, bite-sized skill updates that align with rapidly evolving industry demands, making continuous reskilling more efficient and manageable. This approach enables workers to quickly acquire relevant competencies, improving their employability and responsiveness to technological changes without extensive retraining periods.
Role Hybridization
Adaptability in the job market increasingly hinges on role hybridization, where employees blend multiple skill sets to meet evolving demands, surpassing traditional reskilling efforts focused on isolated competencies. Embracing role hybridization enhances workforce flexibility, drives innovation, and ensures long-term employability amid rapid technological and industry shifts.
Capability Uplift
Adaptability enhances capability uplift by enabling employees to quickly integrate new skills and technologies, ensuring sustained relevance in the evolving job market. Reskilling focuses on acquiring specific new skills, but adaptability drives continuous learning and flexibility, maximizing long-term career growth and organizational resilience.
Future-Readiness Quotient
Adaptability in the job market emphasizes agility and continuous learning, enabling faster response to evolving industry demands compared to reskilling, which focuses on acquiring specific new skills. The Future-Readiness Quotient measures an individual's ability to anticipate changes and pivot effectively, making adaptability a critical factor for sustained career success.
Digital Dexterity
Digital dexterity enhances adaptability in the job market by enabling employees to quickly learn and apply new technologies, making reskilling processes more efficient and targeted. Emphasizing digital dexterity fosters a workforce capable of continuous evolution, bridging skill gaps with agility rather than relying solely on extensive reskilling programs.
Continuous Reinvention
Adaptability in the job market emphasizes continuous reinvention through learning new skills and embracing change, enabling professionals to remain relevant amid evolving industry demands. Reskilling focuses on acquiring specific new competencies, but adaptability fosters a broader mindset of ongoing growth and flexibility to navigate unpredictable career landscapes.
Transferable Expertise
Adaptability hinges on leveraging transferable expertise to swiftly navigate evolving job market demands, enabling professionals to apply core skills across diverse roles and industries. Reskilling complements this by equipping individuals with new technical abilities, but adaptability rooted in versatile competencies drives long-term career resilience and mobility.
Adaptability vs Reskilling for job market Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com