Adaptability in the workplace involves quickly adjusting to new tasks and environments, enhancing overall job versatility by enabling employees to handle various roles effectively. Polymathy represents a broader skill set across multiple disciplines, providing deep knowledge that can solve complex problems and innovate within diverse fields. Combining adaptability with polymathy creates a powerful synergy, allowing professionals to pivot easily while leveraging extensive expertise for exceptional job performance.
Table of Comparison
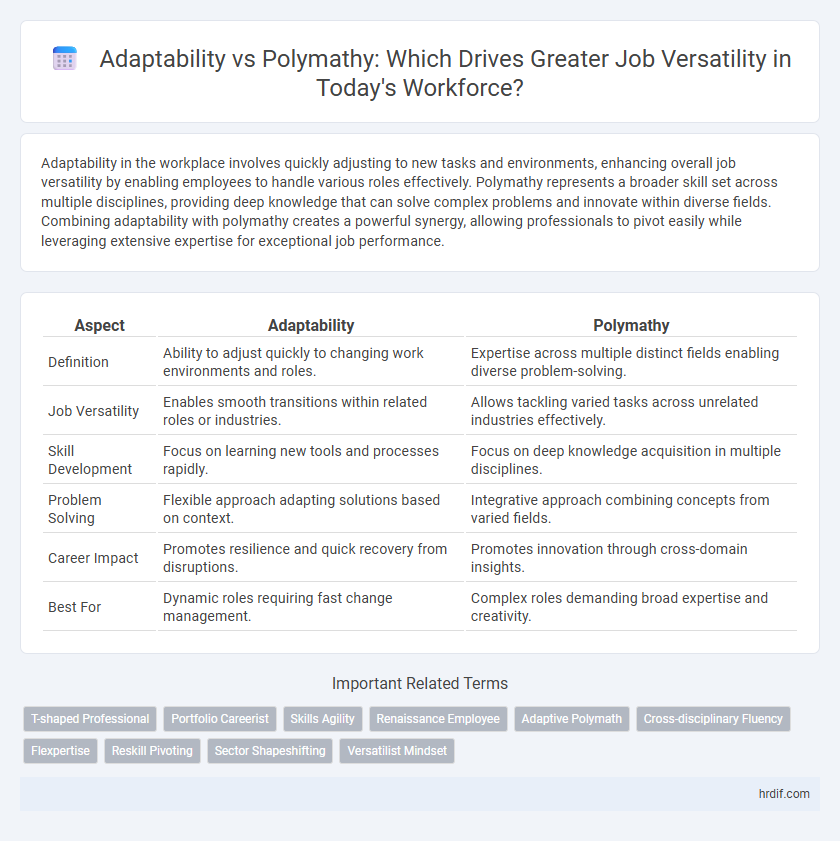
| Aspect | Adaptability | Polymathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust quickly to changing work environments and roles. | Expertise across multiple distinct fields enabling diverse problem-solving. |
| Job Versatility | Enables smooth transitions within related roles or industries. | Allows tackling varied tasks across unrelated industries effectively. |
| Skill Development | Focus on learning new tools and processes rapidly. | Focus on deep knowledge acquisition in multiple disciplines. |
| Problem Solving | Flexible approach adapting solutions based on context. | Integrative approach combining concepts from varied fields. |
| Career Impact | Promotes resilience and quick recovery from disruptions. | Promotes innovation through cross-domain insights. |
| Best For | Dynamic roles requiring fast change management. | Complex roles demanding broad expertise and creativity. |
Understanding Adaptability and Polymathy in the Modern Workplace
Adaptability in the modern workplace involves quickly adjusting to changing environments and new challenges, while polymathy refers to possessing a broad range of diverse skills and knowledge across multiple disciplines. Employers increasingly value adaptability for its role in fostering resilience and agility during rapid organizational shifts, whereas polymathy contributes to innovative problem-solving and cross-functional collaboration. Understanding the balance between adaptability and polymathy enhances individual job versatility by combining flexible mindsets with expansive expertise.
Key Differences Between Adaptability and Polymathy
Adaptability refers to the ability to quickly adjust to new job roles, environments, or challenges, emphasizing flexibility and continuous learning within specific domains. Polymathy involves possessing deep knowledge and skills across multiple disciplines, enabling versatile problem-solving and innovation by integrating diverse expertise. While adaptability enhances responsiveness to change, polymathy provides a broader intellectual foundation for complex, cross-functional job adaptability.
Core Skills: Adaptable Professionals vs. Polymaths
Adaptable professionals excel by mastering core skills that allow them to quickly pivot and respond to changing job demands, ensuring continuous relevance in dynamic work environments. Polymaths, while possessing broad knowledge across multiple domains, may lack the deep proficiency in specific core skills that drive immediate job versatility. Focusing on adaptable core competencies enables professionals to integrate new tools and methodologies effectively, enhancing their practical value across industries.
Navigating Career Changes: Adaptability vs. Polymathic Approaches
Navigating career changes requires a blend of adaptability and polymathic skills to maintain job versatility in dynamic industries. Adaptability enables individuals to quickly adjust to new roles and technologies, while polymathic approaches foster a broad knowledge base that supports innovative problem-solving across diverse fields. Combining both strategies enhances resilience and opportunities for career growth amidst evolving job markets.
Value to Employers: Which Wins—Flexibility or Breadth of Knowledge?
Employers prioritize adaptability for rapid role shifts and evolving industry demands, valuing flexibility that ensures quick learning and seamless integration. Polymathy offers extensive breadth of knowledge, fostering innovation through interdisciplinary insights but may risk depth in specialized tasks. Flexibility often trumps breadth as organizations seek agile employees who can respond swiftly to change and diverse challenges in dynamic work environments.
Leveraging Adaptability for Continuous Career Growth
Leveraging adaptability in the workplace enhances continuous career growth by enabling professionals to navigate changing roles and industry demands with agility. Unlike polymathy, which relies on deep expertise across multiple disciplines, adaptability emphasizes the ability to learn and apply new skills rapidly to diverse challenges. This dynamic approach ensures sustained job versatility and long-term professional resilience in evolving job markets.
Harnessing Polymathic Skills for Cross-Industry Success
Harnessing polymathic skills enhances adaptability, enabling professionals to seamlessly transfer expertise across diverse industries and solve complex, multifaceted problems. Polymaths leverage their interdisciplinary knowledge to innovate and drive growth in dynamic job markets, increasing their versatility and employability. This cross-industry agility fosters resilience, empowering individuals to thrive amid evolving career landscapes and technological advancements.
Modern Job Market Demands: Adaptability or Polymathy?
Adaptability is crucial in the modern job market, enabling professionals to quickly adjust to evolving technologies and shifting industry needs. Polymathy offers breadth by combining diverse expertise, but adaptability ensures continuous learning and agile responses to new challenges. Employers prioritize candidates who demonstrate flexibility, making adaptability a key factor for sustained job versatility and career growth.
Developing Adaptability and Polymathic Traits in Your Career
Developing adaptability and polymathic traits enhances job versatility by fostering continuous learning across diverse fields and the flexibility to navigate changing work environments. Professionals who cultivate broad skill sets alongside specialized knowledge can pivot effectively between roles, responding to evolving industry demands and complex challenges. Emphasizing growth in both adaptability and polymathy accelerates career resilience and opens pathways to innovative problem-solving opportunities.
Choosing the Right Path: When to Prioritize Adaptability or Polymathy
Choosing between adaptability and polymathy depends on career goals and industry demands; adaptability excels in dynamic environments requiring rapid skill adjustments, while polymathy benefits roles demanding deep cross-disciplinary knowledge. Prioritize adaptability when job versatility requires quick learning and flexibility in diverse tasks, especially in fast-evolving sectors like technology or marketing. Opt for polymathy in professions valuing breadth across fields such as entrepreneurship or innovation, where integrated expertise fosters unique problem-solving.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professional
T-shaped professionals exhibit deep expertise in one area complemented by broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling adaptability in dynamic job markets. This combination of specialization and cross-functional knowledge enhances versatility more effectively than polymathy alone, which spreads expertise too thinly across unrelated fields.
Portfolio Careerist
Adaptability enhances a Portfolio Careerist's job versatility by enabling rapid skill acquisition and seamless transition across diverse roles, whereas polymathy relies on deep, broad expertise that may slow immediate responsiveness. Emphasizing adaptability cultivates dynamic problem-solving and continuous learning, essential for navigating the evolving demands of multi-disciplinary careers.
Skills Agility
Skills agility enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to quickly acquire and apply diverse competencies, fostering job versatility across dynamic industries. Polymathy complements this by providing a broad knowledge base, but true adaptability hinges on the ability to pivot and upskill efficiently in response to evolving job demands.
Renaissance Employee
The Renaissance Employee exemplifies adaptability by integrating diverse skills and knowledge from multiple domains, enhancing job versatility beyond specialized polymathy. This holistic approach fosters innovative problem-solving and resilience in dynamic work environments, aligning versatility with continuous learning and cross-disciplinary competence.
Adaptive Polymath
An adaptive polymath combines deep, cross-disciplinary expertise with the flexibility to apply knowledge across diverse job roles, enhancing career versatility beyond typical adaptability. This approach leverages both broad skill sets and specialized insights to navigate complex, evolving professional landscapes effectively.
Cross-disciplinary Fluency
Adaptability enhances job versatility by fostering cross-disciplinary fluency, enabling professionals to seamlessly integrate diverse skill sets and knowledge areas. Polymathy emphasizes deep expertise across multiple fields, but adaptability prioritizes agile learning and application, which drives efficient problem-solving in dynamic work environments.
Flexpertise
Flexpertise combines deep expertise and adaptability, allowing professionals to quickly pivot across roles while maintaining high skill proficiency. Unlike polymathy, which involves broad knowledge in multiple areas, flexpertise emphasizes mastering core skills with flexibility, enhancing job versatility in dynamic industries.
Reskill Pivoting
Adaptability in job versatility emphasizes the ability to quickly reskill and pivot across industries, enabling professionals to meet emerging market demands effectively. Unlike polymathy, which relies on broad but static expertise, adaptability prioritizes dynamic skill acquisition and continuous learning to maintain relevance in rapidly changing career landscapes.
Sector Shapeshifting
Sector shapeshifting highlights adaptability as the ability to navigate and excel across multiple industries by swiftly acquiring sector-specific skills, whereas polymathy emphasizes broad, interdisciplinary knowledge spanning various fields. Employers increasingly value sector adaptability for job versatility, as it enables professionals to respond dynamically to evolving market demands and cross-sector challenges.
Versatilist Mindset
A versatilist mindset integrates adaptability and polymathy by combining deep expertise with the ability to pivot across diverse domains, enhancing job versatility in dynamic environments. Emphasizing continuous learning and multifaceted skills, this approach enables professionals to navigate complex challenges and seize emerging opportunities effectively.
Adaptability vs Polymathy for job versatility. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com