Specialists offer deep expertise in a specific field, providing high value for roles requiring advanced technical skills and focused knowledge. Polymaths possess a broad range of skills across multiple disciplines, enabling versatility and adaptability in dynamic work environments. Employers seeking innovation and cross-functional problem-solving often prefer polymaths, while niche industries typically favor specialists for their precision and mastery.
Table of Comparison
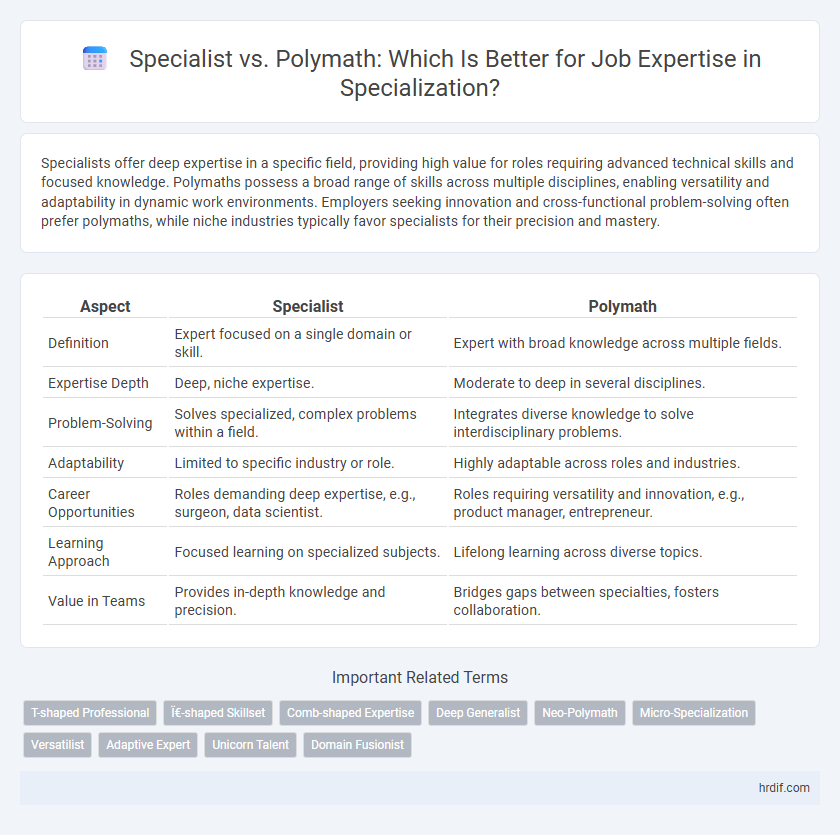
| Aspect | Specialist | Polymath |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expert focused on a single domain or skill. | Expert with broad knowledge across multiple fields. |
| Expertise Depth | Deep, niche expertise. | Moderate to deep in several disciplines. |
| Problem-Solving | Solves specialized, complex problems within a field. | Integrates diverse knowledge to solve interdisciplinary problems. |
| Adaptability | Limited to specific industry or role. | Highly adaptable across roles and industries. |
| Career Opportunities | Roles demanding deep expertise, e.g., surgeon, data scientist. | Roles requiring versatility and innovation, e.g., product manager, entrepreneur. |
| Learning Approach | Focused learning on specialized subjects. | Lifelong learning across diverse topics. |
| Value in Teams | Provides in-depth knowledge and precision. | Bridges gaps between specialties, fosters collaboration. |
Defining Specialists and Polymaths in the Modern Workplace
Specialists possess deep expertise in a specific field, enabling them to solve complex problems with precision in areas such as software engineering or medical research. Polymaths leverage broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, facilitating innovative solutions by integrating insights from fields like design, technology, and business strategy. In the modern workplace, organizations value specialists for their focused skills and polymaths for their adaptability and cross-functional collaboration.
The Advantages of Deep Specialization in Career Growth
Deep specialization enhances career growth by cultivating expertise that distinguishes professionals in competitive job markets. Specialists gain advanced skills and knowledge tailored to specific industries, leading to higher demand and increased earning potential. Employers prioritize specialists for complex problem-solving roles due to their ability to deliver precise, high-quality outcomes efficiently.
Polymaths: Mastering Multiple Domains for Job Flexibility
Polymaths excel by mastering multiple domains, offering unparalleled job flexibility and adaptability in rapidly changing industries. Their diverse skill set enables them to integrate knowledge across disciplines, fostering innovative solutions and enhancing problem-solving capabilities. Employers increasingly value polymaths for their ability to navigate complex challenges and drive cross-functional collaboration.
Comparing Salary Trends: Specialists vs. Polymaths
Specialists often command higher starting salaries due to deep expertise in niche areas, whereas polymaths may see gradual salary growth as their diverse skills become valuable across multiple fields. Salary trends indicate specialists benefit from premium pay in industries requiring cutting-edge knowledge, while polymaths thrive in roles valuing adaptability and interdisciplinary problem-solving. Data shows firms increasingly reward specialists with targeted compensation packages, but polymaths excel in innovative sectors seeking broad expertise.
Job Market Demand: Who Do Employers Prefer?
Employers often prefer specialists due to their deep expertise in a specific field, which directly addresses niche job market needs and ensures higher productivity in specialized roles. However, polymaths are increasingly valued for their versatility and ability to adapt across multiple domains, particularly in dynamic industries requiring innovation and cross-functional skills. Job market demand fluctuates, with technology and creative sectors favoring polymathic abilities, while traditional industries maintain a strong preference for specialized knowledge.
Navigating Career Transitions: Specialist vs. Polymath Paths
Specialists offer deep expertise in a single domain, making them highly sought after for roles requiring precise skills and advanced knowledge. Polymaths bring versatility by integrating diverse skill sets, enabling seamless adaptation across industries during career transitions. Navigating career shifts involves weighing the benefits of focused mastery against the flexibility of interdisciplinary competence.
Innovation and Problem-Solving: One Skillset or Many?
Specialists provide deep expertise in a specific field, enabling precise innovation and efficient problem-solving through focused knowledge. Polymaths draw from diverse skillsets and interdisciplinary insights, fostering creative solutions by integrating multiple perspectives. Organizations seeking breakthrough innovation often benefit from balancing specialists' depth with polymaths' broad adaptability.
Long-Term Job Security: Specialization Versus Versatility
Specialists often achieve long-term job security through deep expertise in niche fields that require advanced skills and knowledge, making them indispensable in specialized industries. Polymaths provide versatility by adapting to diverse roles and evolving market demands, enhancing their employability in dynamic and interdisciplinary environments. Balancing specialization with adaptability increases resilience against job market fluctuations and technological changes.
Workplace Collaboration: The Roles of Specialists and Polymaths
Specialists bring deep expertise in a specific field, enabling precise problem-solving and advanced technical contributions that enhance team performance in focused projects. Polymaths offer versatility by integrating knowledge across multiple domains, fostering innovation and adaptability in dynamic workplace environments. Effective collaboration leverages specialists' depth and polymaths' breadth, creating balanced teams capable of addressing complex challenges with both precision and creativity.
Deciding Your Path: Factors to Consider for Career Success
Choosing between a specialist and a polymath depends on industry demands and personal strengths. Specialists offer deep expertise valuable in niche fields, while polymaths bring versatile skills ideal for dynamic, interdisciplinary roles. Assess job market trends, your adaptability, and long-term career goals to determine the most strategic path.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professional
A T-shaped professional balances deep expertise in a specific domain with broad skills across multiple disciplines, combining the focused knowledge of a specialist with the versatility of a polymath. This hybrid approach enhances collaboration and innovation in complex job roles by leveraging specialized depth alongside interdisciplinary understanding.
π-shaped Skillset
A p-shaped skillset combines deep expertise in two specific fields with broad knowledge across others, bridging the gap between specialists and polymaths by enabling adaptability and cross-disciplinary innovation. Employers increasingly value p-shaped professionals for their ability to integrate specialized skills with versatile competencies, driving complex problem-solving and collaborative success.
Comb-shaped Expertise
Comb-shaped expertise blends deep specialization with broad interdisciplinary skills, enabling professionals to adapt quickly and innovate across complex job functions. Specialists offer profound knowledge in a narrow field, while polymaths contribute versatility, and comb-shaped experts uniquely combine both to maximize problem-solving and collaboration in dynamic work environments.
Deep Generalist
A deep generalist combines the breadth of a polymath with the depth of a specialist, enabling versatile problem-solving across multiple domains while maintaining expert-level knowledge. This unique skill set enhances adaptability in complex job markets, driving innovation through interdisciplinary insights and specialized expertise.
Neo-Polymath
A Neo-Polymath combines deep expertise across multiple disciplines with the ability to integrate knowledge dynamically, surpassing traditional specialization boundaries by fostering innovation and adaptability in complex job roles. This hybrid approach leverages both specialist depth and broad cognitive flexibility to solve multifaceted problems and drive interdisciplinary collaboration in evolving professional environments.
Micro-Specialization
Micro-specialization enhances job expertise by enabling specialists to develop deep knowledge in highly specific areas, increasing their value within niche markets. Polymaths offer broad interdisciplinary skills, but micro-specialists provide targeted solutions that address precise challenges in fields like AI ethics, cybersecurity for finance, or genomic data analysis.
Versatilist
Versatilists combine deep expertise with broad interdisciplinary knowledge, bridging the gap between specialists and polymaths to adapt across various job functions. Their ability to integrate specialized skills with diverse insights enhances problem-solving and innovation in dynamic work environments.
Adaptive Expert
An adaptive expert balances deep specialization with broad polymathic skills, enabling innovative problem-solving and continuous learning within dynamic job environments. This hybrid approach fosters versatility and expertise, empowering professionals to excel across complex challenges while maintaining domain-specific knowledge.
Unicorn Talent
Unicorn talent embodies a rare blend of deep specialization and broad polymathic knowledge, enabling unparalleled innovation and adaptability in complex job roles. Organizations increasingly seek these versatile experts who combine mastery in a niche field with cross-disciplinary insights to drive competitive advantage and strategic growth.
Domain Fusionist
A Domain Fusionist bridges expertise across multiple specialized fields, creating innovative solutions by integrating diverse knowledge areas, unlike traditional specialists who focus deeply on a single niche. This multidisciplinary approach drives competitive advantage in complex job markets by enabling adaptive problem-solving and holistic understanding.
Specialist vs Polymath for job expertise. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com