Productivity thrives when tasks are broken into focused work sprints, enabling individuals to maintain high energy and concentration for short bursts. This approach prevents burnout and enhances efficiency by prioritizing key activities aligned with career goals. Consistent use of work sprints drives measurable progress, transforming overwhelming workloads into achievable milestones.
Table of Comparison
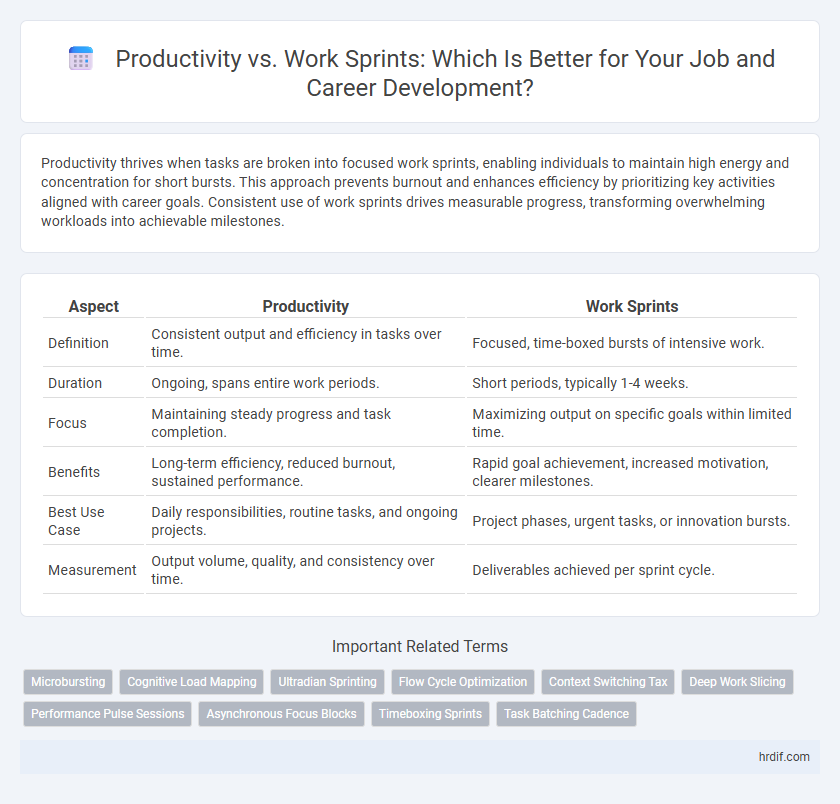
| Aspect | Productivity | Work Sprints |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent output and efficiency in tasks over time. | Focused, time-boxed bursts of intensive work. |
| Duration | Ongoing, spans entire work periods. | Short periods, typically 1-4 weeks. |
| Focus | Maintaining steady progress and task completion. | Maximizing output on specific goals within limited time. |
| Benefits | Long-term efficiency, reduced burnout, sustained performance. | Rapid goal achievement, increased motivation, clearer milestones. |
| Best Use Case | Daily responsibilities, routine tasks, and ongoing projects. | Project phases, urgent tasks, or innovation bursts. |
| Measurement | Output volume, quality, and consistency over time. | Deliverables achieved per sprint cycle. |
Understanding Productivity in the Modern Workplace
Productivity in the modern workplace emphasizes focused work sprints to maximize efficiency and output while minimizing burnout. Structured intervals of intense concentration followed by short breaks enhance cognitive function and sustain motivation over long periods. Adopting sprint methodologies aligns with agile work environments, promoting adaptability and continuous improvement in job performance.
What Are Work Sprints?
Work sprints are focused, time-boxed intervals designed to maximize productivity by concentrating effort on specific tasks or projects, typically lasting between 15 minutes to a few hours. This method helps reduce distractions and maintain high energy levels, fostering deep work and efficient progress. By breaking down larger goals into manageable sprints, professionals can track achievements more effectively and accelerate career growth.
Key Differences: Productivity vs Work Sprints
Productivity measures overall output and efficiency in completing tasks over time, emphasizing sustained performance and goal achievement. Work sprints are short, intense bursts of focused effort designed to maximize concentration and momentum within a limited timeframe. Key differences include productivity's broad scope on continuous results versus work sprints' prioritization of time-boxed, high-intensity work periods to boost task completion.
Benefits of Sustained Productivity
Sustained productivity enhances job performance by enabling consistent achievement of goals without burnout, leading to higher quality output and long-term career growth. Unlike work sprints that emphasize short bursts of intense activity, sustained productivity fosters steady progress and better time management. This approach supports mental resilience and continuous skill development, which are crucial for advancing in competitive career environments.
Advantages of Work Sprints for Career Growth
Work sprints enhance productivity by promoting focused bursts of effort that reduce burnout and maintain high energy levels throughout the day. This method improves time management and task prioritization, allowing professionals to achieve measurable progress and meet deadlines efficiently. Consistent use of work sprints fosters skill development and adaptability, critical factors for accelerated career growth and long-term success.
When to Choose Productivity Over Work Sprints
Choosing productivity over work sprints is ideal when tasks require sustained focus, deep thinking, or strategic planning, ensuring quality and long-term impact rather than short bursts of effort. Productivity emphasizes consistent progress and effective time management, which prevents burnout common in high-intensity sprints and supports steady career growth. For complex projects, prioritizing productivity allows thorough problem-solving and skill development that work sprints may overlook.
Integrating Work Sprints Into Your Productivity Routine
Integrating work sprints into your productivity routine enhances focus and accelerates task completion by breaking projects into timed, manageable segments. Utilizing techniques like the Pomodoro method, professionals can maintain high energy levels and reduce burnout, maximizing output during each sprint. Consistently applying work sprints aligns with goal-setting strategies, improving job performance and career growth through sustained productivity.
Common Pitfalls of Each Approach
Work sprints often lead to burnout due to intense, unfocused bursts of activity without adequate rest, reducing overall productivity and job satisfaction. Traditional productivity methods might encourage multitasking, which can fragment attention and decrease efficiency in career advancement tasks. Balancing focused work sessions with strategic breaks optimizes output and sustains long-term professional growth.
Measuring Success: Productivity Metrics vs Sprint Outcomes
Measuring success in job performance requires balancing productivity metrics, such as task completion rates and time efficiency, with sprint outcomes that emphasize goal achievement and iterative progress. Productivity metrics provide quantitative data on work speed and consistency, while sprint outcomes focus on deliverables, team collaboration, and adaptability within set timeframes. Integrating both approaches offers a comprehensive evaluation of performance, ensuring alignment with career growth and project objectives.
Finding the Right Balance for Career Advancement
Balancing productivity with work sprints is essential for sustainable career advancement, as focused bursts of high-intensity effort can maximize output without causing burnout. Research shows that integrating planned breaks and sprint intervals, such as the Pomodoro Technique, enhances cognitive function and long-term efficiency. Professionals who optimize their workflow by aligning task complexity with appropriate sprint durations consistently achieve higher performance and faster career growth.
Related Important Terms
Microbursting
Microbursting leverages short, intense work sprints to maximize focus and output, aligning with the brain's natural attention span and reducing burnout. Integrating microbursting into career strategies enhances productivity by breaking tasks into manageable intervals, fostering sustained motivation and efficient task completion.
Cognitive Load Mapping
Cognitive Load Mapping enhances productivity by structuring work sprints to align tasks with mental capacity, thereby reducing cognitive overload and improving focus. Integrating this approach in job and career management optimizes task execution and accelerates skill development through targeted effort bursts.
Ultradian Sprinting
Ultradian sprinting leverages natural 90-120 minute energy cycles to maximize focus and output, aligning work sprints with peak cognitive performance periods. Integrating these biologically timed intervals enhances productivity by reducing burnout and sustaining high-quality work in job and career tasks.
Flow Cycle Optimization
Maximizing productivity through optimized work sprints aligns with the neuroscience of flow cycles, enhancing focus and reducing burnout by timing bursts of deep work with strategic breaks. Implementing structured sprint intervals tailored to personal energy rhythms promotes sustained performance and accelerates career growth by improving task efficiency and cognitive engagement.
Context Switching Tax
Frequent context switching during work sprints significantly reduces productivity by increasing cognitive load and time lost to refocusing on tasks. Minimizing task changes within focused work intervals can optimize output and accelerate career advancement by preserving mental energy.
Deep Work Slicing
Deep Work Slicing enhances productivity by breaking tasks into focused, distraction-free sprints that align with cognitive capacity peaks, maximizing output quality and job satisfaction. This method contrasts with traditional multitasking by fostering sustained attention during work sprints, leading to more efficient career progression and skill mastery.
Performance Pulse Sessions
Performance Pulse Sessions enhance productivity by structuring work sprints into focused intervals that maximize output and maintain momentum. This method leverages concentrated bursts of effort followed by strategic breaks, promoting sustained performance and reducing burnout in demanding job environments.
Asynchronous Focus Blocks
Asynchronous Focus Blocks enhance productivity by allowing deep, uninterrupted work periods tailored to individual peak performance times, contrasting with rigid Work Sprints that often disrupt flow through synchronized breaks. Implementing Asynchronous Focus Blocks fosters higher job efficiency and career growth by aligning tasks with natural cognitive rhythms, reducing burnout and increasing output quality.
Timeboxing Sprints
Timeboxing sprints enhance productivity by breaking tasks into focused, manageable intervals, preventing burnout and improving task prioritization. Using fixed-duration work sprints increases efficiency and accountability, enabling clearer progress tracking and better alignment with career goals.
Task Batching Cadence
Task batching cadence enhances productivity by grouping similar tasks into focused work sprints, minimizing context switching and maximizing efficiency. Implementing regular intervals for concentrated task batches improves job performance and accelerates career growth by maintaining sustained momentum and reducing burnout.
Productivity vs Work Sprints for job and career. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com