The To-Do List offers a straightforward way to organize daily tasks, helping users track what needs to be done without prioritizing. The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks into urgent and important quadrants, enabling effective time management and focus on high-impact activities. Choosing between these methods depends on individual needs for simplicity or strategic prioritization in task management.
Table of Comparison
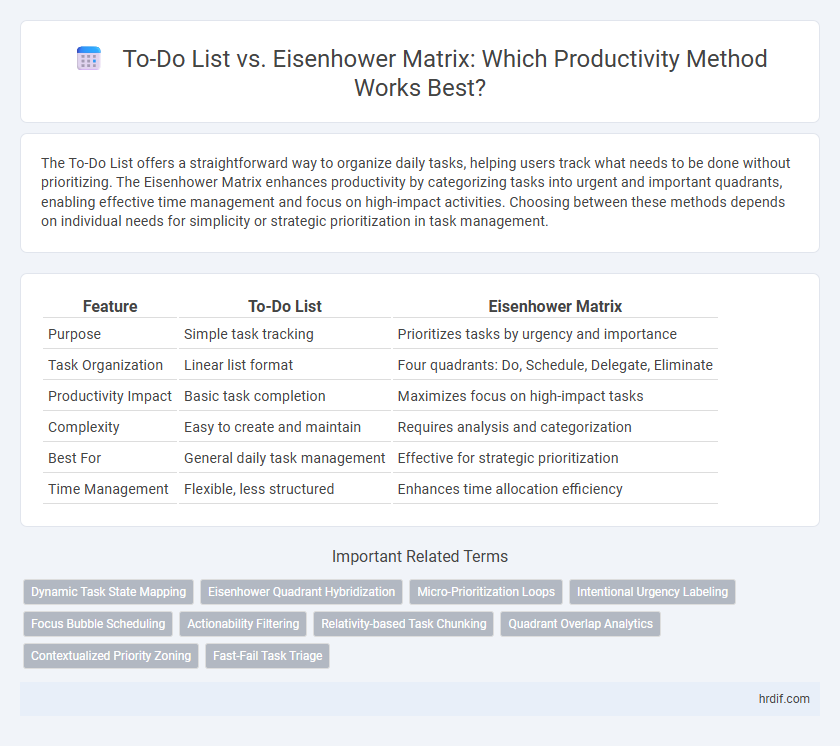
| Feature | To-Do List | Eisenhower Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Simple task tracking | Prioritizes tasks by urgency and importance |
| Task Organization | Linear list format | Four quadrants: Do, Schedule, Delegate, Eliminate |
| Productivity Impact | Basic task completion | Maximizes focus on high-impact tasks |
| Complexity | Easy to create and maintain | Requires analysis and categorization |
| Best For | General daily task management | Effective for strategic prioritization |
| Time Management | Flexible, less structured | Enhances time allocation efficiency |
Understanding the Basics: To-Do List vs Eisenhower Matrix
The To-Do List organizes tasks by simple enumeration, helping track activities without inherent prioritization, while the Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, enhancing decision-making efficiency. Utilizing the Eisenhower Matrix facilitates focusing on high-impact activities by distinguishing between urgent and non-urgent tasks, which is often missing in traditional To-Do Lists. Adopting the appropriate method depends on the complexity of tasks and the need for prioritization in managing productivity.
Key Principles of the To-Do List Approach
The key principles of the To-Do List approach emphasize task organization, prioritization based on urgency and importance, and breaking down complex projects into manageable actions. This method enhances focus by providing a clear, linear sequence of tasks, promoting accountability and progress tracking. By maintaining a dynamic list, users can adapt to changing priorities while maintaining productivity momentum.
The Eisenhower Matrix: A Strategic Productivity Tool
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, enabling efficient prioritization and decision-making. This strategic tool helps users focus on high-impact activities while delegating or deferring less critical tasks, reducing time spent on low-value actions. Compared to a standard to-do list, the Eisenhower Matrix promotes proactive task management and minimizes overwhelm, driving sustained productivity gains.
Categorizing Tasks: Urgency and Importance Defined
Categorizing tasks using the Eisenhower Matrix distinguishes between urgency and importance, allowing users to prioritize activities that impact long-term goals versus immediate demands. A traditional to-do list organizes tasks linearly without explicit prioritization, often leading to inefficiencies and overlooked critical tasks. Implementing the Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by clearly segmenting tasks into four quadrants: urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, and neither urgent nor important.
Strengths and Weaknesses of To-Do Lists
To-do lists excel at providing a simple, clear overview of daily tasks, enhancing task tracking and accountability. However, they often lack prioritization, leading to potential overwhelm or focus on less important activities. Without strategic sorting, to-do lists may contribute to procrastination and reduced productivity.
The Pros and Cons of the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance, enabling focused decision-making and better time management. However, its rigid categorization can overlook nuanced task complexities and lead to misclassification of activities, potentially causing key tasks to be neglected. Users may struggle with subjective assessments of urgency and importance, reducing the matrix's effectiveness in fast-paced or dynamic work environments.
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right productivity tool depends on task complexity, urgency, and personal workflow preferences. The To-Do List excels at straightforward task tracking and daily routine management, while the Eisenhower Matrix prioritizes tasks based on urgency and importance, enhancing decision-making for high-stakes projects. Evaluating factors such as task volume, deadline sensitivity, and cognitive load helps optimize productivity through tailored task management systems.
Real-World Examples: Productivity in Action
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks into urgent-important quadrants, as demonstrated by CEOs who prioritize strategic decisions while delegating less critical activities. In contrast, traditional to-do lists often lead to burnout due to their linear approach, exemplified by freelancers who struggle with overwhelming task accumulation. Companies like Google implement the Eisenhower method to focus on impactful innovation, showcasing measurable improvements in time management and project completion rates.
Tips for Integrating Both Methods Effectively
Combining the To-Do List with the Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks based on urgency and importance while maintaining a clear task overview. Prioritize daily tasks by first sorting them into the Eisenhower Matrix's four quadrants, then create a detailed To-Do List for high-priority items to ensure focused execution. Use digital tools like Trello or Microsoft To Do to seamlessly integrate both methods, allowing real-time adjustments and efficient task management throughout the day.
Maximizing Career Growth Through Smart Task Management
To-do lists offer a straightforward method for tracking daily tasks, while the Eisenhower Matrix prioritizes tasks based on urgency and importance, enabling more strategic focus on high-impact activities. Implementing the Eisenhower Matrix can maximize career growth by helping professionals concentrate on tasks that drive long-term success and skill development. Combining both tools creates a balanced approach that enhances productivity and ensures critical goals are consistently met.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Task State Mapping
Dynamic task state mapping within the Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks based on urgency and importance, enabling real-time adjustment of priorities unlike static To-Do Lists. This adaptive framework supports efficient decision-making and resource allocation, optimizing workflow management and reducing task overload.
Eisenhower Quadrant Hybridization
Eisenhower Matrix hybridization enhances productivity by blending urgent-important task prioritization with flexible to-do list structures, enabling dynamic task management tailored to evolving deadlines and workload. This approach optimizes focus and efficiency by categorizing activities into four quadrants while maintaining the adaptability and detailed tracking of traditional to-do lists.
Micro-Prioritization Loops
Micro-prioritization loops enhance productivity by breaking tasks into smaller, actionable steps with clear urgency and importance, which the Eisenhower Matrix distinctly categorizes into four quadrants for focused decision-making. Unlike traditional to-do lists, the Eisenhower Matrix minimizes overwhelm by continuously reprioritizing tasks, facilitating efficient time management and higher task completion rates.
Intentional Urgency Labeling
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks based on intentional urgency and importance, allowing users to focus on what truly drives results rather than simply completing items on a to-do list. Intentional urgency labeling in the matrix prevents time-wasting on less critical tasks, optimizing decision-making and prioritization for effective time management.
Focus Bubble Scheduling
Focus Bubble Scheduling enhances productivity by integrating the Eisenhower Matrix's prioritization with timed work intervals, allowing users to tackle urgent and important tasks within concentrated time blocks. Unlike a traditional To-Do List that merely catalogs tasks, this method reduces decision fatigue and improves task completion rates through structured focus sessions aligned with priority levels.
Actionability Filtering
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks into urgent and important quadrants, enabling effective actionability filtering that prioritizes critical activities over less impactful to-do list items. This strategic approach reduces decision fatigue and ensures focus on high-value tasks, contrasting with traditional to-do lists that often lack dynamic prioritization mechanisms.
Relativity-based Task Chunking
Relativity-based task chunking enhances productivity by categorizing tasks with the Eisenhower Matrix, prioritizing urgent and important items over less critical to-dos, which optimizes focus and time management. Unlike traditional to-do lists that often present tasks linearly, the Eisenhower Matrix's quadrant system leverages task urgency and impact, reducing cognitive overload and promoting strategic task execution.
Quadrant Overlap Analytics
Analyzing quadrant overlap in the Eisenhower Matrix reveals how tasks often span urgent-important and non-urgent-important categories, helping prioritize workload more effectively than a simple to-do list. This overlap insight enhances productivity by ensuring high-impact tasks receive focused attention while minimizing time spent on less critical activities.
Contextualized Priority Zoning
The Eisenhower Matrix enhances productivity by categorizing tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, enabling contextualized priority zoning that helps users focus on high-impact activities rather than merely completing items on a to-do list. Unlike traditional to-do lists that can lead to task overload, the Eisenhower Matrix promotes strategic decision-making, improving time management and goal alignment through prioritization.
Fast-Fail Task Triage
The Eisenhower Matrix accelerates fast-fail task triage by categorizing tasks into urgent-important quadrants, enabling immediate identification and elimination of low-priority activities that drain productivity. In contrast, traditional to-do lists often lack this prioritization framework, leading to slower decision-making and inefficiency in managing critical versus non-essential tasks.
To-Do List vs Eisenhower Matrix for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com