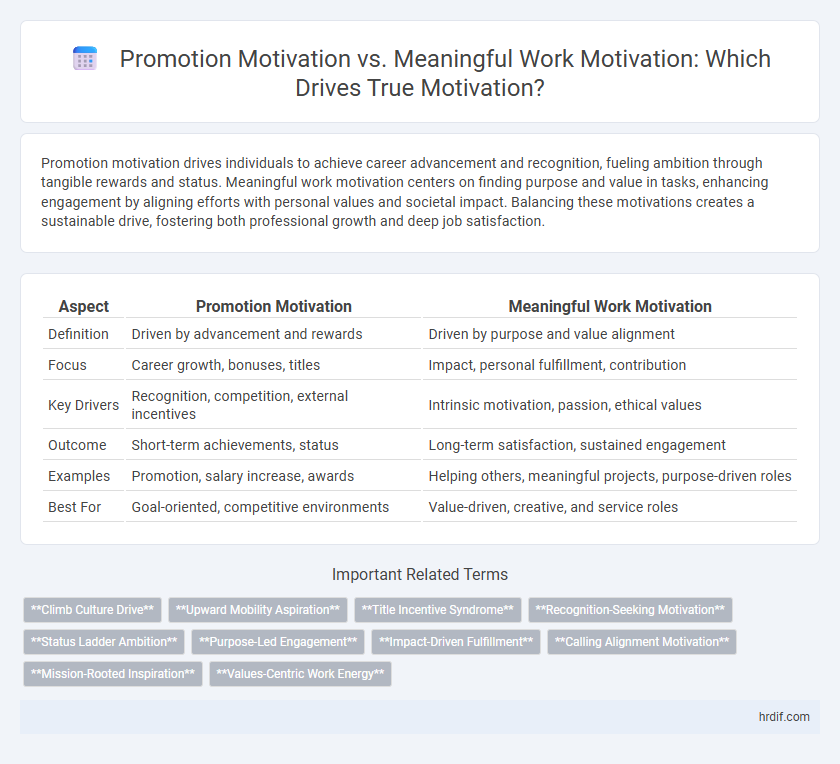
Promotion motivation drives individuals to achieve career advancement and recognition, fueling ambition through tangible rewards and status. Meaningful work motivation centers on finding purpose and value in tasks, enhancing engagement by aligning efforts with personal values and societal impact. Balancing these motivations creates a sustainable drive, fostering both professional growth and deep job satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Promotion Motivation | Meaningful Work Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Driven by advancement and rewards | Driven by purpose and value alignment |
| Focus | Career growth, bonuses, titles | Impact, personal fulfillment, contribution |
| Key Drivers | Recognition, competition, external incentives | Intrinsic motivation, passion, ethical values |
| Outcome | Short-term achievements, status | Long-term satisfaction, sustained engagement |
| Examples | Promotion, salary increase, awards | Helping others, meaningful projects, purpose-driven roles |
| Best For | Goal-oriented, competitive environments | Value-driven, creative, and service roles |
Understanding Promotion Motivation in Career Advancement
Promotion motivation centers on the desire for tangible career advancement, such as salary raises, titles, and increased responsibilities, driving employees to achieve organizational goals. Meaningful work motivation emphasizes intrinsic satisfaction, where employees find purpose and alignment with personal values, enhancing commitment and job fulfillment. Understanding promotion motivation enables organizations to tailor incentives that boost performance and retention by recognizing the importance of external rewards in career development.
The Drive Behind Meaningful Work Motivation
Meaningful work motivation stems from an intrinsic desire to find purpose and fulfillment in tasks that align with personal values and contribute to a greater good. Unlike promotion motivation, which is driven by external rewards such as salary increases or career advancement, meaningful work motivation fuels sustained engagement through emotional and psychological satisfaction. This drive enhances creativity, resilience, and long-term commitment by connecting individuals to the impact of their work beyond tangible incentives.
Key Differences Between Promotion and Meaningful Work Motivations
Promotion motivation centers on achieving external rewards such as salary increases, titles, and career advancement, driving individuals to pursue tangible, outcome-based goals. In contrast, meaningful work motivation is driven by intrinsic satisfaction derived from purposeful tasks that align with personal values and contribute to a greater cause. These key differences highlight that promotion motivation emphasizes external validation, while meaningful work motivation prioritizes internal fulfillment and long-term engagement.
How Promotion Motivation Impacts Job Satisfaction
Promotion motivation significantly enhances job satisfaction by providing clear career advancement opportunities and recognition, which fosters employee engagement and goal orientation. Employees driven by promotion motivation tend to exhibit increased productivity and commitment, as the prospect of upward mobility aligns with their personal success metrics. This type of motivation creates a performance-driven work environment where achieving milestones leads to tangible rewards, boosting overall morale and satisfaction levels.
The Role of Meaningful Work in Employee Engagement
Meaningful work motivation significantly enhances employee engagement by fostering a deeper connection between individual values and job roles, leading to higher job satisfaction and commitment. Unlike promotion motivation, which centers on external rewards and career advancement, meaningful work instills intrinsic motivation through purpose and personal fulfillment. Organizations prioritizing meaningful tasks and aligning roles with employee passions experience increased productivity, reduced turnover, and sustained workplace enthusiasm.
Balancing Advancement Ambitions with Personal Fulfillment
Promotion motivation drives individuals to seek higher positions, increased responsibilities, and tangible rewards such as salary raises and status recognition. Meaningful work motivation centers on finding purpose, alignment with personal values, and fulfillment through the impact of one's contributions. Balancing advancement ambitions with personal fulfillment ensures sustained engagement, preventing burnout and enhancing long-term career satisfaction.
Identifying Your Core Workplace Motivators
Identifying your core workplace motivators requires distinguishing between promotion motivation, driven by the desire for advancement and rewards, and meaningful work motivation, which stems from finding purpose and value in tasks. Employees motivated by promotion often seek recognition, career growth, and financial incentives, while those driven by meaningful work prioritize alignment with personal values and impactful contributions. Understanding which motivator predominates helps tailor strategies for engagement, satisfaction, and long-term productivity in the workplace.
Organizational Strategies to Foster Both Motivation Types
Organizational strategies to enhance promotion motivation involve setting clear career advancement paths, offering performance-based incentives, and recognizing achievements to stimulate ambition and goal-oriented behavior. To foster meaningful work motivation, companies should emphasize aligning job roles with employees' values, providing opportunities for skill development, and cultivating a purpose-driven culture that highlights the impact of work on broader social or organizational goals. Integrating these approaches ensures a balanced motivation framework that drives both achievement and intrinsic satisfaction within the workforce.
The Long-term Effects of Different Motivation Styles
Promotion motivation, driven by external rewards and career advancement, often results in short-term boosts in productivity but may lead to burnout and decreased satisfaction over time. Meaningful work motivation, grounded in intrinsic values and purpose, fosters sustained engagement, resilience, and long-term well-being. Research shows that employees motivated by meaningful work exhibit greater job commitment and lower turnover rates compared to those primarily driven by promotion incentives.
Choosing Between Climbing the Ladder and Finding Purpose
Choosing between promotion motivation and meaningful work motivation often hinges on individual values and long-term goals. Promotion motivation drives employees to pursue career advancement, higher salaries, and status, while meaningful work motivation emphasizes personal fulfillment, alignment with core values, and positive social impact. Balancing these motivations can lead to sustained engagement and overall job satisfaction, as both financial incentives and purposeful work are critical for motivation.
Related Important Terms
Climb Culture Drive
Climb Culture Drive thrives when employees find motivation through meaningful work that aligns with their personal values, fostering intrinsic engagement rather than relying solely on promotion-based incentives. Emphasizing purpose and impact within organizational goals cultivates sustained motivation beyond hierarchical advancement, empowering individuals to contribute authentically.
Upward Mobility Aspiration
Upward mobility aspiration significantly drives promotion motivation by encouraging employees to pursue higher positions and rewards within an organization, enhancing goal-directed behavior and performance. Conversely, meaningful work motivation fosters intrinsic satisfaction and commitment, which can sustain long-term engagement even when immediate promotion opportunities are limited.
Title Incentive Syndrome
Title Incentive Syndrome often drives motivation through external rewards like promotions, overshadowing intrinsic drivers such as meaningful work motivation, which fosters deeper engagement and lasting satisfaction. Organizations aiming to enhance employee performance should balance recognition-based incentives with opportunities for meaningful contributions to mitigate the pitfalls of Title Incentive Syndrome.
Recognition-Seeking Motivation
Recognition-seeking motivation drives employees to pursue promotions as a tangible symbol of achievement and social status within the workplace, reinforcing their professional identity and self-worth. In contrast, meaningful work motivation stems from intrinsic fulfillment and purpose, where recognition is valued less for status and more as validation of contributing to impactful and engaging tasks.
Status Ladder Ambition
Promotion motivation drives individuals to climb the status ladder through increased responsibility and rewards, emphasizing external recognition and career advancement. Meaningful work motivation, in contrast, fuels ambition by aligning personal values with job purpose, fostering sustained engagement beyond hierarchical status.
Purpose-Led Engagement
Purpose-led engagement flourishes when promotion motivation, driven by career advancement and recognition, aligns with meaningful work motivation rooted in personal values and impact. This synergy fosters sustained employee commitment by integrating extrinsic rewards with intrinsic fulfillment, enhancing overall motivation and organizational performance.
Impact-Driven Fulfillment
Promotion motivation centers on external rewards such as career advancement and increased status, often driving short-term goals, while meaningful work motivation fosters impact-driven fulfillment by aligning tasks with personal values and long-term purpose. Employees fueled by meaningful work show higher engagement, resilience, and sustained productivity due to the intrinsic rewards of contributing to impactful outcomes.
Calling Alignment Motivation
Calling alignment motivation, rooted in an individual's sense of purpose and alignment with personal values, drives sustained engagement and fulfillment more effectively than promotion motivation, which focuses on external rewards and career advancement. Research shows that employees experiencing calling alignment exhibit higher intrinsic motivation, increased job satisfaction, and greater resilience against burnout compared to those motivated primarily by promotion opportunities.
Mission-Rooted Inspiration
Promotion motivation drives individuals through the pursuit of career advancement and external rewards, while meaningful work motivation stems from alignment with a mission-rooted inspiration that fosters deeper engagement and intrinsic fulfillment. Employees inspired by a compelling organizational mission exhibit heightened commitment, creativity, and sustained motivation beyond traditional promotion incentives.
Values-Centric Work Energy
Promotion motivation drives individuals through external rewards and career advancement opportunities, emphasizing status and financial gains, while meaningful work motivation fuels intrinsic satisfaction by aligning tasks with personal values and purpose. Values-centric work energy emerges when meaningful work motivation transforms daily efforts into fulfilling experiences, promoting sustained engagement and authentic performance.
Promotion Motivation vs Meaningful Work Motivation for motivation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com