Extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards such as salary, bonuses, or recognition, driving individuals to perform tasks primarily for tangible gains. Ikigai motivation, rooted in Japanese philosophy, emphasizes finding purpose and joy in work by aligning personal passions, talents, and societal contributions, leading to deep job fulfillment. Combining extrinsic incentives with Ikigai creates a balanced approach that sustains motivation both materially and spiritually.
Table of Comparison
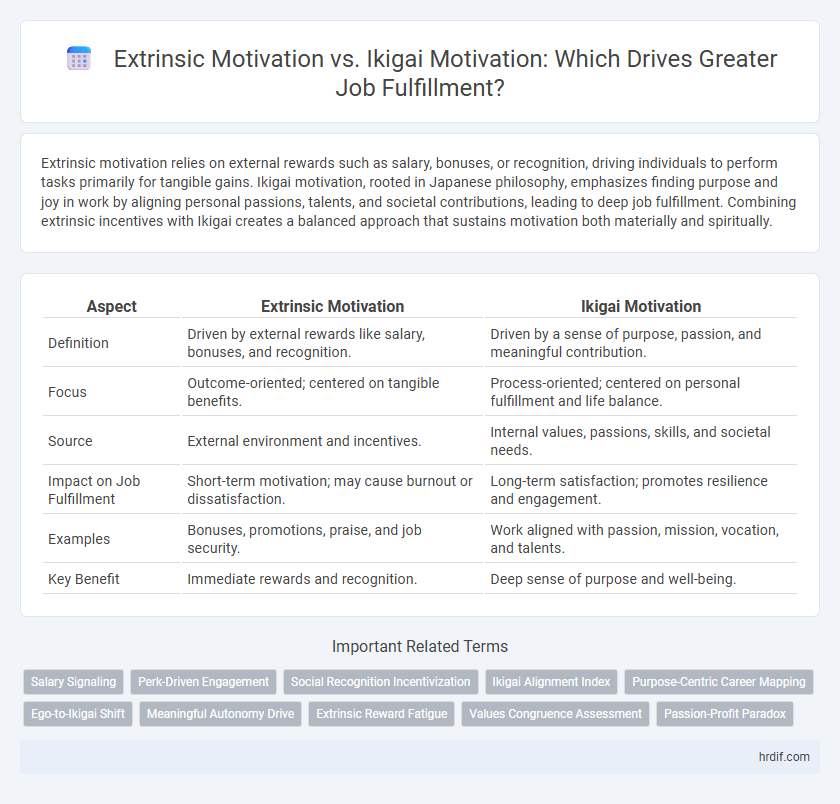
| Aspect | Extrinsic Motivation | Ikigai Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Driven by external rewards like salary, bonuses, and recognition. | Driven by a sense of purpose, passion, and meaningful contribution. |
| Focus | Outcome-oriented; centered on tangible benefits. | Process-oriented; centered on personal fulfillment and life balance. |
| Source | External environment and incentives. | Internal values, passions, skills, and societal needs. |
| Impact on Job Fulfillment | Short-term motivation; may cause burnout or dissatisfaction. | Long-term satisfaction; promotes resilience and engagement. |
| Examples | Bonuses, promotions, praise, and job security. | Work aligned with passion, mission, vocation, and talents. |
| Key Benefit | Immediate rewards and recognition. | Deep sense of purpose and well-being. |
Understanding Extrinsic Motivation in the Workplace
Extrinsic motivation in the workplace relies on external rewards such as salary increases, bonuses, and recognition to drive employee performance and job fulfillment. Unlike Ikigai motivation, which stems from a deep sense of purpose and personal satisfaction, extrinsic motivation often leads to short-term engagement but may lack sustainable long-term commitment. Employers aiming to optimize productivity should balance extrinsic incentives with intrinsic factors that align with employees' values and passions.
What Is Ikigai Motivation?
Ikigai motivation stems from a deep sense of purpose that intertwines passion, mission, vocation, and profession, fostering profound job fulfillment beyond external rewards. Unlike extrinsic motivation driven by tangible incentives such as salary or bonuses, Ikigai motivation encourages individuals to engage in work aligned with their core values and personal meaning. This intrinsic form of motivation enhances long-term satisfaction, resilience, and productivity by making work an expression of one's true self.
Core Differences: Extrinsic vs Ikigai Motivation
Extrinsic motivation in job fulfillment is driven by external rewards such as salary, bonuses, and recognition, often focusing on tangible outcomes and short-term goals. In contrast, Ikigai motivation emphasizes finding purpose and meaning in work, aligning personal values with professional activities to foster long-lasting satisfaction and intrinsic fulfillment. The core difference lies in extrinsic motivation relying on external validation, whereas Ikigai motivation centers on internal passion and a deeper sense of contribution.
The Short-Term Gains of Extrinsic Rewards
Extrinsic motivation in the workplace often drives short-term gains through tangible rewards such as bonuses, promotions, and recognition, which can quickly boost employee performance and engagement. However, relying solely on extrinsic rewards may lead to diminished long-term job satisfaction and decreased intrinsic interest in the work itself. In contrast, Ikigai motivation, centered on purpose and meaning, fosters sustained fulfillment by aligning personal values with professional goals, promoting deeper commitment beyond immediate incentives.
Ikigai: Aligning Passion With Profession
Extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards such as salary, bonuses, and recognition, driving job performance through tangible incentives. Ikigai motivation emphasizes finding deeper fulfillment by aligning one's passion, mission, vocation, and profession, fostering sustainable engagement and purpose in work. This alignment enhances intrinsic satisfaction, boosts creativity, and promotes long-term career resilience beyond traditional extrinsic motivators.
Impact of Extrinsic Motivation on Job Satisfaction
Extrinsic motivation, driven by external rewards such as salary, bonuses, and recognition, often leads to short-term job satisfaction but may fail to sustain long-term engagement. In contrast, Ikigai motivation, rooted in finding purpose and meaning at work, fosters deeper fulfillment and persistent commitment. Research shows that jobs aligned with intrinsic purpose yield higher overall satisfaction and reduced burnout compared to those primarily motivated by extrinsic factors.
How Ikigai Drives Long-Term Career Fulfillment
Extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards such as salary and recognition, often leading to short-term job satisfaction but limited long-term fulfillment. Ikigai motivation integrates passion, mission, profession, and vocation, fostering a deeper sense of purpose and sustained engagement in one's career. Aligning work with ikigai promotes resilience and intrinsic satisfaction, driving long-term career fulfillment beyond mere external incentives.
Case Studies: Real-World Outcomes of Both Motivations
Case studies reveal that extrinsic motivation, driven by external rewards such as salary and recognition, often leads to short-term job performance but lower long-term satisfaction and higher burnout rates. In contrast, employees motivated by ikigai--the Japanese concept of finding purpose and meaning in work--exhibit higher engagement, creativity, and sustained fulfillment, resulting in improved mental health and consistent productivity. Organizations that integrate ikigai-based motivation frameworks report increased employee retention and overall organizational success compared to those relying solely on extrinsic incentives.
Balancing Extrinsic Rewards and Ikigai in Your Career
Balancing extrinsic motivation, such as salary and benefits, with ikigai motivation, which emphasizes purpose and personal fulfillment, creates a sustainable approach to job satisfaction. Prioritizing ikigai helps align your career with deep values and passions, fostering long-term engagement beyond immediate rewards. Integrating both extrinsic incentives and ikigai principles supports holistic motivation, enhancing productivity and well-being in the workplace.
Choosing the Right Motivation for Sustainable Success
Extrinsic motivation, driven by external rewards such as salary and recognition, often leads to short-term job fulfillment but may result in burnout or disengagement over time. Ikigai motivation, rooted in finding purpose, passion, and contribution in work, fosters long-lasting satisfaction and sustainable success by aligning personal values with professional goals. Choosing the right motivation involves prioritizing intrinsic meaning and alignment with one's core beliefs while balancing external incentives to maintain both drive and well-being.
Related Important Terms
Salary Signaling
Extrinsic motivation driven by salary signaling often influences job choice by emphasizing financial rewards and social status, while Ikigai motivation centers on finding intrinsic purpose and personal fulfillment in work. Salary signaling may boost short-term job commitment, but Ikigai-driven employees typically experience deeper long-term satisfaction and sustained engagement at work.
Perk-Driven Engagement
Extrinsic motivation in the workplace often relies on tangible rewards such as bonuses and perks to drive employee engagement, which can result in short-term productivity spikes but may not sustain long-term job fulfillment. Ikigai motivation, rooted in a deeper sense of purpose and personal fulfillment, fosters enduring commitment and intrinsic satisfaction that surpasses external incentives alone.
Social Recognition Incentivization
Extrinsic motivation in job fulfillment often relies on social recognition incentivization, where external rewards like praise, promotions, or bonuses drive performance and engagement. In contrast, Ikigai motivation integrates social recognition with intrinsic purpose, fostering deeper job satisfaction by aligning personal values and community impact.
Ikigai Alignment Index
The Ikigai Alignment Index quantitatively measures how closely an individual's job aligns with their Ikigai, the intersection of passion, mission, vocation, and profession, which enhances intrinsic motivation and long-term fulfillment. Unlike extrinsic motivation driven by external rewards such as salary or recognition, Ikigai motivation fosters deeper engagement and sustainable productivity by fulfilling core personal values and purpose.
Purpose-Centric Career Mapping
Extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards such as salary and bonuses, while Ikigai motivation centers on finding deep personal purpose and meaning in work, fostering sustained job fulfillment through alignment with core values. Purpose-centric career mapping integrates this intrinsic drive by identifying roles that resonate with one's passion, mission, vocation, and profession, leading to enhanced engagement and long-term satisfaction.
Ego-to-Ikigai Shift
Extrinsic motivation, driven by external rewards like salary and recognition, often leads to short-term job fulfillment, whereas the Ego-to-Ikigai shift emphasizes intrinsic purpose and alignment with personal values for sustained engagement and deeper satisfaction. Embracing Ikigai motivation encourages individuals to find meaning beyond ego-driven goals, fostering resilience, creativity, and long-term professional growth.
Meaningful Autonomy Drive
Extrinsic motivation relies on external rewards such as salary and recognition, while Ikigai motivation centers on finding meaningful autonomy and a deep personal drive that aligns with one's values and passions, leading to sustainable job fulfillment. Emphasizing meaningful autonomy enhances intrinsic satisfaction and long-term engagement by fostering a sense of purpose and self-determination in the workplace.
Extrinsic Reward Fatigue
Extrinsic motivation often leads to reward fatigue as employees become desensitized to external incentives like bonuses or promotions, diminishing long-term job satisfaction. In contrast, Ikigai motivation, rooted in finding purpose and meaning in work, fosters sustained fulfillment by aligning personal values with professional goals.
Values Congruence Assessment
Extrinsic motivation drives job performance through external rewards like salary and recognition, while Ikigai motivation centers on aligning work with personal purpose and intrinsic values, leading to deeper fulfillment. Values Congruence Assessment measures the harmony between an individual's core beliefs and organizational culture, enhancing job satisfaction and long-term engagement by prioritizing meaningful alignment over material incentives.
Passion-Profit Paradox
Extrinsic motivation drives job fulfillment through external rewards like salary and promotions, often leading to the Passion-Profit Paradox where financial gain conflicts with personal passion. Ikigai motivation harmonizes passion, mission, vocation, and profession, fostering long-term fulfillment by aligning meaningful work with both intrinsic satisfaction and sustainable income.
Extrinsic motivation vs Ikigai motivation for job fulfillment Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com