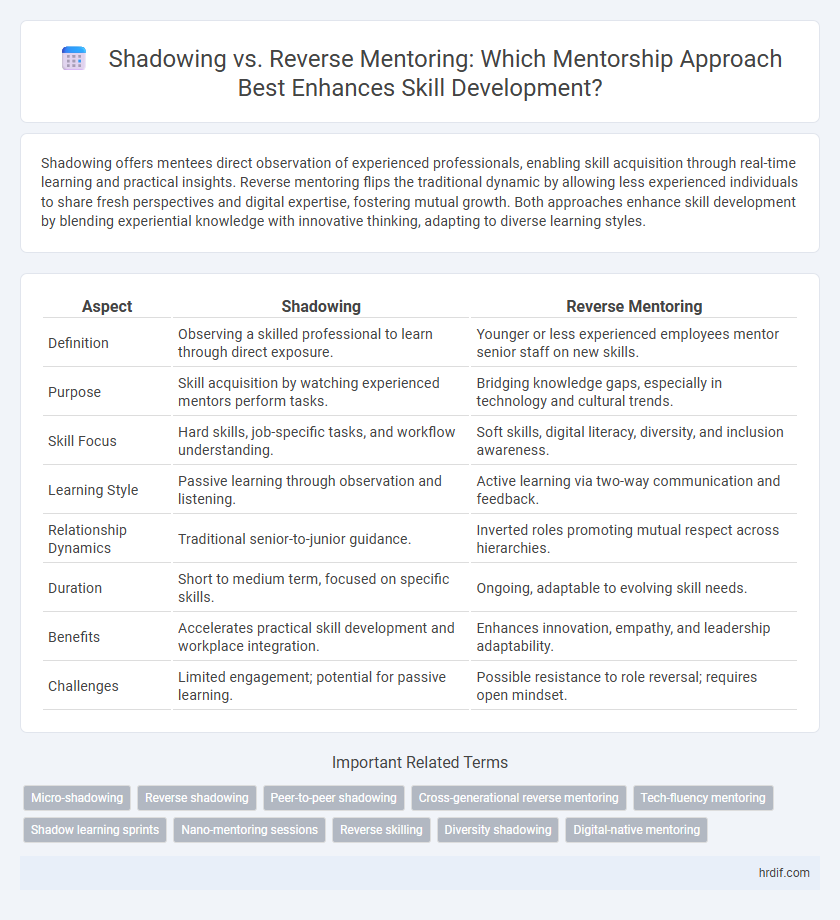
Shadowing offers mentees direct observation of experienced professionals, enabling skill acquisition through real-time learning and practical insights. Reverse mentoring flips the traditional dynamic by allowing less experienced individuals to share fresh perspectives and digital expertise, fostering mutual growth. Both approaches enhance skill development by blending experiential knowledge with innovative thinking, adapting to diverse learning styles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shadowing | Reverse Mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Observing a skilled professional to learn through direct exposure. | Younger or less experienced employees mentor senior staff on new skills. |
| Purpose | Skill acquisition by watching experienced mentors perform tasks. | Bridging knowledge gaps, especially in technology and cultural trends. |
| Skill Focus | Hard skills, job-specific tasks, and workflow understanding. | Soft skills, digital literacy, diversity, and inclusion awareness. |
| Learning Style | Passive learning through observation and listening. | Active learning via two-way communication and feedback. |
| Relationship Dynamics | Traditional senior-to-junior guidance. | Inverted roles promoting mutual respect across hierarchies. |
| Duration | Short to medium term, focused on specific skills. | Ongoing, adaptable to evolving skill needs. |
| Benefits | Accelerates practical skill development and workplace integration. | Enhances innovation, empathy, and leadership adaptability. |
| Challenges | Limited engagement; potential for passive learning. | Possible resistance to role reversal; requires open mindset. |
Understanding Shadowing and Reverse Mentoring
Shadowing involves observing experienced professionals to gain practical insights and real-time problem-solving skills, enhancing observational learning and hands-on experience. Reverse mentoring flips traditional roles, allowing junior employees to share digital literacy and new perspectives with senior leaders, promoting a two-way knowledge exchange. Both methods foster skill development by combining experiential learning with innovative ideas, creating a dynamic environment for professional growth.
Key Differences Between Shadowing and Reverse Mentoring
Shadowing involves a less experienced employee observing a senior professional to gain insights into job functions and workplace culture, while reverse mentoring flips this dynamic by having younger or less experienced employees mentor senior staff, often on digital skills or contemporary trends. Shadowing emphasizes learning through observation and imitation, whereas reverse mentoring fosters two-way knowledge exchange and challenges traditional hierarchies. Both methods enhance skill development but target different learning objectives and relationships within organizational structures.
Benefits of Shadowing for Career Growth
Shadowing offers invaluable firsthand exposure to expert decision-making and real-time problem-solving, accelerating skill acquisition and industry understanding. By observing experienced professionals, mentees gain practical insights into workplace dynamics and leadership styles, fostering confidence and competence. This immersive learning method directly enhances career growth by building a strong foundation of relevant skills and professional relationships.
Advantages of Reverse Mentoring in the Workplace
Reverse mentoring enhances skill development by fostering knowledge exchange between junior and senior employees, promoting technological literacy and fresh perspectives. It accelerates cultural competence and adaptability, bridging generational gaps and improving collaboration across teams. Companies implementing reverse mentoring report increased innovation, employee engagement, and retention due to more inclusive and dynamic learning environments.
Skill Development Through Shadowing
Skill development through shadowing allows individuals to closely observe experienced professionals in real-time work environments, facilitating the acquisition of practical knowledge and nuanced skills. This hands-on learning method enhances contextual understanding and accelerates competency by providing direct exposure to tasks and decision-making processes. Shadowing effectively bridges the gap between theoretical learning and applied expertise, fostering improved performance and confidence in skill execution.
How Reverse Mentoring Enhances Digital Skills
Reverse mentoring accelerates digital skill development by pairing less experienced employees with tech-savvy younger colleagues who provide real-time insights into emerging technologies and digital tools. This dynamic learning approach fosters continuous knowledge exchange, bridges generational gaps, and rapidly upskills teams in areas such as social media strategy, data analytics, and cybersecurity. Unlike traditional shadowing, reverse mentoring encourages active collaboration and innovation, driving a more agile and digitally proficient workforce.
Choosing the Right Approach: Shadowing or Reverse Mentoring
Shadowing offers skill development through direct observation and hands-on learning from experienced professionals, ideal for gaining industry-specific expertise and practical insights. Reverse mentoring fosters skill enhancement by enabling junior employees to share fresh perspectives and digital proficiency with senior staff, promoting intergenerational knowledge exchange and innovation. Selecting the right approach depends on organizational goals, the skills targeted for development, and the existing knowledge gap between mentors and mentees.
Challenges and Solutions in Shadowing Programs
Shadowing programs often face challenges such as limited engagement, passive learning, and scheduling conflicts, which can hinder effective skill development. Addressing these issues requires structured shadowing plans, active participation guidelines, and flexible timing to maximize learning outcomes. Integrating feedback mechanisms and pairing participants based on complementary goals enhances the overall impact of shadowing initiatives.
Effective Implementation of Reverse Mentoring
Reverse mentoring fosters skill development by enabling junior employees to share fresh perspectives and digital expertise with senior leaders, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Effective implementation requires clear goal-setting, mutual respect, and structured feedback to ensure knowledge transfer aligns with organizational objectives. Utilizing technology platforms for communication and progress tracking further optimizes engagement and measurable outcomes.
Measuring Success: Impact on Professional Development
Shadowing allows mentees to observe and absorb skills from experienced professionals, with success measured through improvements in task proficiency and confidence. Reverse mentoring promotes knowledge exchange where senior staff gain digital or contemporary insights, assessed by enhanced leadership agility and innovation adoption. Both methods contribute to professional development, as indicated by increased performance metrics, employee engagement, and career progression.
Related Important Terms
Micro-shadowing
Micro-shadowing accelerates skill development by enabling brief, focused observational sessions where less experienced employees learn specific techniques from experts, contrasting with reverse mentoring which promotes knowledge exchange by having junior staff guide senior colleagues on emerging trends. This targeted approach in micro-shadowing enhances practical learning efficiency and immediate application in workplace scenarios.
Reverse shadowing
Reverse shadowing accelerates skill development by enabling less experienced employees to observe and learn from senior leaders' strategic decision-making in real-time, fostering a dynamic two-way exchange of knowledge and innovative perspectives. Unlike traditional shadowing, reverse shadowing empowers emerging talent to influence senior professionals, enhancing leadership adaptability and promoting a culture of continuous learning within the organization.
Peer-to-peer shadowing
Peer-to-peer shadowing in mentorship accelerates skill development by allowing mentees to observe real-time expertise and practical problem-solving techniques directly from peers, fostering immediate knowledge application and contextual learning. Reverse mentoring complements this by enabling junior employees to share fresh digital skills and diverse perspectives with senior colleagues, promoting a dynamic exchange that enhances overall organizational competence.
Cross-generational reverse mentoring
Cross-generational reverse mentoring accelerates skill development by enabling younger employees to share digital expertise and contemporary trends with senior leaders, fostering mutual learning and innovation. Shadowing offers observational learning primarily through experienced mentors, while reverse mentoring emphasizes active knowledge exchange, bridging generational gaps and enhancing organizational adaptability.
Tech-fluency mentoring
Shadowing offers real-time observation of experienced professionals, enabling mentees to grasp technical workflows and tool usage directly, while reverse mentoring fosters tech-fluency by empowering younger, digitally native employees to teach seasoned leaders emerging technologies and innovative platforms. This dual approach accelerates skill development by combining experiential learning with fresh digital insights, essential for navigating rapidly evolving tech landscapes.
Shadow learning sprints
Shadow learning sprints in mentorship accelerate skill development by immersing mentees in real-time tasks alongside experienced professionals, enhancing practical knowledge and fostering quicker adaptability. This hands-on approach contrasts with reverse mentoring, which emphasizes knowledge transfer from junior to senior staff, making shadowing more effective for immediate skill acquisition and contextual learning.
Nano-mentoring sessions
Shadowing in nano-mentoring sessions allows mentees to observe expert processes directly, accelerating skill acquisition through real-time learning, while reverse mentoring fosters bi-directional knowledge exchange by enabling junior members to share fresh insights and digital expertise with seniors. Both approaches optimize skill development in compact sessions by combining observational learning with innovative perspectives tailored to rapidly evolving workplace demands.
Reverse skilling
Reverse mentoring accelerates skill development by enabling experienced professionals to learn emerging technologies and modern trends directly from younger employees, fostering a dynamic knowledge exchange that traditional shadowing often lacks. This approach bridges generational gaps, enhances digital literacy, and promotes continuous learning cultures within organizations.
Diversity shadowing
Shadowing offers employees immersive observation opportunities to learn established skills from experienced colleagues, while reverse mentoring promotes bi-directional knowledge exchange that enhances diversity by empowering junior or minority employees to share unique perspectives. Diversity-focused shadowing specifically enables skill development through exposure to varied cultural and professional approaches, fostering inclusive innovation and comprehensive understanding in the workplace.
Digital-native mentoring
Shadowing provides mentees with hands-on observation of digital-native experts, enabling real-time skill acquisition and practical insights into evolving technologies. Reverse mentoring fosters a two-way exchange where digital natives share advanced tech fluency and innovative digital strategies, accelerating organizational skill development and cultural adaptability.
Shadowing vs Reverse mentoring for skill development Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com