Mentors provide experienced guidance and personalized advice, drawing from their expertise to foster growth and development in mentorship pet programs. Peer mentors offer relatable support through shared experiences, creating a collaborative environment that encourages mutual learning and confidence-building. Both roles complement each other by combining professional insight with empathetic understanding, enhancing overall collaboration and support.
Table of Comparison
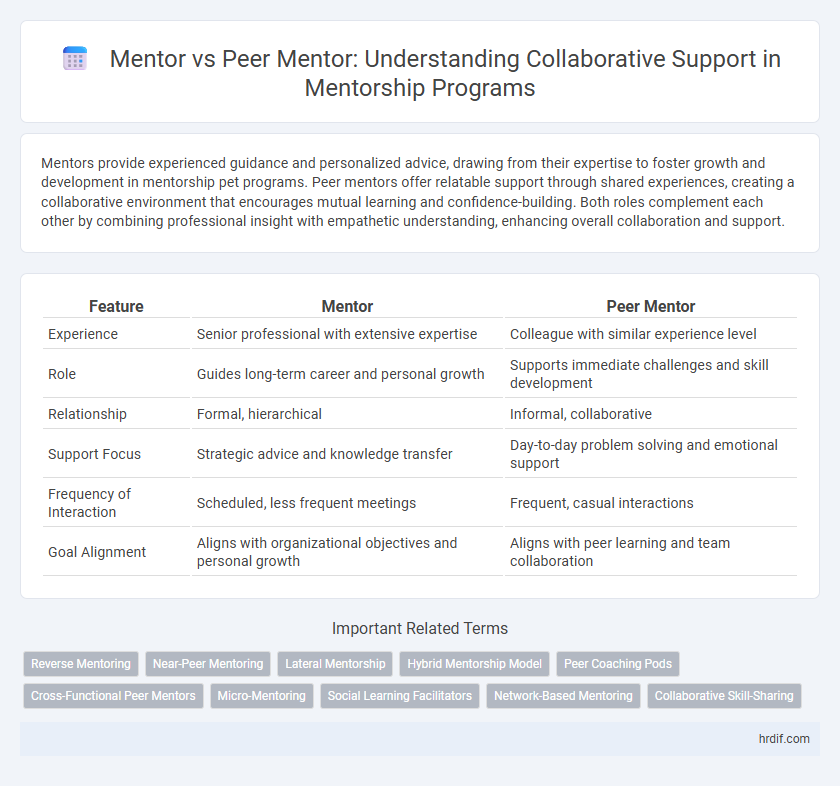
| Feature | Mentor | Peer Mentor |
|---|---|---|
| Experience | Senior professional with extensive expertise | Colleague with similar experience level |
| Role | Guides long-term career and personal growth | Supports immediate challenges and skill development |
| Relationship | Formal, hierarchical | Informal, collaborative |
| Support Focus | Strategic advice and knowledge transfer | Day-to-day problem solving and emotional support |
| Frequency of Interaction | Scheduled, less frequent meetings | Frequent, casual interactions |
| Goal Alignment | Aligns with organizational objectives and personal growth | Aligns with peer learning and team collaboration |
Understanding the Roles: Mentor vs Peer Mentor
Mentors provide expert guidance and long-term career development through their extensive experience and industry knowledge, facilitating goal-setting and skill enhancement. Peer mentors offer collaborative support by sharing relatable experiences and fostering mutual learning within similar stages of their professional journey. Recognizing these distinct roles enables organizations to effectively leverage both mentorship types for comprehensive personal and professional growth.
Core Differences Between Mentors and Peer Mentors
Mentors typically possess extensive experience and offer guidance based on their professional expertise, while peer mentors provide support as equals, sharing relatable experiences and fostering mutual growth. The core difference lies in the mentor's role as an authoritative advisor versus the peer mentor's position as a collaborative partner. This distinction influences the dynamics of trust, advice delivery, and the depth of personal connection within collaborative support.
Benefits of Traditional Mentorship in Career Development
Traditional mentorship offers personalized guidance from experienced professionals, providing deep industry insights and valuable networking opportunities. This one-on-one relationship fosters long-term career growth through tailored feedback and strategic advice. Unlike peer mentorship, traditional mentorship connects mentees with established leaders who can open doors to advanced career milestones.
Advantages of Peer Mentoring for Collaborative Growth
Peer mentoring fosters a dynamic environment of collaborative growth by promoting reciprocal learning and shared experiences among individuals at similar stages. This approach enhances communication skills, boosts confidence, and creates a supportive network where mentees feel understood and motivated. The mutual accountability inherent in peer mentoring accelerates problem-solving and personal development more effectively than traditional mentor-mentee relationships.
Key Skills Gained: Mentor-Guided vs Peer-Guided Support
Mentor-guided support develops strategic thinking, leadership, and industry-specific expertise through experienced insights, while peer-guided support enhances communication, empathy, and collaborative problem-solving by fostering mutual learning. Mentors provide targeted feedback that accelerates professional growth, whereas peer mentors create a supportive environment encouraging confidence and shared accountability. Both approaches build essential skills, but mentor guidance often delivers a more structured development pathway compared to the dynamic, reciprocal nature of peer mentorship.
Collaborative Dynamics: How Mentor and Peer Mentor Support Vary
Mentors provide expert guidance based on extensive experience, facilitating long-term professional growth and strategic insight. Peer mentors offer relatable, real-time support through shared experiences, fostering a collaborative environment that enhances problem-solving and peer learning. The complementary dynamic between mentors and peer mentors creates a robust support system, combining authoritative advice with empathetic peer engagement to optimize mentee development.
Workplace Integration: Choosing the Right Support System
Mentors offer seasoned expertise and strategic guidance, essential for navigating complex workplace dynamics and accelerating career growth, while peer mentors provide relatable experiences and immediate support, fostering a collaborative learning environment. Selecting the right support system depends on the new employee's integration needs; mentors excel in long-term professional development, whereas peer mentors enhance daily adjustment and team cohesion. Effective workplace integration blends both approaches, leveraging mentor wisdom with peer accessibility to maximize collaborative support.
Enhancing Employee Engagement through Mentorship Models
Mentor and peer mentor models both enhance employee engagement by fostering collaborative support, but they serve different roles in development. Traditional mentors provide experienced guidance and strategic career insights, while peer mentors offer relatable, day-to-day advice and emotional support, creating a balanced mentorship ecosystem. Combining both approaches accelerates skill growth, increases job satisfaction, and strengthens workplace relationships.
How to Match with a Mentor or Peer Mentor Effectively
To match effectively with a mentor or peer mentor, clearly identify your learning objectives and preferences for communication style, expertise level, and availability. Use platforms or networks that facilitate detailed profiles and compatibility algorithms to ensure alignment in goals, industry experience, and personality traits. Regular feedback and goal reassessment enhance the mentorship relationship, maximizing collaborative support and growth.
Measuring Success: Impact of Mentors vs Peer Mentors in the Workplace
Mentor and peer mentor programs differ significantly in their impact on workplace collaboration, with traditional mentors offering strategic guidance while peer mentors provide real-time, relatable support. Measuring success involves metrics such as employee engagement, skill acquisition, and productivity improvements, where peer mentors often excel in fostering immediate problem-solving and team cohesion. Data from organizational studies reveal that integrating both types enhances overall mentoring effectiveness, creating a balanced environment for professional growth.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Mentoring
Mentorship fosters growth through experienced mentors guiding less experienced individuals, while peer mentoring emphasizes reciprocal support among equals, enhancing collaboration through shared experiences. Reverse mentoring, where younger or less experienced peers offer insights to senior mentors, promotes innovative thinking and bridges generational knowledge gaps.
Near-Peer Mentoring
Near-peer mentoring bridges the gap between formal mentorship and peer support by pairing individuals with mentors who are slightly more experienced, fostering relatable guidance and practical advice. This approach enhances collaborative support by encouraging open communication and shared learning experiences within a close developmental stage.
Lateral Mentorship
Lateral mentorship fosters collaborative support by enabling peers with similar experience levels to exchange knowledge and skills, enhancing problem-solving through mutual understanding and shared challenges. Unlike traditional mentorship, where a senior mentor guides a junior mentee, peer mentorship emphasizes equitable relationships that promote reciprocal learning and collective growth within professional or educational environments.
Hybrid Mentorship Model
The hybrid mentorship model leverages both traditional mentors with extensive experience and peer mentors who offer relatable insights, fostering a dynamic and inclusive support environment. Integrating expert guidance from mentors with the empathetic camaraderie of peer mentors enhances collaborative learning and professional growth outcomes.
Peer Coaching Pods
Peer Mentor coaching pods foster collaborative support by enabling participants to share diverse perspectives and co-develop solutions, enhancing mutual learning and accountability. Unlike traditional mentorship where guidance flows top-down, peer coaching pods create dynamic environments promoting equal contribution and collective growth.
Cross-Functional Peer Mentors
Cross-functional peer mentors provide collaborative support by leveraging diverse expertise across departments, fostering innovation and holistic problem-solving in ways traditional mentors may not. Their real-time feedback and shared experiences create agile learning environments, enhancing team cohesion and accelerating skill development.
Micro-Mentoring
Micro-mentoring leverages concise, targeted interactions where mentors provide expert guidance while peer mentors offer relatable experiences and mutual support, enhancing collaborative learning and problem-solving. This approach fosters rapid skill development and accountability by combining the depth of traditional mentorship with the accessibility and empathy of peer connections.
Social Learning Facilitators
Mentors provide expert guidance and long-term support based on experience, while peer mentors facilitate collaborative social learning by sharing relatable insights and fostering mutual growth in real-time settings. Social learning facilitators leverage the dynamic interactions between peers to enhance knowledge exchange, motivation, and skill development.
Network-Based Mentoring
Network-based mentoring leverages both mentor and peer mentor roles to enhance collaborative support, where mentors provide expert guidance and peer mentors offer relatable, experience-based advice fostering mutual growth. This dynamic combination strengthens professional development by integrating hierarchical expertise with peer-level empathy and shared learning experiences.
Collaborative Skill-Sharing
Mentors provide expert guidance and strategic insights, fostering growth through experienced knowledge, while peer mentors facilitate collaborative skill-sharing by promoting mutual learning and real-time problem solving among equals. This dynamic supports diverse perspectives, enhances communication, and accelerates skill development within teamwork environments.
Mentor vs Peer Mentor for collaborative support. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com