Mentorship fosters professional growth by allowing experienced individuals to share knowledge and industry insights, enhancing the mentee's skills and confidence. Reverse mentorship provides fresh perspectives and technological expertise from younger professionals, fostering innovation and adaptability in senior leaders. Balancing both approaches creates a dynamic learning environment that accelerates development and drives organizational success.
Table of Comparison
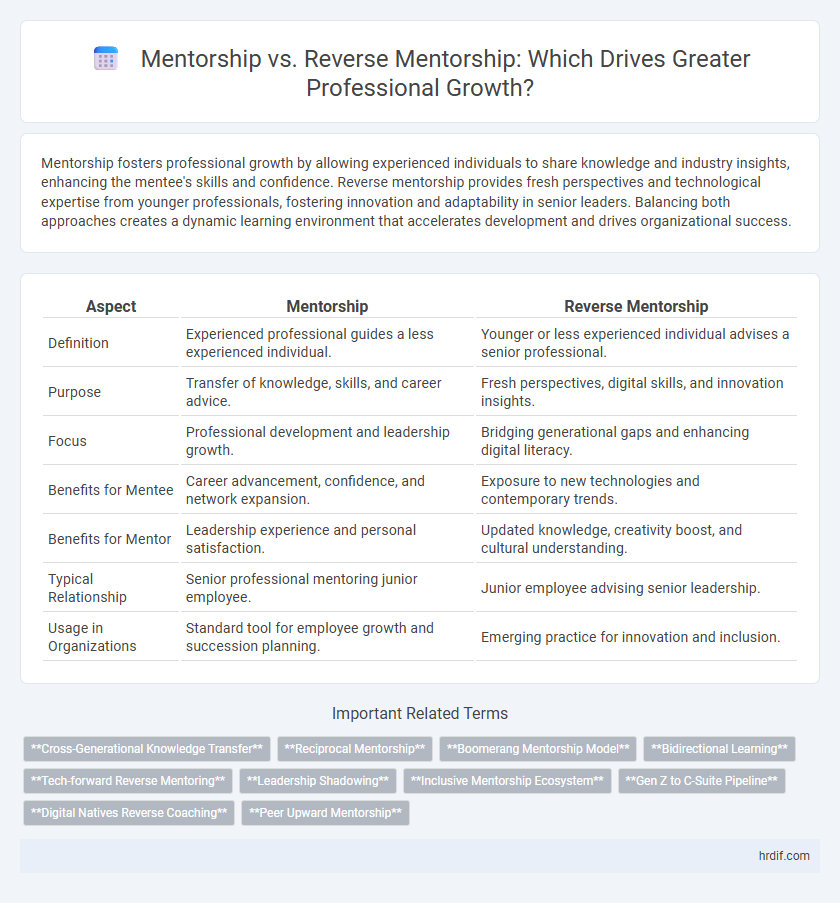
| Aspect | Mentorship | Reverse Mentorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Experienced professional guides a less experienced individual. | Younger or less experienced individual advises a senior professional. |
| Purpose | Transfer of knowledge, skills, and career advice. | Fresh perspectives, digital skills, and innovation insights. |
| Focus | Professional development and leadership growth. | Bridging generational gaps and enhancing digital literacy. |
| Benefits for Mentee | Career advancement, confidence, and network expansion. | Exposure to new technologies and contemporary trends. |
| Benefits for Mentor | Leadership experience and personal satisfaction. | Updated knowledge, creativity boost, and cultural understanding. |
| Typical Relationship | Senior professional mentoring junior employee. | Junior employee advising senior leadership. |
| Usage in Organizations | Standard tool for employee growth and succession planning. | Emerging practice for innovation and inclusion. |
Understanding Traditional Mentorship in the Workplace
Traditional mentorship in the workplace involves an experienced professional guiding a less experienced colleague by sharing knowledge, skills, and career advice to foster growth. This hierarchical relationship emphasizes expertise transfer, professional development, and long-term support. Traditional mentorship remains a key strategy for enhancing employee performance and leadership skills.
What is Reverse Mentorship?
Reverse mentorship is a dynamic professional development process where junior employees provide guidance and insights to senior leaders, fostering a two-way exchange of knowledge and skills. This approach helps bridge generational gaps, enhances technological understanding, and promotes innovative thinking within organizations. By leveraging the fresh perspectives of younger talent, reverse mentorship drives continuous learning and adaptability in rapidly evolving business environments.
Key Differences Between Mentorship and Reverse Mentorship
Mentorship typically involves an experienced professional guiding a less experienced individual to develop skills, knowledge, and career growth, whereas reverse mentorship features younger or less experienced employees providing insights on emerging trends, technology, and fresh perspectives to senior leaders. The key difference lies in the direction of knowledge transfer: traditional mentorship flows from senior to junior, while reverse mentorship flows upward, fostering mutual learning and innovation. Both models enhance professional growth but target different developmental needs within an organization.
Benefits of Mentorship for Professional Development
Mentorship accelerates professional growth by providing personalized guidance, industry insights, and skill development tailored to individual career goals. Experienced mentors offer valuable feedback, networking opportunities, and strategic advice that enhance decision-making and confidence in the workplace. This traditional knowledge transfer strengthens leadership capabilities, fosters continuous learning, and improves job performance across diverse industries.
Advantages of Reverse Mentorship in Modern Careers
Reverse mentorship accelerates skill acquisition by enabling younger professionals to share expertise in digital technologies and social media trends with senior leaders. This dynamic fosters reciprocal learning, improves organizational adaptability, and enhances intergenerational collaboration crucial for modern career success. Embracing reverse mentorship cultivates innovation and empowers diverse perspectives in evolving professional environments.
Potential Challenges in Mentorship vs Reverse Mentorship
Mentorship often faces challenges such as generational gaps, resistance to feedback, and potential misalignment of expectations between experienced mentors and mentees. Reverse mentorship can encounter obstacles including power dynamics, credibility concerns, and hesitancy from senior professionals to fully engage with junior insights. Both models require open communication and adaptability to overcome barriers and maximize professional growth opportunities.
Integrating Both Mentorship Models for Organizational Success
Integrating traditional mentorship and reverse mentorship creates a dynamic professional growth environment by blending experienced insights with fresh perspectives, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing across all organizational levels. Leveraging seasoned expertise alongside emerging talent encourages continuous learning, enhances leadership development, and strengthens company culture. Organizations that adopt both models experience accelerated skill development, improved employee engagement, and increased adaptability in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Real-World Examples of Mentorship and Reverse Mentorship
Mentorship often involves experienced professionals guiding younger employees, as seen in companies like General Electric where senior leaders mentor rising talent to transfer institutional knowledge and leadership skills. Reverse mentorship flips this dynamic, exemplified by Cisco's program where younger employees teach veterans about emerging technologies and digital trends, fostering mutual growth. These real-world examples demonstrate how both mentorship and reverse mentorship accelerate professional development by leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Career Growth
Mentorship offers seasoned professionals guidance based on extensive industry experience, while reverse mentorship provides fresh perspectives from younger or less experienced colleagues, fostering innovation and adaptability. Selecting the right approach depends on your current career stage and growth objectives, where traditional mentorship enhances foundational skills and reverse mentorship encourages embracing new technologies and cultural trends. Evaluating your professional goals and learning preferences ensures a tailored mentorship strategy that maximizes skill development and network expansion.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Professional Mentorship
Mentorship and reverse mentorship are reshaping professional growth by fostering bidirectional knowledge flow, with forward-thinking companies integrating technology-driven platforms to facilitate real-time collaboration across generations. Future trends highlight the rise of AI-powered mentorship tools that personalize learning experiences and track progress, enhancing the effectiveness of both traditional and reverse mentorship frameworks. Emphasizing diversity and inclusivity, organizations are leveraging reverse mentorship to bridge generational gaps while accelerating skill development aligned with emerging industry demands.
Related Important Terms
Cross-Generational Knowledge Transfer
Mentorship facilitates cross-generational knowledge transfer by enabling experienced professionals to share industry insights and leadership skills with younger employees. Reverse mentorship complements this process by allowing younger workers to impart digital expertise and contemporary trends, fostering mutual professional growth and innovation across age groups.
Reciprocal Mentorship
Reciprocal mentorship fosters mutual professional growth by enabling both parties to share knowledge, skills, and insights across generational or hierarchical boundaries, enhancing adaptability and innovation within organizations. This dynamic exchange contrasts traditional mentorship and reverse mentorship by emphasizing a continuous, collaborative learning process that benefits mentors and mentees equally.
Boomerang Mentorship Model
The Boomerang Mentorship Model blends traditional mentorship with reverse mentorship, enabling experienced professionals to gain fresh perspectives from younger colleagues while fostering bi-directional knowledge exchange that accelerates professional growth. This hybrid approach enhances adaptability, innovation, and leadership skills by leveraging the diverse insights across generational divides in the workplace.
Bidirectional Learning
Mentorship and reverse mentorship both facilitate bidirectional learning by enabling experienced professionals and younger employees to exchange knowledge, fostering mutual growth and adaptability in a dynamic workplace. This two-way knowledge transfer enhances leadership skills, technological proficiency, and cultural awareness essential for professional development.
Tech-forward Reverse Mentoring
Tech-forward reverse mentoring accelerates professional growth by enabling senior leaders to gain firsthand insights into emerging technologies and digital trends from younger, tech-savvy employees. This dynamic fosters innovation and agility within organizations, bridging generational knowledge gaps and driving strategic adaptation in fast-evolving tech landscapes.
Leadership Shadowing
Leadership shadowing in traditional mentorship allows emerging leaders to learn directly from experienced executives by observing decision-making processes and leadership styles. Reverse mentorship enhances professional growth by enabling senior leaders to gain fresh perspectives on digital trends and workplace culture through close interaction with younger employees.
Inclusive Mentorship Ecosystem
An inclusive mentorship ecosystem integrates Mentorship and Reverse Mentorship to promote diverse perspectives, fostering professional growth across all levels by bridging generational and cultural gaps. This dynamic approach enhances organizational learning, drives innovation, and cultivates an equitable environment where knowledge flows bi-directionally between mentors and mentees.
Gen Z to C-Suite Pipeline
Mentorship programs that integrate reverse mentorship leverage Gen Z insights to accelerate leadership development within the C-Suite pipeline, fostering innovation and adaptability in executive decision-making. This dynamic exchange equips senior leaders with emerging digital trends and fresh perspectives while empowering younger employees with strategic organizational knowledge essential for professional growth.
Digital Natives Reverse Coaching
Digital Natives Reverse Coaching leverages the expertise of younger professionals to accelerate digital transformation in organizations, enhancing skills like social media strategy, data analytics, and emerging technologies among senior leaders. This reverse mentorship model fosters reciprocal learning, driving innovation and bridging generational gaps crucial for sustained professional growth.
Peer Upward Mentorship
Peer upward mentorship accelerates professional growth by empowering less experienced employees to share fresh perspectives and innovative ideas with senior colleagues, fostering mutual learning and organizational agility. This dynamic contrasts traditional mentorship by enabling junior peers to influence leadership decisions, enhancing collaboration and driving career development for both parties.
Mentorship vs Reverse Mentorship for professional growth Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com