Apprenticeship offers immersive, long-term job training with hands-on experience and sustained guidance, ideal for mastering complex skills. Micro-mentoring provides targeted, short-term advice or support, allowing quick insights and flexible learning for specific challenges. Combining both approaches maximizes skill development by balancing depth and agility in professional growth.
Table of Comparison
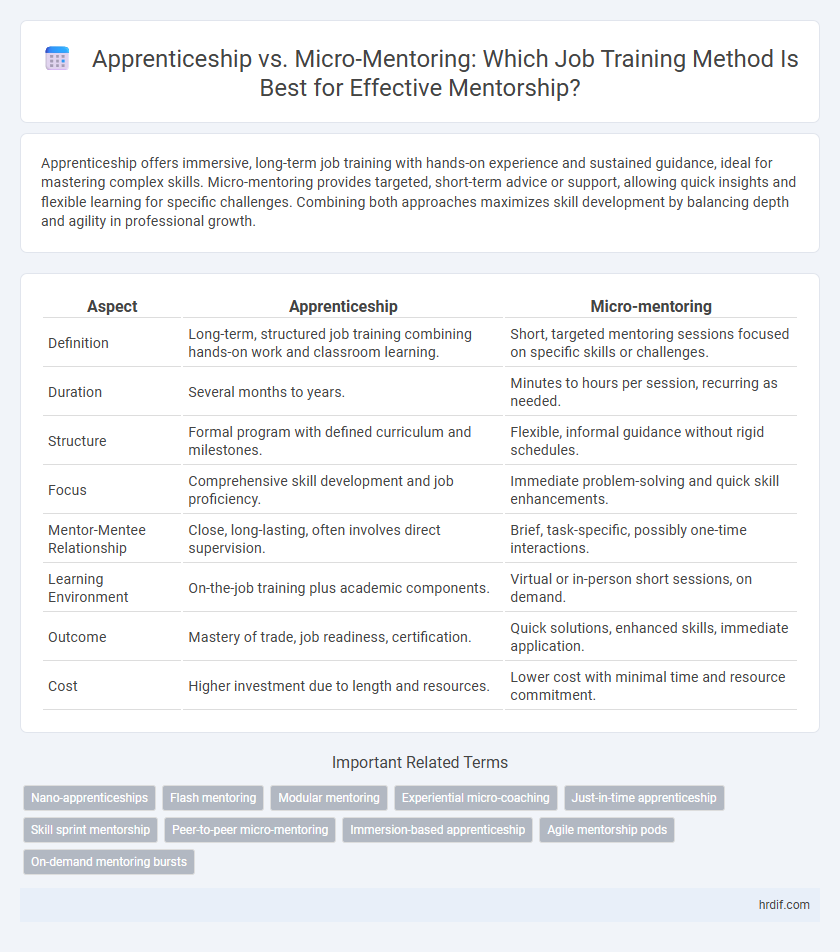
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Micro-mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term, structured job training combining hands-on work and classroom learning. | Short, targeted mentoring sessions focused on specific skills or challenges. |
| Duration | Several months to years. | Minutes to hours per session, recurring as needed. |
| Structure | Formal program with defined curriculum and milestones. | Flexible, informal guidance without rigid schedules. |
| Focus | Comprehensive skill development and job proficiency. | Immediate problem-solving and quick skill enhancements. |
| Mentor-Mentee Relationship | Close, long-lasting, often involves direct supervision. | Brief, task-specific, possibly one-time interactions. |
| Learning Environment | On-the-job training plus academic components. | Virtual or in-person short sessions, on demand. |
| Outcome | Mastery of trade, job readiness, certification. | Quick solutions, enhanced skills, immediate application. |
| Cost | Higher investment due to length and resources. | Lower cost with minimal time and resource commitment. |
Understanding Apprenticeship: Traditional Pathways to Skill Mastery
Apprenticeship represents a structured, long-term training approach where individuals gain comprehensive, hands-on experience under expert guidance, often spanning months to years. This traditional pathway emphasizes deep skill mastery and industry-specific knowledge, combining practical work with formal education. Unlike micro-mentoring's brief, focused interactions, apprenticeships involve sustained commitment, fostering thorough competence and professional development in a chosen trade or profession.
What is Micro-Mentoring? A Modern Approach to On-the-Job Learning
Micro-mentoring is a modern approach to on-the-job learning that emphasizes short, focused interactions between mentors and mentees, enabling quick skill acquisition and immediate application in the workplace. Unlike traditional apprenticeships, which involve long-term, structured training programs, micro-mentoring delivers targeted guidance through brief sessions, often leveraging digital platforms for flexibility and accessibility. This method supports continuous learning and rapid adaptation to evolving job requirements, making it an effective solution for fast-paced industries.
Key Benefits of Apprenticeship Programs in Career Development
Apprenticeship programs offer hands-on job training that combines practical experience with structured learning, significantly enhancing skill acquisition and workplace readiness. These programs foster long-term career growth by providing industry-recognized certifications and direct access to professional networks. Apprenticeships also improve employee retention and wage growth, making them a valuable investment for both individuals and employers in career development.
Advantages of Micro-Mentoring for Rapid Skill Acquisition
Micro-mentoring accelerates skill acquisition by delivering focused, bite-sized guidance tailored to specific job tasks, enabling learners to quickly apply new knowledge in real-world settings. Unlike traditional apprenticeships, micro-mentoring offers greater flexibility, allowing professionals to engage with experts on-demand without long-term commitments. This approach enhances accessibility and responsiveness, fostering continuous learning and immediate problem-solving in fast-paced work environments.
Apprenticeship vs. Micro-Mentoring: Comparing Learning Outcomes
Apprenticeship programs provide extended, hands-on training with in-depth skill development and long-term career growth, often resulting in stronger job proficiency and retention rates. Micro-mentoring offers targeted, short-term guidance that enhances specific competencies and quick problem-solving but may lack the comprehensive skill mastery seen in apprenticeships. Both approaches contribute to effective job training, with apprenticeships excelling in foundational expertise and micro-mentoring optimizing agile learning and immediate application.
Workplace Integration: How Each Model Fosters Professional Growth
Apprenticeship provides structured, long-term training with hands-on experience, enabling apprentices to deeply integrate into workplace culture and develop comprehensive skills under expert guidance. Micro-mentoring offers short, focused interactions aimed at addressing specific challenges or skill gaps, accelerating professional growth through targeted advice and flexible support. Both models enhance workplace integration by fostering practical learning and building confidence, but apprenticeships are better suited for sustained growth while micro-mentoring excels in rapid, situational development.
Duration and Structure: Time Commitment in Apprenticeship vs. Micro-Mentoring
Apprenticeships typically involve a long-term commitment spanning several months to years, offering structured, immersive training with comprehensive skill development. Micro-mentoring features short, focused engagements that usually last from a single session to a few weeks, allowing targeted guidance without extensive time investment. The significant difference in duration and structure between apprenticeships and micro-mentoring caters to varying levels of career development needs and availability of both mentors and mentees.
Accessibility and Flexibility: Which Suits Today’s Workforce Better?
Apprenticeships offer structured, long-term job training with comprehensive skill development but often require significant time commitment and geographic stability, limiting accessibility for many workers. Micro-mentoring provides flexible, bite-sized guidance accessible remotely, catering to diverse schedules and learning paces, making it more adaptable to the dynamic needs of today's workforce. Employers seeking scalable, on-demand skill-building solutions favor micro-mentoring for its convenience and broader reach.
Success Stories: Real-World Examples of Apprenticeship and Micro-Mentoring
Apprenticeship programs in industries like manufacturing and healthcare have consistently demonstrated high job placement rates, with companies such as Siemens reporting up to 90% employment for graduates. Micro-mentoring initiatives, exemplified by platforms like MentorcliQ, enable quick, targeted guidance that boosts employee skills and confidence in technology sectors. These success stories highlight how both apprenticeship and micro-mentoring drive workforce development by matching diverse skill-building needs across various job markets.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider for Effective Job Training
Apprenticeship offers structured, long-term training combining hands-on experience with formal education, ideal for complex skill development and industry certifications. Micro-mentoring provides flexible, short-term guidance focused on specific skills or challenges, making it suitable for rapid learning and immediate job performance improvements. Evaluating factors such as training duration, skill complexity, resource availability, and desired outcomes helps organizations select the most effective approach for job training.
Related Important Terms
Nano-apprenticeships
Nano-apprenticeships offer focused, short-term job training opportunities that combine the structured skill-building of traditional apprenticeships with the flexibility and scalability of micro-mentoring sessions. This hybrid model accelerates workforce readiness by providing targeted, hands-on experience and personalized guidance within a condensed timeframe.
Flash mentoring
Apprenticeship programs provide structured, long-term job training combining hands-on experience with formal education, whereas micro-mentoring, particularly flash mentoring, offers brief, targeted guidance sessions designed to quickly address specific skill gaps or career questions. Flash mentoring maximizes efficiency in mentorship by connecting mentees with experts for focused interactions, enhancing job readiness in a shorter timeframe compared to traditional apprenticeships.
Modular mentoring
Modular mentoring in job training offers a flexible, task-focused approach compared to traditional apprenticeships by breaking skills development into manageable, targeted sessions that address specific competencies. This method enhances adaptability, allowing mentees to gain practical expertise quickly while aligning training modules with evolving industry demands.
Experiential micro-coaching
Experiential micro-coaching in job training emphasizes short, targeted interactions that deliver immediate, practical skill development, making it more adaptable and scalable than traditional apprenticeships. Unlike apprenticeships' long-term commitment, micro-mentoring leverages real-time feedback and situational learning to accelerate career readiness through focused, experience-based guidance.
Just-in-time apprenticeship
Just-in-time apprenticeship delivers targeted, real-time job training by embedding learners directly within workflow, contrasting with micro-mentoring's brief, often generalized guidance sessions. This approach accelerates skill acquisition through hands-on experience and immediate application, optimizing workforce readiness and adaptability.
Skill sprint mentorship
Skill sprint mentorship offers focused, short-term coaching that accelerates skill acquisition through targeted challenges, contrasting with the longer, immersive learning experience of traditional apprenticeships. This micro-mentoring approach emphasizes rapid competency development, making it ideal for dynamic job training environments where specific expertise is needed quickly.
Peer-to-peer micro-mentoring
Peer-to-peer micro-mentoring offers job trainees targeted, real-time guidance through short, focused interactions that accelerate skill development compared to the longer, structured format of traditional apprenticeships. This approach enhances practical learning and fosters collaborative knowledge exchange among peers, optimizing workforce readiness with flexible, scalable support.
Immersion-based apprenticeship
Immersion-based apprenticeship provides extended, hands-on experience within a real work environment, enabling deep skill acquisition and professional growth over time. Micro-mentoring, by contrast, offers brief, targeted guidance sessions that support immediate problem-solving but lack the comprehensive exposure of apprenticeship models.
Agile mentorship pods
Apprenticeship offers extensive, hands-on job training through long-term, immersive experiences, while micro-mentoring within Agile mentorship pods emphasizes targeted, time-efficient guidance for rapid skill acquisition. Agile mentorship pods leverage collaborative, cross-functional teams to facilitate dynamic feedback loops, accelerating professional growth and adaptability in fast-paced environments.
On-demand mentoring bursts
Apprenticeship provides long-term, structured job training with comprehensive skill development, while micro-mentoring delivers on-demand mentoring bursts tailored to specific challenges or tasks. On-demand mentoring bursts enhance workforce agility by offering targeted, time-efficient guidance that accelerates problem-solving and skill acquisition.
Apprenticeship vs Micro-mentoring for job training Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com