Command-and-control leaders rely on strict oversight and clear directives, which may stifle creativity and reduce employee engagement. Coaching leaders foster a supportive environment by encouraging personal growth and open communication, leading to higher motivation and commitment. Emphasizing collaboration over control enhances trust and drives long-term performance improvement.
Table of Comparison
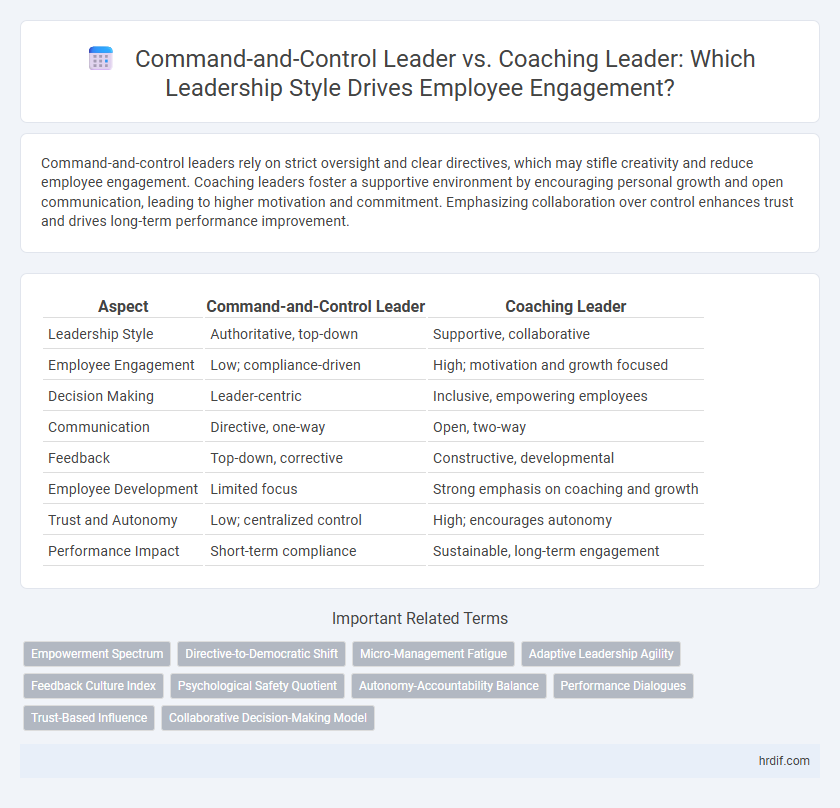
| Aspect | Command-and-Control Leader | Coaching Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, top-down | Supportive, collaborative |
| Employee Engagement | Low; compliance-driven | High; motivation and growth focused |
| Decision Making | Leader-centric | Inclusive, empowering employees |
| Communication | Directive, one-way | Open, two-way |
| Feedback | Top-down, corrective | Constructive, developmental |
| Employee Development | Limited focus | Strong emphasis on coaching and growth |
| Trust and Autonomy | Low; centralized control | High; encourages autonomy |
| Performance Impact | Short-term compliance | Sustainable, long-term engagement |
Understanding Command-and-Control Leadership
Command-and-control leadership relies on hierarchical authority and strict adherence to rules, often limiting employee autonomy and stifling creativity. This leadership style typically results in lower employee engagement, as workers feel undervalued and disconnected from decision-making processes. Organizations seeking higher engagement should recognize the constraints of command-and-control methods and consider more participative approaches.
The Coaching Leadership Approach Defined
The Coaching Leadership Approach fosters employee engagement by emphasizing personalized development, active listening, and collaborative problem-solving. Unlike Command-and-Control leaders who rely on authority and top-down directives, coaching leaders build trust and empower employees to take initiative, enhancing motivation and productivity. This leadership style drives sustained performance improvements by aligning individual goals with organizational objectives through continuous feedback and support.
Key Differences Between Command-and-Control and Coaching Leaders
Command-and-control leaders prioritize authority and top-down directives, often limiting employee autonomy and stifling engagement through rigid oversight. In contrast, coaching leaders foster open communication, support skill development, and empower employees to take ownership, driving higher motivation and commitment. The key difference lies in command-and-control's focus on compliance versus coaching leadership's emphasis on collaboration and personal growth.
Impact on Employee Engagement: Command-and-Control Style
The command-and-control leadership style often results in lower employee engagement due to its rigid structure and emphasis on authority, which can stifle creativity and autonomy. Employees under this style may feel undervalued and less motivated, leading to decreased job satisfaction and higher turnover rates. Research indicates that such leaders typically struggle to foster trust and open communication, key factors in driving sustained employee engagement.
How Coaching Leaders Drive Employee Engagement
Coaching leaders drive employee engagement by fostering a supportive environment that encourages professional growth and open communication. They prioritize active listening, personalized feedback, and empowerment, which boosts motivation and commitment among team members. This approach contrasts with command-and-control leadership, resulting in higher employee satisfaction and retention rates.
Communication Styles: Directive vs. Collaborative
Command-and-control leaders use directive communication styles, issuing clear instructions and expecting compliance, which can limit employee creativity and reduce engagement. Coaching leaders adopt collaborative communication, encouraging open dialogue and active participation, fostering trust and higher motivation. This shift toward collaboration enhances employee involvement and promotes a positive workplace culture.
Trust and Autonomy in the Workplace
Command-and-control leaders often hinder employee engagement by limiting trust and restricting autonomy, creating a work environment where employees feel micromanaged and undervalued. Coaching leaders foster higher trust levels by empowering employees through autonomy, encouraging open communication, and supporting personal growth. This leadership style enhances motivation, collaboration, and overall workplace satisfaction, driving better performance and retention.
Performance, Motivation, and Retention Compared
Command-and-control leaders often rely on strict oversight and directive communication, which can hinder performance by limiting employee autonomy and motivation. In contrast, coaching leaders foster a supportive environment that enhances motivation through personalized development, leading to higher engagement and improved retention rates. Studies reveal organizations with coaching leadership styles report increased employee productivity and a 25% lower turnover compared to those dominated by command-and-control approaches.
Adapting Leadership Styles for Modern Workplaces
Command-and-control leaders often face challenges in employee engagement due to their rigid structures and limited empowerment. Coaching leaders foster higher engagement by encouraging autonomy, active feedback, and personal development aligned with modern workplace values. Adapting leadership styles to incorporate coaching principles enhances motivation, innovation, and collaboration in dynamic organizational environments.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Your Team
Command-and-control leadership often limits employee autonomy, reducing engagement and innovation. Coaching leadership fosters open communication and personal growth, significantly boosting motivation and productivity. Selecting a leadership style aligned with team needs enhances collaboration and drives sustainable success.
Related Important Terms
Empowerment Spectrum
Command-and-Control leaders often limit employee engagement by focusing on strict directives, reducing autonomy and empowerment within the workforce. Coaching leaders enhance engagement by fostering development and autonomy, positioning employees higher on the empowerment spectrum, which drives motivation and performance.
Directive-to-Democratic Shift
A command-and-control leader prioritizes strict adherence to rules and top-down directives, often limiting employee autonomy and engagement. Transitioning to a coaching leader fosters a democratic environment by encouraging collaboration, personalized feedback, and empowerment, significantly enhancing employee motivation and commitment.
Micro-Management Fatigue
Command-and-control leaders often cause micro-management fatigue by excessively monitoring and controlling employees, leading to decreased engagement and motivation. Coaching leaders foster higher employee engagement by empowering staff, encouraging autonomy, and providing constructive feedback, which reduces stress and burnout associated with micro-management.
Adaptive Leadership Agility
Command-and-control leaders rely on rigid structures and top-down directives, limiting employee engagement and stifling innovation, whereas coaching leaders employ adaptive leadership agility by fostering collaboration, empowering teams, and encouraging continuous learning to enhance engagement and drive performance. Adaptive leadership agility enables coaching leaders to respond dynamically to employee needs and organizational changes, creating an environment where engagement thrives through trust and shared decision-making.
Feedback Culture Index
Command-and-Control leaders often hinder employee engagement by limiting open communication and suppressing feedback, resulting in a lower Feedback Culture Index. In contrast, Coaching leaders foster a positive feedback culture by encouraging continuous dialogue and employee development, significantly boosting engagement scores.
Psychological Safety Quotient
Command-and-control leaders often undermine employee engagement by limiting psychological safety quotient, as their rigid structures inhibit open communication and risk-taking. In contrast, coaching leaders enhance psychological safety by fostering trust, encouraging feedback, and supporting personal growth, which significantly boosts employee engagement and innovation.
Autonomy-Accountability Balance
Command-and-control leaders often restrict employee autonomy, resulting in lower engagement and reduced accountability as employees may feel micromanaged and disengaged. Coaching leaders foster a balanced environment where autonomy is encouraged alongside accountability, leading to higher employee motivation and sustained engagement through empowerment and trust.
Performance Dialogues
Command-and-Control leaders often limit employee engagement by enforcing rigid performance dialogues that emphasize compliance over development, resulting in reduced motivation and creativity. Coaching leaders enhance engagement through collaborative performance dialogues that focus on growth, feedback, and individualized support, fostering higher employee commitment and improved outcomes.
Trust-Based Influence
Command-and-control leadership often limits employee engagement by enforcing strict directives that suppress autonomy and reduce trust, whereas coaching leadership fosters trust-based influence through active listening and personalized feedback, enhancing motivation and collaboration. Employees under coaching leaders experience higher trust levels, leading to increased commitment, creativity, and overall performance.
Collaborative Decision-Making Model
The Collaborative Decision-Making Model enhances employee engagement by shifting leadership from a Command-and-Control style, characterized by top-down directives, to a Coaching Leader approach that fosters open communication and shared responsibility. This model empowers employees through active participation in decision processes, boosting motivation, accountability, and overall workplace satisfaction.
Command-and-Control Leader vs Coaching Leader for employee engagement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com