Internship programs offer immersive, hands-on experience within a professional work environment, allowing interns to develop industry-specific skills and build networks. Project-based placements focus on completing targeted tasks or assignments, providing practical exposure to particular challenges but often with limited interaction in the broader workplace. Choosing between internships and project-based placements depends on the desired depth of learning and level of engagement with real-world business processes.
Table of Comparison
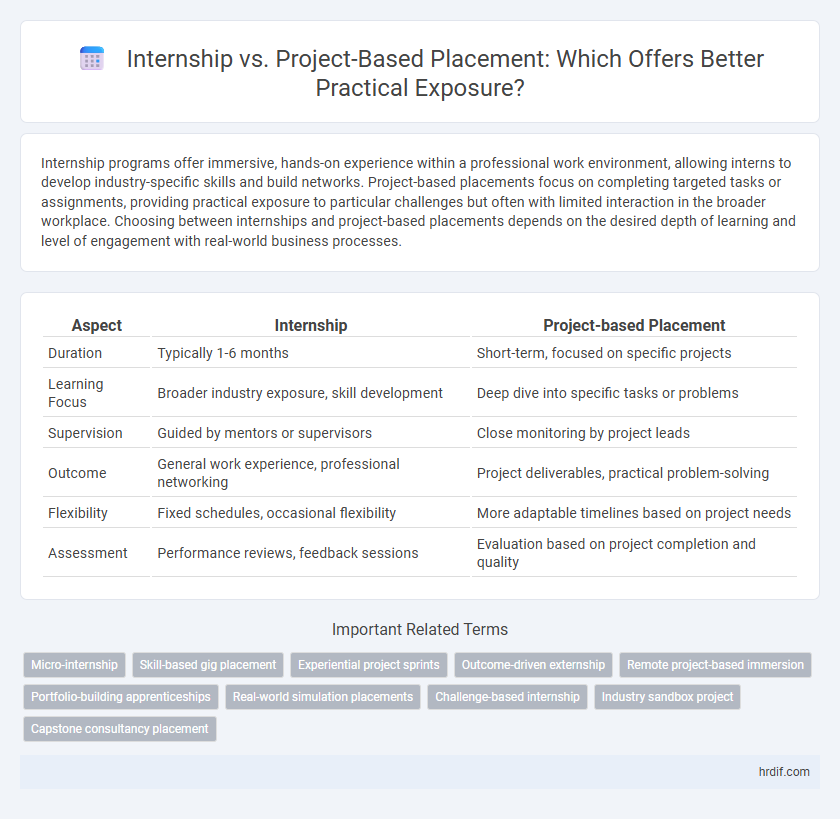
| Aspect | Internship | Project-based Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Typically 1-6 months | Short-term, focused on specific projects |
| Learning Focus | Broader industry exposure, skill development | Deep dive into specific tasks or problems |
| Supervision | Guided by mentors or supervisors | Close monitoring by project leads |
| Outcome | General work experience, professional networking | Project deliverables, practical problem-solving |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedules, occasional flexibility | More adaptable timelines based on project needs |
| Assessment | Performance reviews, feedback sessions | Evaluation based on project completion and quality |
Introduction: Understanding Practical Exposure in Careers
Internship programs provide structured, real-world work experience within a company, enabling students to develop industry-specific skills and professional networks. Project-based placements focus on completing targeted assignments that simulate practical challenges, fostering problem-solving and technical expertise. Both methods enhance career readiness by offering hands-on learning, though internships often provide broader organizational insights compared to the task-oriented nature of project-based work.
Defining Internships: Structure and Purpose
Internships are structured, time-bound programs designed to provide students or entry-level professionals with hands-on experience within a real-world work environment, often lasting from a few weeks to several months. They focus on comprehensive skill development, professional networking, and understanding workplace culture, bridging academic knowledge and practical application. Unlike project-based placements, internships offer broader exposure through diverse tasks, mentoring, and performance feedback, emphasizing holistic career growth.
What are Project-Based Placements?
Project-based placements involve students or interns working on specific, real-world projects within an organization, allowing hands-on experience and direct application of academic knowledge to practical challenges. Unlike general internships, these placements focus on delivering tangible outcomes or solutions, fostering skills such as problem-solving, teamwork, and industry-specific technical expertise. This immersive approach enhances practical exposure by aligning tasks closely with professional standards and project timelines.
Skill Development: Internship vs Project-Based Placement
Internships provide hands-on industry experience by immersing students in real workplace environments, fostering adaptive skills and professional networking. Project-based placements emphasize deep knowledge acquisition and problem-solving through focused, goal-oriented tasks that simulate specific job functions. Both methods enhance skill development, with internships promoting holistic workplace competencies and project-based placements sharpening technical expertise.
Industry Networking Opportunities
Internships offer extensive industry networking opportunities by placing students within professional environments where they interact directly with mentors, colleagues, and industry leaders. Project-based placements typically focus on task completion with limited exposure to broader organizational dynamics and fewer chances to build lasting professional relationships. The immersive nature of internships facilitates valuable connections that often lead to job offers and career growth.
Flexibility and Time Commitment Compared
Internship programs typically offer structured schedules with fixed durations, providing consistent practical exposure aligned with academic calendars. Project-based placements allow greater flexibility, enabling students to tailor time commitments according to project complexity and personal availability. Time commitment in internships is often more rigid, while project-based placements accommodate variable hours, making them suitable for individuals seeking adaptable learning experiences.
Evaluation and Feedback Mechanisms
Internship programs offer structured evaluation and continuous feedback from supervisors, enhancing real-world skill development through direct workplace interaction. Project-based placements provide targeted assessment based on specific deliverables, enabling precise measurement of task completion and technical proficiency. Effective feedback mechanisms in both formats are crucial for refining practical competencies and preparing candidates for professional challenges.
Long-term Career Impact
Internships provide structured industry experience, fostering professional networks and real-world problem-solving skills critical for long-term career growth. Project-based placements emphasize specific task completion and technical skills development, which may limit exposure to broader workplace dynamics and mentorship opportunities. Prioritizing internships often leads to stronger career trajectories due to comprehensive skill acquisition and industry integration.
Which Option Suits Your Career Goals?
Choosing between an internship and a project-based placement depends on your career goals and desired practical exposure. Internships offer broad experience through varied tasks and networking opportunities, ideal for exploring different roles within an industry. Project-based placements focus on specific skills and deliverables, suitable for building specialized expertise and a targeted portfolio.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Practical Experience
Internships provide immersive, hands-on experience within a professional environment, fostering industry-specific skills and networking opportunities. Project-based placements, while offering focused skill development on particular tasks, may lack the broader organizational context that internships deliver. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize comprehensive workplace exposure or targeted skill acquisition for practical learning.
Related Important Terms
Micro-internship
Micro-internships provide focused, short-term practical exposure by allowing students to complete specific tasks within a project-based framework, enhancing skill application and real-world experience more effectively than traditional long-term internships. These bite-sized engagements enable flexible learning opportunities aligned with industry demands, making them a strategic alternative for gaining targeted professional insights.
Skill-based gig placement
Skill-based gig placements offer targeted, real-world tasks that enhance specific competencies more effectively than traditional internships or project-based placements, which often provide broader but less specialized experience. This focused approach accelerates practical skill development and portfolio building, aligning closely with industry demands for job-ready professionals.
Experiential project sprints
Experiential project sprints in internships offer immersive, hands-on learning opportunities that accelerate skill acquisition compared to traditional project-based placements. These focused, time-bound projects simulate real-world challenges, fostering rapid professional growth and practical expertise.
Outcome-driven externship
Outcome-driven externships emphasize real-world skill acquisition and measurable professional growth, often surpassing traditional internships by providing targeted project-based placements that deliver concrete results and industry-relevant experience. Selecting an externship centered on specific deliverables ensures enhanced employability by aligning practical exposure with career objectives and employer expectations.
Remote project-based immersion
Remote project-based immersion offers targeted, real-world experience by allowing interns to engage with specific tasks and deliverables within a flexible schedule, enhancing skill application and portfolio development. Unlike traditional internships, this model prioritizes outcome-driven learning and autonomy, making it ideal for gaining practical exposure in digital and global work environments.
Portfolio-building apprenticeships
Internship programs offer hands-on experience through real-world tasks that enhance practical skills, while project-based placements focus on specific deliverables, providing targeted expertise and measurable outcomes. Portfolio-building apprenticeships combine both approaches, enabling apprentices to develop a diverse collection of work samples that demonstrate competencies to potential employers.
Real-world simulation placements
Internship programs offer immersive real-world simulation placements that enable students to gain hands-on experience through day-to-day operational roles, fostering practical skills and professional networking. In contrast, project-based placements focus on specific tasks or deliverables, providing targeted skill development but with less exposure to continuous workplace dynamics and problem-solving challenges.
Challenge-based internship
Challenge-based internships provide immersive real-world problem-solving experiences that surpass traditional project-based placements by enhancing critical thinking and adaptability under dynamic conditions. Interns engage directly with complex challenges, fostering deeper industry insights and practical skills essential for professional growth in competitive environments.
Industry sandbox project
Internship programs provide structured, real-world industry sandbox projects that offer comprehensive practical exposure by immersing students in actual work environments, enhancing skills through direct collaboration and problem-solving. Project-based placements often focus on specific tasks with limited scope, whereas internships deliver broader industry insights, professional networking, and hands-on experience vital for career readiness.
Capstone consultancy placement
Capstone consultancy placements provide deeper practical exposure by integrating real-world client challenges into the learning process, unlike traditional internships that may focus on routine tasks. Project-based placements emphasize applied problem-solving skills and strategic thinking, making them more aligned with industry demands and enhancing professional readiness.
Internship vs Project-based placement for practical exposure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com