Internships provide structured learning opportunities with mentorship and skill development tailored to specific industries, offering valuable professional connections and career growth potential. Gig work offers flexible project-based experience and immediate income but may lack consistent guidance and long-term skill-building benefits. Choosing between an internship and gig work depends on individual goals for experience depth, networking, and career trajectory.
Table of Comparison
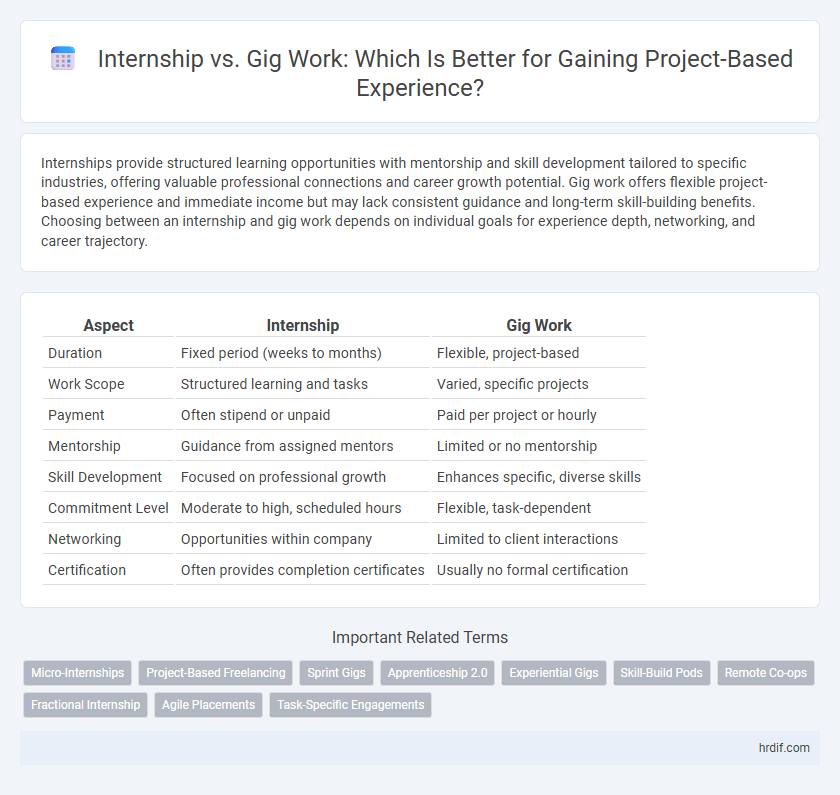
| Aspect | Internship | Gig Work |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Fixed period (weeks to months) | Flexible, project-based |
| Work Scope | Structured learning and tasks | Varied, specific projects |
| Payment | Often stipend or unpaid | Paid per project or hourly |
| Mentorship | Guidance from assigned mentors | Limited or no mentorship |
| Skill Development | Focused on professional growth | Enhances specific, diverse skills |
| Commitment Level | Moderate to high, scheduled hours | Flexible, task-dependent |
| Networking | Opportunities within company | Limited to client interactions |
| Certification | Often provides completion certificates | Usually no formal certification |
Defining Internship and Gig Work in the Modern Job Market
Internships offer structured, often longer-term project-based learning experiences within established companies, providing mentorship, skill development, and potential pathways to full-time employment. Gig work, characterized by short-term, flexible assignments or freelance projects, delivers hands-on experience across diverse tasks without formal organizational ties. Both models enhance project-based expertise but differ in commitment, learning environment, and professional networking opportunities.
Key Differences Between Internships and Gig Work
Internships offer structured, often longer-term learning experiences with mentorship, while gig work involves short-term, flexible projects without formal guidance. Internships typically provide comprehensive skill development and resume-building through consistent tasks related to a specific career field. Gig work focuses on immediate deliverables, paying per project, and lacks the educational components found in traditional internships.
Skills Gained: Internship vs Gig Project Work
Internships provide structured skill development through mentorship and exposure to company processes, enhancing teamwork, communication, and industry-specific expertise. Gig project work offers hands-on, diverse experience with rapid adaptation to varied client requirements and autonomous problem-solving skills. Both pathways cultivate practical abilities, but internships often emphasize professional growth within organizational frameworks, while gig work prioritizes flexibility and self-directed learning.
Flexibility and Time Commitment Comparison
Internships typically require a fixed time commitment, ranging from several weeks to months, with structured schedules designed for comprehensive learning experiences. Gig work offers greater flexibility, allowing individuals to choose projects and set their own hours, which benefits those needing adaptable work arrangements. However, internships provide consistent, immersive engagement ideal for in-depth skill development, while gigs emphasize short-term, task-specific expertise.
Networking Opportunities: Which Path Opens More Doors?
Internships provide structured networking opportunities through company events, mentorship, and team collaborations, fostering long-term professional relationships. Gig work offers diverse project experiences with clients across industries, expanding contacts but often limiting deeper connections. For sustained career growth, internships typically open more doors by facilitating consistent interaction within a professional network.
Mentorship and Guidance: Structured vs Self-Directed Learning
Internships provide structured mentorship and guidance, enabling interns to receive personalized feedback and develop skills through supervised project-based experiences. Gig work relies on self-directed learning, requiring individuals to independently navigate tasks without consistent access to expert advice or formal training. The presence of dedicated mentors in internships facilitates deeper professional growth compared to the autonomous nature of gig projects.
Compensation and Financial Considerations
Internship compensation often includes a fixed stipend or hourly wage with potential benefits, providing financial stability during project-based experience. Gig work typically offers variable pay based on individual task completion, which can lead to inconsistent earnings and less financial predictability. Evaluating compensation structures is crucial when choosing between internships and gig work for sustainable income in project-based roles.
Resume Value: How Employers View Internships vs Gigs
Internships provide structured learning environments with mentorship, making them highly valuable on resumes as evidence of teamwork and industry-specific skills. Gig work demonstrates initiative, adaptability, and real-world problem-solving, appealing to employers seeking independent and diverse project experience. However, internships are often perceived as more credible due to formal evaluation and consistent scope, enhancing candidates' professional reputation.
Long-Term Career Impact and Advancement Prospects
Internships offer structured learning environments with mentorship, fostering skill development and networking opportunities that enhance long-term career growth. Gig work provides flexible project-based experience but often lacks consistent guidance and formal recognition, potentially limiting advancement prospects. Employers frequently value internships for demonstrating commitment and adaptability, which translate into stronger career trajectories.
Choosing the Right Project-Based Experience for Your Career Goals
Selecting between internships and gig work for project-based experience depends on your career objectives and desired skill development. Internships typically offer structured learning environments, mentorship, and industry exposure crucial for long-term career growth. Gig work provides flexibility and diverse project opportunities, allowing you to quickly build a varied portfolio and adapt to different client demands.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Internships
Micro-internships offer structured, project-based experiences with clear learning objectives, providing more targeted skill development compared to gig work's often fragmented and transactional tasks. These short-term, supervised assignments enable interns to build relevant portfolios and receive feedback, enhancing employability within industries seeking practical, verifiable experience.
Project-Based Freelancing
Project-based freelancing offers flexible, diverse opportunities for hands-on experience across multiple industries, enabling interns to develop specialized skills and build a robust portfolio independently. Unlike traditional internships, gig work emphasizes short-term, outcome-driven projects that enhance adaptability and real-world problem-solving abilities in fast-paced environments.
Sprint Gigs
Internships offer structured learning environments with mentorship, while Sprint Gigs provide flexible, project-based work enabling rapid skill application and portfolio growth. Sprint Gigs facilitate real-world experience through short-term, high-impact projects ideal for career agility and diverse industry exposure.
Apprenticeship 2.0
Internship programs offer structured learning environments with mentorship and skill development tailored to long-term career growth, whereas gig work provides flexible, short-term projects that emphasize immediate task completion without consistent guidance. Apprenticeship 2.0 blends these models by integrating project-based experiences with ongoing mentorship, enabling apprentices to acquire practical skills through real-world tasks while receiving continuous professional support.
Experiential Gigs
Experiential gigs offer flexible, project-based opportunities allowing individuals to develop specialized skills and build diverse portfolios without long-term commitments typical of internships. These gigs provide real-world exposure and hands-on experience, often leading to faster skill acquisition and adaptability in dynamic work environments.
Skill-Build Pods
Skill-Build Pods enhance project-based experience by offering structured internships that provide mentorship, goal-oriented learning, and real-world application, unlike gig work which often lacks continuity and skill development pathways. Internships through Skill-Build Pods cultivate in-depth expertise and professional growth, making them more effective for building a comprehensive skill set compared to the task-specific nature of gig work.
Remote Co-ops
Remote co-op internships provide structured learning environments with mentorship and skill development opportunities, whereas gig work offers flexibility and varied project exposure but often lacks formal guidance and long-term career progression. Prioritizing remote co-ops enhances professional growth through consistent feedback and industry-relevant experience, making them ideal for building a comprehensive project-based portfolio.
Fractional Internship
Fractional internships offer flexible, project-based experience similar to gig work but provide structured mentorship and skill development within a professional setting. Unlike gig work, fractional internships enhance long-term career growth by integrating real-world projects with personalized feedback and networking opportunities.
Agile Placements
Internship programs offer structured project-based experience with mentorship and skill development tailored to Agile placements, enhancing long-term career growth in agile environments. Gig work provides flexible, short-term Agile projects but often lacks the comprehensive training and collaborative learning found in internships.
Task-Specific Engagements
Internships provide structured learning environments with mentorship and skill development, offering comprehensive exposure to company workflows, while gig work emphasizes task-specific engagements allowing flexibility and immediate application of specialized skills. Project-based experience in internships often involves collaborative objectives and long-term goals, contrasting with gig assignments that target discrete, short-term deliverables tailored to specific client needs.
Internship vs Gig work for project-based experience. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com