Internships offer extended, immersive work experience, allowing individuals to develop in-depth skills and build professional relationships over weeks or months. Micro-internships provide short-term, project-based tasks that deliver quick, focused exposure to specific job functions and industries. Both formats enhance work readiness, but micro-internships offer greater flexibility and faster insights into career fit.
Table of Comparison
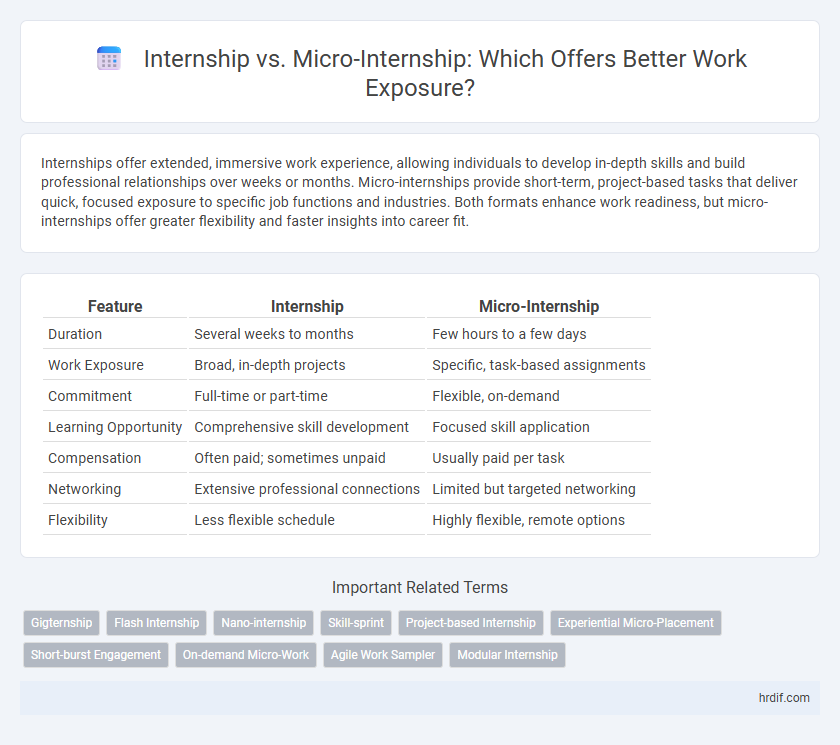
| Feature | Internship | Micro-Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Several weeks to months | Few hours to a few days |
| Work Exposure | Broad, in-depth projects | Specific, task-based assignments |
| Commitment | Full-time or part-time | Flexible, on-demand |
| Learning Opportunity | Comprehensive skill development | Focused skill application |
| Compensation | Often paid; sometimes unpaid | Usually paid per task |
| Networking | Extensive professional connections | Limited but targeted networking |
| Flexibility | Less flexible schedule | Highly flexible, remote options |
Understanding Traditional Internships
Traditional internships provide extended work exposure by allowing interns to engage deeply in projects, often lasting several months and offering hands-on experience in a professional environment. These internships enable students to develop industry-specific skills, build professional networks, and gain a comprehensive understanding of workplace dynamics. The structured nature of traditional internships contrasts with shorter micro-internships, which are typically project-based and last a few days to weeks.
Defining Micro-internships
Micro-internships are short-term, project-based work assignments that typically last from a few hours to a few weeks, designed to provide practical experience without the time commitment of traditional internships. Unlike traditional internships, which often require extended periods and structured roles within organizations, micro-internships offer flexible, skill-specific tasks that allow students and early-career professionals to build portfolios and gain diverse industry exposure. Companies benefit from micro-internships by accessing a broad pool of talent for immediate projects, enhancing recruitment efficiency and workforce agility.
Key Differences Between Internships and Micro-internships
Internships typically last several months and provide comprehensive work experience, allowing interns to develop skills through long-term projects and mentorship in a structured environment. Micro-internships are short-term, task-based assignments lasting from a few hours to a few weeks, offering quick exposure to specific job functions without extended commitment. The key differences lie in duration, depth of learning, and level of engagement, with internships focused on broad professional development and micro-internships emphasizing flexibility and targeted skill application.
Benefits of Traditional Internships for Career Growth
Traditional internships provide extensive, hands-on experience in a professional setting, allowing interns to build long-term relationships with industry mentors and develop a deeper understanding of company culture. These internships often offer structured learning opportunities and access to comprehensive projects, enhancing skill development and boosting a competitive resume. Employers frequently view traditional internships as a strong indicator of commitment and practical expertise, which can significantly improve career prospects.
Advantages of Micro-internships for Skill Development
Micro-internships offer targeted, short-term projects that enable rapid skill development by providing hands-on experience in specific areas such as data analysis, digital marketing, or coding. These micro-experiences allow interns to build a diverse portfolio while adapting quickly to various professional environments, enhancing both technical and soft skills. The flexibility and focused nature of micro-internships make them ideal for gaining practical expertise and improving employability in a competitive job market.
Duration and Commitment: Internship vs Micro-internship
Internships typically require a longer duration, often spanning several weeks to months, demanding a significant time commitment from participants. In contrast, micro-internships offer short-term engagements lasting a few days to a couple of weeks, providing flexible opportunities for quick skill acquisition and work exposure. This shorter commitment makes micro-internships ideal for students or professionals seeking practical experience without a long-term obligation.
Application Process and Selection Criteria
Internship application processes typically involve submitting detailed resumes, cover letters, and sometimes portfolios, followed by interviews and assessments to evaluate candidates' skills and fit. Micro-internships, being shorter and project-based, often require streamlined applications with quick submissions and may prioritize specific skill sets or task-related competencies. Selection criteria for internships emphasize academic background, experience, and long-term potential, whereas micro-internships focus on immediate skill applicability, availability, and the ability to deliver results in condensed timeframes.
Types of Projects and Roles Offered
Internships typically offer long-term projects with in-depth responsibilities, allowing interns to engage in comprehensive tasks and gain substantial industry experience. Micro-internships provide short-term, specific assignments that focus on particular skills or tasks, making them ideal for quick exposure and skill diversification. The roles in traditional internships often involve collaborative team efforts, while micro-internships emphasize independent project completion and targeted outcomes.
Impact on Resume and Future Job Prospects
Traditional internships provide comprehensive work experience, often leading to stronger resume entries through extended project involvement and skill development. Micro-internships offer concise, task-oriented experiences that highlight adaptability and quick learning, appealing to employers seeking immediate impact. Both formats enhance future job prospects but serve different needs: internships build deep expertise while micro-internships demonstrate versatility and initiative.
Choosing the Right Opportunity: Internship or Micro-internship
Internships provide comprehensive work experience through extended projects and team collaboration, allowing interns to deeply develop industry-specific skills and professional networks. Micro-internships offer short-term, project-based tasks ideal for gaining quick exposure and testing different career paths without long-term commitment. Choosing between internship and micro-internship depends on your career goals, time availability, and desire for in-depth learning versus flexible, diverse experiences.
Related Important Terms
Gigternship
Gigternships offer a flexible, project-based alternative to traditional internships, allowing individuals to gain targeted work exposure in shorter time frames and diverse industries. Unlike micro-internships, which are typically brief and task-specific, Gigternships blend comprehensive skill application with real-world experience, enhancing professional growth and portfolio development.
Flash Internship
Flash internships offer a condensed, project-based work exposure that contrasts with traditional internships by providing real-world experience in a shorter timeframe, typically lasting a few days to weeks. These micro-internships enable students and early-career professionals to rapidly develop specific skills and build their portfolios through targeted, outcome-driven tasks aligned with Flash Internship programs.
Nano-internship
Nano-internships offer brief, project-based work experiences that provide immediate skill application and targeted exposure, contrasting with traditional internships that demand longer commitments and broader responsibilities. These micro-internships deliver flexible opportunities for real-world engagement, making them ideal for quickly building a focused resume and gaining specific industry insights.
Skill-sprint
Micro-internships offer a condensed, skill-sprint approach to work exposure, enabling students to quickly develop specific competencies through short-term, project-based tasks. Traditional internships provide broader, long-term experiential learning but may lack the intense focus and immediate skill application that micro-internships emphasize for rapid professional growth.
Project-based Internship
Project-based internships offer focused, hands-on experience by completing specific assignments within a set timeframe, allowing interns to develop practical skills and showcase tangible outcomes. In contrast, micro-internships provide short-term, task-oriented opportunities that deliver quick insights but often lack the depth and comprehensive exposure found in project-based internships.
Experiential Micro-Placement
Experiential micro-placements offer focused work exposure through short-term, skill-specific projects that provide immediate, practical experience, contrasting traditional internships often longer in duration with broader responsibilities. These micro-internships optimize learning efficiency and resume impact by immersing participants in real-world tasks aligned with industry demands.
Short-burst Engagement
Internships typically involve longer commitments ranging from several weeks to months, providing in-depth industry experience, while micro-internships offer short-burst engagement of a few days to weeks, allowing rapid skill application and diverse project exposure. Micro-internships serve as flexible, low-risk opportunities for students to build resumes and gain practical work experience without the extensive time commitment of traditional internships.
On-demand Micro-Work
Internships traditionally offer extended work experience but often require long-term commitments, while on-demand micro-internships provide flexible, short-term projects that deliver immediate, targeted skills and industry exposure. Micro-internships leverage digital platforms to connect candidates with real-world tasks, enhancing employability through practical, resume-building experiences in a condensed timeframe.
Agile Work Sampler
Agile Work Sampler offers a focused micro-internship experience that delivers concentrated, real-world projects within a shorter timeframe compared to traditional internships, enhancing skill acquisition and professional adaptability. This approach maximizes work exposure by providing targeted, outcome-driven tasks, allowing interns to demonstrate competencies and receive immediate feedback in a dynamic work environment.
Modular Internship
Modular internships offer flexible work exposure through short, focused projects that provide targeted skill development compared to traditional internships, which often require longer commitments. Micro-internships prioritize specific tasks with immediate impact, while modular internships blend structured learning with practical experience in manageable segments.
Internship vs Micro-internship for work exposure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com