Internships typically provide short-term, practical work experience that complements academic learning without requiring extensive time commitments, making them suitable for students seeking flexibility. Co-op programs integrate multiple work terms into the academic curriculum, allowing students to alternate semesters of study with full-time employment, fostering deeper industry immersion and skill development. This structured approach enhances academic integration by aligning work experience with coursework, resulting in a cohesive learning journey.
Table of Comparison
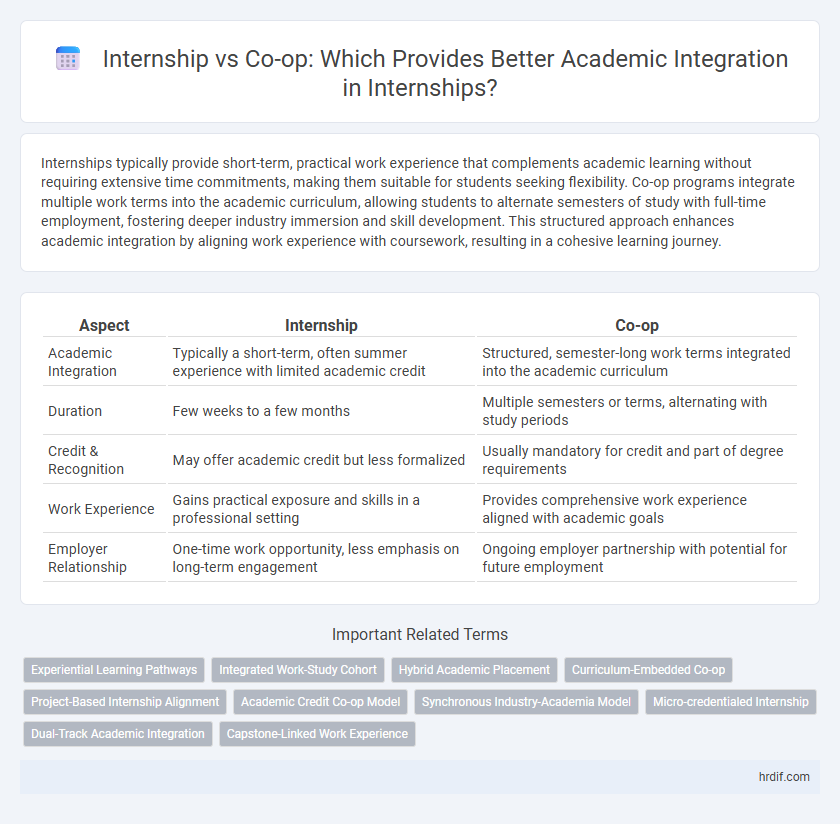
| Aspect | Internship | Co-op |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Integration | Typically a short-term, often summer experience with limited academic credit | Structured, semester-long work terms integrated into the academic curriculum |
| Duration | Few weeks to a few months | Multiple semesters or terms, alternating with study periods |
| Credit & Recognition | May offer academic credit but less formalized | Usually mandatory for credit and part of degree requirements |
| Work Experience | Gains practical exposure and skills in a professional setting | Provides comprehensive work experience aligned with academic goals |
| Employer Relationship | One-time work opportunity, less emphasis on long-term engagement | Ongoing employer partnership with potential for future employment |
Understanding Internships and Co-ops
Internships provide short-term, practical work experience often completed during academic breaks, allowing students to apply classroom knowledge in real-world settings. Co-ops integrate academic coursework with multiple work terms, extending over longer periods and typically alternating between study and full-time employment. This structured approach offers deeper industry immersion and stronger alignment with academic credit requirements, enhancing career readiness.
Key Differences Between Internships and Co-ops
Internships typically last a few months and are often completed during summer breaks, providing students with short-term, practical work experience related to their academic studies. Co-op programs involve longer, alternating work terms integrated into the academic curriculum, allowing students to gain extensive, paid work experience while earning academic credit. The key differences lie in duration, academic credit, and the depth of professional exposure, with co-ops offering more structured, immersive learning aligned with degree requirements.
Academic Credit: Internship vs Co-op
Academic credit awarded for internships typically depends on the duration and relevance of the work experience to the student's curriculum, often resulting in fewer credits than co-op programs. Co-op programs are usually structured to integrate multiple semesters of work experience with academic coursework, allowing students to earn substantial academic credit while gaining practical skills. The organized rotation between on-campus studies and full-time employment in co-op programs ensures a stronger alignment with academic requirements compared to most internships.
Duration and Structure of Internships vs Co-ops
Internships typically last a few weeks to a few months and are often part-time or full-time during academic breaks, offering short-term practical experience. Co-op programs extend over multiple academic terms, integrating alternating periods of study and full-time work to provide immersive, long-term industry exposure. The structured nature of co-ops ensures deeper skill development through prolonged engagement compared to the shorter, more flexible internship duration.
Integration with Academic Curriculum
Internships often provide practical experiences that complement specific academic courses, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings aligned with their curriculum. Co-op programs integrate structured work terms as a required component of the academic program, offering extended periods of professional experience directly tied to course credits and learning outcomes. This seamless alignment of co-op placements with academic requirements ensures deeper integration and continual skill development throughout the student's educational journey.
Skill Development: Internship vs Co-op
Internships typically offer short-term, project-based experiences that help students develop specific skills within a focused time frame, enhancing their ability to quickly adapt and contribute to professional settings. Co-op programs provide extended work terms integrated into academic curricula, allowing deeper immersion and progressive skill mastery through real-world practice aligned with course objectives. The prolonged engagement in co-ops often results in stronger industry connections and comprehensive skill development compared to the more limited scope of internships.
Employer Expectations: Internship vs Co-op
Employers expect internships to provide students with short-term, hands-on experience that enhances specific skills and exposes them to workplace culture. Co-op programs demand a longer commitment, allowing students to integrate academic knowledge with practical applications through structured work terms, often leading to a deeper understanding of industry practices. While internships typically focus on skill acquisition and networking, co-ops emphasize continuity and academic integration, aligning work experience closely with the student's curriculum and career goals.
Financial Considerations and Compensation
Internship programs typically offer stipends or hourly wages that may be lower than co-op positions, reflecting their shorter duration and less intensive time commitment. Co-op programs often provide higher financial compensation due to their extended period and integration into the company's workflow, enabling students to earn a more substantial income while gaining work experience. Financial considerations should factor in the potential for tuition reductions or academic credits linked to co-op placements, which can offset education costs more effectively than internships.
Career Outcomes and Networking Opportunities
Internships and co-ops both enhance career outcomes by providing practical experience, but co-ops typically offer longer-term, full-time positions that deepen industry knowledge and improve job placement rates after graduation. Networking opportunities are more extensive in co-ops due to extended workplace exposure, allowing students to build stronger professional relationships and mentorships. Internships provide valuable snapshots of workplace environments, while co-ops integrate academic learning with real-world applications, maximizing career readiness and industry connections.
Choosing the Right Program for Academic Success
Internship programs offer short-term practical experience primarily aimed at skill enhancement, while co-op programs integrate longer, structured work terms directly aligned with academic curricula, promoting deeper learning and professional growth. Selecting the right program depends on aligning career goals with program duration, academic credit opportunities, and industry relevance to maximize academic success and employability. Evaluating factors such as program flexibility, company partnerships, and curriculum integration ensures optimal alignment with your educational objectives and career aspirations.
Related Important Terms
Experiential Learning Pathways
Internship programs offer short-term experiential learning opportunities that integrate academic theories with practical industry applications, while co-op programs extend this model by alternating semesters of full-time work and study for deeper academic integration. Both pathways enhance professional skills, but co-op experiences typically provide more comprehensive exposure to workplace dynamics and long-term project involvement.
Integrated Work-Study Cohort
The Integrated Work-Study Cohort enhances academic integration by combining structured internships with co-op programs, providing students with continuous professional experience aligned with their coursework. This approach facilitates deeper industry engagement and academic reflection, ensuring practical skills complement theoretical learning.
Hybrid Academic Placement
Hybrid academic placements blend internship and co-op models, offering students flexible, real-world experience integrated with academic credit. This hybrid approach enhances skill application by combining short-term, project-based tasks of internships with the extended, immersive work periods typical of co-ops.
Curriculum-Embedded Co-op
Curriculum-embedded co-ops provide a structured integration of work experience within the academic curriculum, allowing students to earn credit while gaining practical skills directly related to their field of study. Unlike traditional internships, co-ops offer extended, paid work terms aligned with academic schedules, enhancing both learning outcomes and professional development.
Project-Based Internship Alignment
Project-based internships offer targeted experiential learning that directly mirrors academic coursework, enhancing skill application in real-world environments. Co-op programs integrate alternating academic terms with extended work placements, fostering deeper industry immersion but often requiring more prolonged time commitments than internships.
Academic Credit Co-op Model
The Academic Credit Co-op Model integrates work experience directly into the curriculum, offering students paid, semester-long positions that provide both academic credit and professional development. This model enhances learning by aligning co-op placements with specific degree requirements, fostering practical skills while maintaining rigorous academic standards.
Synchronous Industry-Academia Model
The Synchronous Industry-Academia Model integrates internships and co-ops by aligning academic curricula with real-time industry projects, enhancing practical learning through simultaneous engagement in coursework and professional experience. This model fosters seamless knowledge transfer, allowing students to apply theoretical concepts during internships while gaining extended hands-on skills through co-op placements within the academic semester framework.
Micro-credentialed Internship
Micro-credentialed internships offer a structured integration of academic learning and practical experience, providing students with verified skills and competencies that enhance employability. Unlike traditional co-op programs, these internships emphasize focused skill acquisition through digital badges and certificates aligned with industry standards.
Dual-Track Academic Integration
Dual-track academic integration through internship and co-op programs enhances experiential learning by aligning practical work experience directly with curricular goals; internships typically offer shorter, project-based exposure while co-ops provide extended, full-time employment periods that deepen industry immersion. This structured approach supports skill acquisition and professional development, fostering stronger connections between academic theory and workplace application.
Capstone-Linked Work Experience
Capstone-linked work experience through internships offers focused, project-based learning aligned with academic goals, while co-op programs provide extended, integrated work terms that alternate with semesters, enhancing sustained practical knowledge. Both models support academic integration but differ in duration and depth of industry immersion, influencing skill application and professional development outcomes.
Internship vs Co-op for academic integration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com