Internships provide structured short-term work experiences focused on gaining practical skills and exploring career interests, often without long-term commitment or formal certification. Apprenticeships combine paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction, leading to recognized qualifications and mastery of specific trades or professions. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, with internships offering broad exposure and apprenticeships delivering specialized expertise.
Table of Comparison
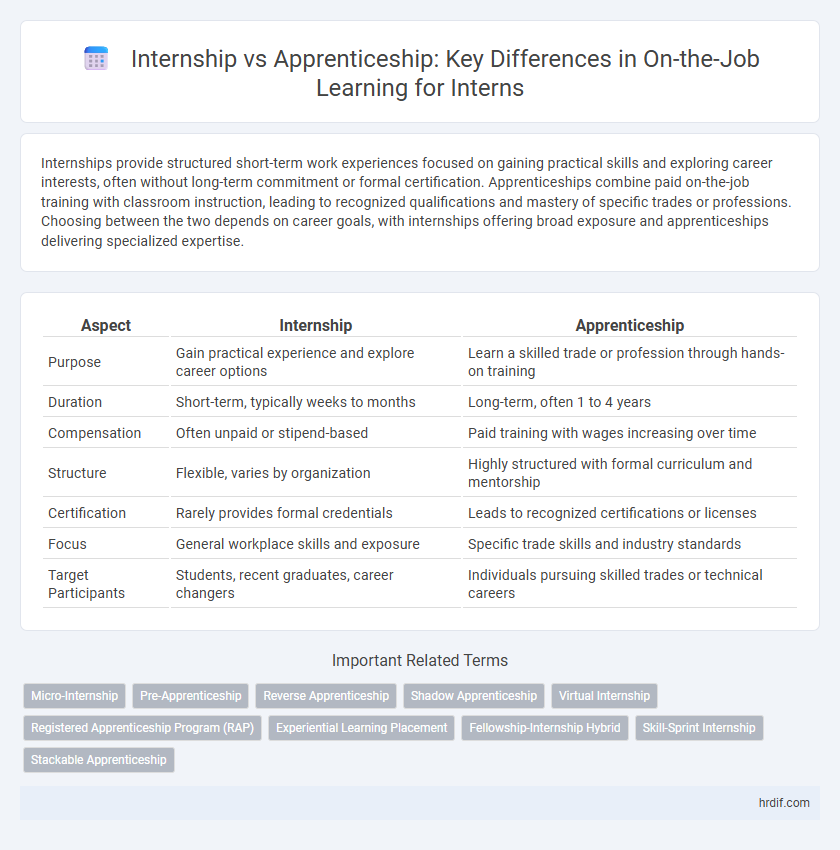
| Aspect | Internship | Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gain practical experience and explore career options | Learn a skilled trade or profession through hands-on training |
| Duration | Short-term, typically weeks to months | Long-term, often 1 to 4 years |
| Compensation | Often unpaid or stipend-based | Paid training with wages increasing over time |
| Structure | Flexible, varies by organization | Highly structured with formal curriculum and mentorship |
| Certification | Rarely provides formal credentials | Leads to recognized certifications or licenses |
| Focus | General workplace skills and exposure | Specific trade skills and industry standards |
| Target Participants | Students, recent graduates, career changers | Individuals pursuing skilled trades or technical careers |
Understanding Internships and Apprenticeships
Internships offer structured, short-term work experiences primarily focused on gaining practical exposure and professional networking within a specific industry, often targeted at students or recent graduates. Apprenticeships provide longer-term, hands-on training combined with formal education, aimed at developing specialized skills and certifications in skilled trades or technical fields. Both pathways enhance on-the-job learning, but internships emphasize exploration and resume building, while apprenticeships prioritize skill mastery and career readiness.
Key Differences Between Internships and Apprenticeships
Internships primarily provide short-term, practical experience in a professional environment, often geared towards students or recent graduates seeking exposure to a specific industry. Apprenticeships involve longer-term, structured training combining paid work with formal education, focusing on mastering a skilled trade or profession. Key differences include duration, compensation, training structure, and the balance between hands-on tasks versus educational components.
Duration and Commitment: Internship vs Apprenticeship
Internships typically last from a few weeks to several months, offering flexible commitment and short-term practical experience for students or recent graduates. Apprenticeships involve longer durations, often spanning one to four years, requiring a significant commitment to mastering specific trades or skills through structured, hands-on training. The extended timeline of apprenticeships results in deeper expertise and often includes certification or credentials upon completion.
Industry Focus: Where Are Each Most Common?
Internships are most common in industries like finance, marketing, technology, and media, where short-term projects and exposure to corporate environments are prioritized. Apprenticeships dominate skilled trades such as construction, manufacturing, electrical, and plumbing, emphasizing hands-on training and certification over extended periods. Companies in healthcare and engineering often blend both models to provide comprehensive on-the-job learning tailored to technical and professional skill development.
Training Structure and Learning Outcomes
Internships typically offer a flexible, short-term training structure focused on providing broad exposure to a workplace environment, allowing interns to develop foundational skills and gain practical insights across various departments. Apprenticeships feature a more rigid, long-term training framework combining hands-on work with structured technical education, designed to develop specialized expertise and industry-recognized competencies. While internships prioritize exploration and basic skill acquisition, apprenticeships ensure mastery through comprehensive skill development and direct mentorship, resulting in higher employability within specific trades or professions.
Compensation: Stipends, Wages, and Benefits
Internships often provide unpaid or modest stipends primarily focused on gaining experience, whereas apprenticeships typically offer structured wages aligned with skill progression and industry standards. Apprentices receive comprehensive benefits including health coverage and paid leave, reflecting their employee status, while interns may have limited or no benefits. Compensation models in apprenticeships ensure long-term financial stability, contrasting with internships that prioritize short-term educational value.
Entry Requirements and Eligibility
Internships often require candidates to be enrolled in or recently graduated from an academic program, making them accessible to students seeking practical experience with minimal prior qualifications. Apprenticeships typically mandate a high school diploma or equivalent and sometimes specific age requirements, focusing on hands-on skill development in trades under licensed professionals. Entry eligibility for apprenticeships generally involves formal agreements and longer commitments compared to the more flexible, short-term nature of internships.
Career Advancement and Job Opportunities
Internships provide valuable hands-on experience and industry exposure, often enhancing resumes and opening doors to full-time positions in competitive fields. Apprenticeships combine structured training with paid work, offering in-depth skill development and a clear pathway to certified careers, especially in trades and technical professions. Both experiences improve career advancement prospects, but internships tend to suit those seeking entry-level roles in corporate or creative industries, while apprenticeships lead to specialized job opportunities with long-term employment stability.
Ideal Candidates: Who Should Choose What?
Ideal candidates for internships are typically students or recent graduates seeking exposure to professional environments and skill development without long-term commitment. Apprenticeships suit individuals aiming for hands-on, structured training in a specific trade or craft, often leading to certification or direct employment. Those prioritizing career-oriented learning with mentorship and practical experience in a specialized field should consider apprenticeships over internships.
Which On-the-Job Learning Path Is Right for You?
Internships offer short-term, often unpaid experiences focused on gaining exposure and building foundational skills, ideal for students exploring career options. Apprenticeships provide structured, paid training with mentorship, emphasizing hands-on skill development and qualifications in trades or specialized fields. Choosing between an internship and apprenticeship depends on your career goals, desired level of commitment, and the type of practical learning environment you seek.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Internship
Micro-internships offer short-term, project-based on-the-job learning opportunities that differ from traditional apprenticeships by emphasizing flexibility and diverse skill application in a condensed timeframe. These experiences allow students to gain practical insights and build professional networks without the longer commitment or deep specialization typical of apprenticeships.
Pre-Apprenticeship
Pre-apprenticeships provide foundational skills and industry exposure essential for successful transition into formal apprenticeships, offering hands-on experience and technical training in a structured work environment. Unlike internships that emphasize general work experience, pre-apprenticeships focus on skill mastery and certification pathways tailored to specific trades or professions.
Reverse Apprenticeship
Reverse apprenticeship enhances on-the-job learning by allowing experienced professionals to mentor interns, fostering knowledge exchange that blends fresh perspectives with established expertise. This approach accelerates skill development and innovation, distinguishing it from traditional internships that primarily emphasize observation and basic task execution.
Shadow Apprenticeship
Shadow apprenticeship offers an immersive on-the-job learning experience by allowing interns to closely observe and emulate skilled professionals, fostering rapid skill acquisition and practical knowledge. Unlike traditional internships, shadow apprenticeships emphasize hands-on mentorship and real-time feedback, accelerating career readiness in specialized trades and industries.
Virtual Internship
Virtual internships offer flexible, remote work experiences that emphasize gaining professional skills and industry exposure without long-term commitment. Unlike apprenticeships, which provide hands-on, in-depth training in specific trades or professions, virtual internships prioritize digital collaboration and project-based learning for diverse career insights.
Registered Apprenticeship Program (RAP)
The Registered Apprenticeship Program (RAP) provides a structured, industry-recognized pathway combining paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction, offering deeper skill development compared to traditional internships. Unlike internships, RAP emphasizes formal credentialing and long-term career advancement in skilled trades and technical professions.
Experiential Learning Placement
Internships provide structured, short-term experiential learning placements focused on gaining industry exposure and developing practical skills in a professional environment. Apprenticeships offer longer-term, hands-on training combining paid employment with classroom instruction, emphasizing mastery of specific trades or professions through sustained on-the-job learning.
Fellowship-Internship Hybrid
The Fellowship-Internship Hybrid combines the structured mentorship of apprenticeships with the experiential learning typical of internships, providing a balanced on-the-job training experience that accelerates skill acquisition and professional development. This model enhances career readiness by offering real-world project involvement alongside personalized guidance, making it an effective approach for immersive workforce preparation.
Skill-Sprint Internship
Skill-Sprint Internships provide focused, project-based experiences designed to accelerate skill acquisition through real-time problem-solving, distinguishing them from traditional apprenticeships that emphasize long-term craftsmanship under direct mentorship. These internships empower candidates to rapidly develop industry-relevant competencies, making them ideal for fast-track career entry and practical learning in dynamic work environments.
Stackable Apprenticeship
Stackable Apprenticeships offer a modular approach to on-the-job learning, allowing interns to progressively build industry-recognized credentials and skills tailored to evolving career paths. Unlike traditional internships, these programs integrate formal training with work experience, enhancing employability through clearly defined competency milestones.
Internship vs Apprenticeship for on-the-job learning. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com