Internships provide structured learning experiences within established organizations, offering mentoring and skill development in a professional setting. Gigternships combine the flexibility of freelance work with internship goals, allowing participants to undertake short-term projects that build practical experience and a diverse portfolio. Choosing between internships and gigternships depends on the desire for structured guidance versus flexible, project-based work tailored to individual interests.
Table of Comparison
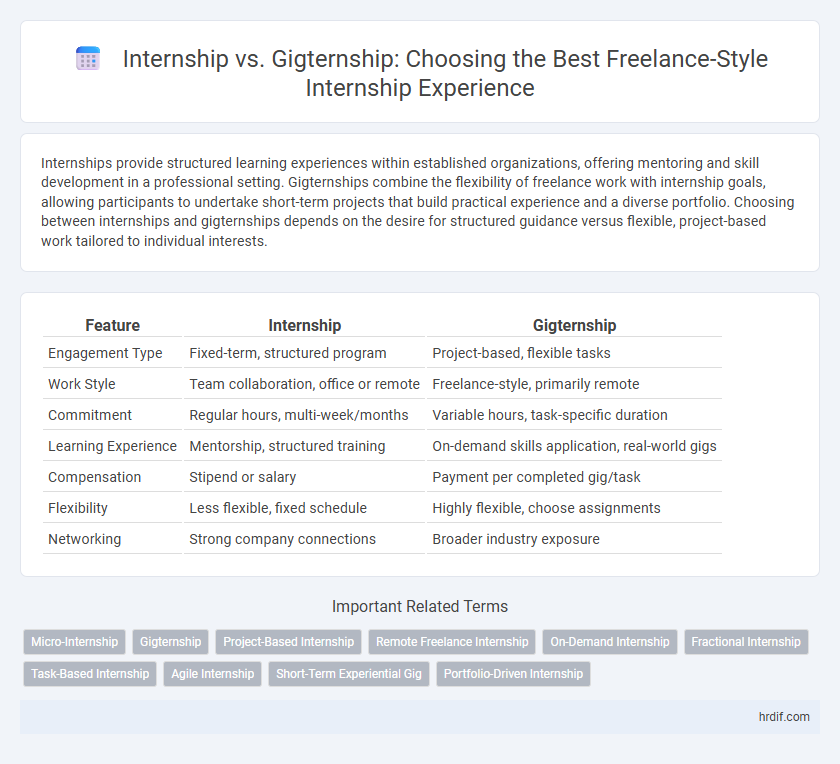
| Feature | Internship | Gigternship |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Type | Fixed-term, structured program | Project-based, flexible tasks |
| Work Style | Team collaboration, office or remote | Freelance-style, primarily remote |
| Commitment | Regular hours, multi-week/months | Variable hours, task-specific duration |
| Learning Experience | Mentorship, structured training | On-demand skills application, real-world gigs |
| Compensation | Stipend or salary | Payment per completed gig/task |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed schedule | Highly flexible, choose assignments |
| Networking | Strong company connections | Broader industry exposure |
Defining Internship and Gigternship
An internship is a structured, often long-term program designed to provide practical work experience in a specific field, typically within a company or organization. A gigternship, by contrast, offers freelance-style, project-based opportunities that are shorter and more flexible, allowing participants to work remotely on discrete tasks or gigs. Both formats deliver valuable real-world experience, but gigternships emphasize autonomy and adaptability in diverse work environments.
Key Differences Between Internships and Gigternships
Internships typically involve structured, long-term learning experiences within a company, offering consistent mentorship and clear performance evaluations, while gigternships provide short-term, project-based freelance tasks with flexible schedules and less direct supervision. Interns often engage in a variety of roles to gain comprehensive industry exposure, whereas gigterns focus on specialized skills to complete discrete assignments. Compensation models differ as well, with internships sometimes unpaid or stipend-based, and gigternships usually paying per completed project or hour worked.
Flexibility: Internship vs Gigternship
Internships typically follow structured schedules with set hours and defined tasks, offering limited flexibility for students balancing multiple commitments. Gigternships provide freelance-style opportunities that allow interns to choose projects and work hours, promoting greater adaptability and autonomy. This flexibility in gigternships makes them ideal for individuals seeking experience without the constraints of traditional internship timelines.
Skills Gained: Traditional vs Freelance-Style Internships
Traditional internships cultivate foundational skills such as time management, teamwork, and industry-specific knowledge through structured, long-term projects. Freelance-style internships, or gigternships, emphasize adaptability, self-promotion, digital communication, and diverse skill application by engaging in short-term, task-oriented assignments. Both formats enhance professional growth, but gigternships offer a broader spectrum of practical skills aligned with the gig economy's dynamic demands.
Compensation Structures Compared
Internships typically offer fixed stipends or hourly wages based on predefined roles and schedules, providing financial stability for students gaining structured experience. Gigternships, designed for freelance-style opportunities, employ project-based or task-specific payments that vary widely in amount and frequency, aligning compensation directly with deliverables rather than hours worked. This flexible pay model appeals to candidates seeking autonomy and diverse, short-term assignments but may lack the consistent income associated with traditional internships.
Networking Opportunities in Each Model
Internships typically provide structured networking opportunities through organized events, mentorship programs, and direct access to industry professionals within the host company. Gigternships, designed for freelance-style internships, offer more flexible but less formal networking chances, often relying on digital platforms and remote collaboration to connect freelancers with a broader range of clients and peers. While traditional internships build deeper, long-term relationships, gigternships enable interns to diversify their professional network across multiple projects and industries.
Resume Value: Internship vs Gigternship Experience
Internship experience often provides structured, long-term projects and direct mentorship, enhancing resume value with demonstrated commitment and skill development. Gigternship experience offers diverse, short-term freelance-style tasks that showcase adaptability and a broad skill set but may lack depth in specific areas. Employers may favor traditional internships for career stability, while gigternships highlight versatility and initiative in dynamic work environments.
Industry Acceptance and Recognition
Industry acceptance of internships remains higher than gigternships, as traditional internships are widely recognized by employers and often provide structured mentorship and skill validation. Gigternships, emerging as flexible freelance-style internships, are gaining traction in creative and tech sectors but lack uniform accreditation and standardized assessment. Companies increasingly value gigternships for agility and real-world project experience, though official recognition and resume weight still favor conventional internships.
Best Fit: Who Should Choose Which Path?
Internships offer structured learning environments ideal for students seeking comprehensive skill development and mentorship within traditional company settings. Gigternships provide flexible, project-based opportunities suited for freelancers preferring autonomy and diverse experiences across multiple clients. Choosing between internship and gigternship depends on whether the individual prioritizes steady guidance and depth (internship) or flexibility and breadth of work (gigternship).
Future Career Implications
Internships provide structured learning experiences with clear mentorship, enhancing long-term career prospects through skill development and industry networking. Gigternships, characterized by flexible freelance-style projects, offer diverse exposure but may result in less consistent skill acquisition and limited professional guidance. Choosing between the two impacts future employability; traditional internships generally yield stronger credentials for full-time roles, while gigternships can build a varied portfolio suited to entrepreneurial or freelance careers.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Internship
Micro-Internships offer flexible, project-based opportunities that resemble freelance gigs, enabling students to gain real-world experience and build portfolios without long-term commitments. Unlike traditional internships, these short-term, skill-specific tasks provide immediate value to employers and practical learning for interns in diverse industries.
Gigternship
Gigternships offer flexible, project-based freelance internships that enable interns to gain practical experience while managing their own schedules, unlike traditional internships that often require fixed hours and on-site presence. This model benefits companies by providing access to diverse talent pools and allowing quicker adaptation to workload fluctuations without long-term commitments.
Project-Based Internship
Project-based internships offer structured, goal-oriented experiences with defined deliverables, contrasting with gigternships that provide flexible, short-term freelance tasks lacking comprehensive mentorship and skill development. This model enhances professional growth by emphasizing real-world project completion, ensuring measurable outcomes and stronger portfolio building for aspiring freelancers.
Remote Freelance Internship
Remote freelance internships offer flexible project-based experiences where interns complete specific tasks independently, contrasting traditional internships that emphasize structured learning and mentorship within a company. Gigternships blend gig economy dynamics with internships, providing short-term freelance opportunities that enhance portfolio diversity and real-world skills in a remote setting.
On-Demand Internship
On-demand internships offer flexible, project-based work tailored to individual schedules, contrasting with traditional internships' fixed timelines. Gigternships integrate gig economy principles, enabling freelancers to gain diverse, short-term experiences that enhance skills and professional networks efficiently.
Fractional Internship
Fractional internships offer flexible, project-based work tailored for freelance-style experiences, contrasting traditional internships that demand fixed hours and longer commitments. This gigternship model enables interns to gain diverse industry exposure while balancing multiple roles, optimizing skill development and networking opportunities.
Task-Based Internship
Task-based internships emphasize completing specific projects or assignments, offering clear deliverables and skill application, while gigternships resemble freelance gigs with flexible, short-term tasks that adapt to market demands. Internships provide structured learning experiences and mentorship, whereas gigternships prioritize autonomy and varied tasks suited for independent freelancers.
Agile Internship
Agile internships emphasize flexibility and skill adaptability, making Gigternships an ideal format for freelance-style internships that require project-based, short-term commitments. Unlike traditional internships, Gigternships allow interns to work remotely on diverse Agile projects, enhancing real-time problem-solving and collaborative skills in dynamic environments.
Short-Term Experiential Gig
Short-term experiential gigs offer flexible, project-based learning opportunities that differ from traditional internships by emphasizing freelance-style autonomy and immediate practical application. Gigternships prioritize skill-specific tasks and real-world experience without long-term commitment, allowing interns to build a diverse portfolio rapidly.
Portfolio-Driven Internship
Portfolio-driven internships prioritize real-world project experience and tangible deliverables, offering deeper skill development and industry relevance compared to gigternships, which typically involve short-term, task-based freelance assignments. Interns build comprehensive portfolios demonstrating sustained contributions, enhancing employability and long-term career opportunities more effectively than piecemeal gigternship work.
Internship vs Gigternship for freelance-style internships. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com