Professional experience demonstrates a candidate's proven ability to perform specific job functions and adapt to workplace environments, making them more attractive to employers. Apprenticeship experience provides hands-on training and skill development under expert guidance, which builds foundational knowledge and practical expertise. Job seekers benefit most by combining both types of experience to showcase a well-rounded skill set and readiness for diverse job responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
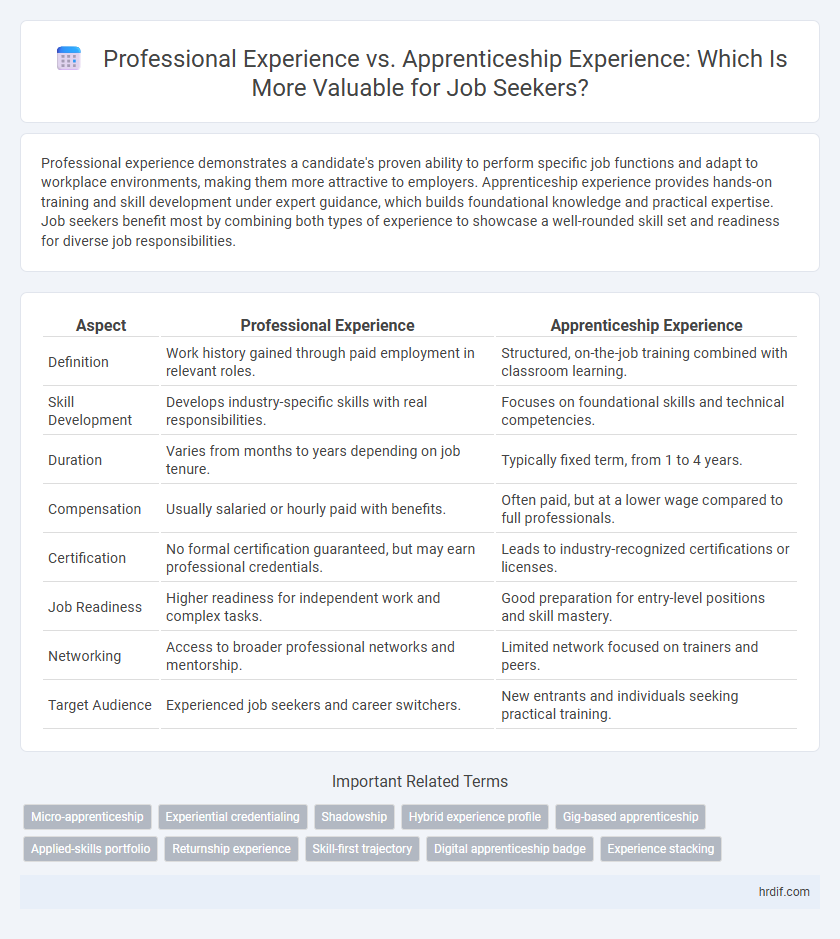
| Aspect | Professional Experience | Apprenticeship Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work history gained through paid employment in relevant roles. | Structured, on-the-job training combined with classroom learning. |
| Skill Development | Develops industry-specific skills with real responsibilities. | Focuses on foundational skills and technical competencies. |
| Duration | Varies from months to years depending on job tenure. | Typically fixed term, from 1 to 4 years. |
| Compensation | Usually salaried or hourly paid with benefits. | Often paid, but at a lower wage compared to full professionals. |
| Certification | No formal certification guaranteed, but may earn professional credentials. | Leads to industry-recognized certifications or licenses. |
| Job Readiness | Higher readiness for independent work and complex tasks. | Good preparation for entry-level positions and skill mastery. |
| Networking | Access to broader professional networks and mentorship. | Limited network focused on trainers and peers. |
| Target Audience | Experienced job seekers and career switchers. | New entrants and individuals seeking practical training. |
Defining Professional Experience and Apprenticeship Experience
Professional experience refers to the work history gained through paid employment, where individuals apply specialized skills and knowledge within their industry. Apprenticeship experience involves structured, hands-on training under the guidance of a skilled mentor, combining practical work with educational components. Both types of experience contribute uniquely to career development, with professional experience emphasizing job performance and apprenticeship experience fostering skill acquisition and industry-specific learning.
Key Differences Between Professional and Apprenticeship Roles
Professional experience involves roles requiring independent decision-making, specialized skills, and often management responsibilities, whereas apprenticeship experience centers on structured learning and on-the-job training under mentorship. Key differences include the level of autonomy, with professional roles demanding higher self-direction, and the purpose, as apprenticeships focus on skill acquisition and practical education. Employers often value professional experience for demonstrated expertise but recognize apprenticeships as foundational for hands-on learning and career development.
Skills Acquired Through Professional Experience
Professional experience offers job seekers practical skills honed through real-world challenges, including project management, client communication, and problem-solving under pressure. These skills demonstrate an ability to perform independently and adapt to workplace dynamics, often making candidates more attractive to employers. In contrast, apprenticeship experience primarily focuses on learning under supervision, providing foundational skills but less exposure to autonomous decision-making.
Skills Developed During Apprenticeships
Apprenticeship experience enables job seekers to develop hands-on technical skills and industry-specific knowledge that complement theoretical learning. This practical training often enhances problem-solving abilities, adaptability, and teamwork, which are highly valued in professional environments. Skills acquired through apprenticeships provide a strong foundation, bridging the gap between academic concepts and real-world applications.
Industry Perceptions: Professional Experience vs Apprenticeship
Industry perceptions often prioritize professional experience for job seekers due to its direct alignment with job responsibilities and proven workload management. Apprenticeship experience, while valued for hands-on training and skill development, is sometimes viewed as less comprehensive than full-time professional roles. Employers increasingly recognize apprenticeships as viable pathways when paired with measurable performance outcomes and relevant technical skills.
Career Growth Opportunities for Both Pathways
Professional experience offers job seekers direct industry exposure, skill refinement, and higher earning potential, accelerating career advancement through expanded networks and leadership roles. Apprenticeship experience provides structured learning, hands-on training, and industry-recognized certifications, fostering foundational skills essential for entry-level positions and long-term career stability. Both pathways enhance employability, with apprenticeships emphasizing skill acquisition and on-the-job training while professional experience prioritizes expertise development and career progression.
Transferability of Skills to Different Job Sectors
Professional experience often provides specialized skills that can be directly applied within a specific industry, enhancing job performance and career growth. Apprenticeship experience, while typically more hands-on and foundational, fosters transferable skills such as teamwork, problem-solving, and technical proficiency applicable across diverse job sectors. Employers value both types of experience for their roles in developing adaptable candidates capable of succeeding in various professional environments.
Salary Prospects: Professional vs Apprenticeship Background
Professional experience typically leads to higher salary prospects than apprenticeship experience due to direct exposure to industry-specific responsibilities and advanced skill development. Job seekers with professional experience often command better compensation packages and faster salary growth compared to those with apprenticeship backgrounds. The increased value employers place on proven job performance and specialized expertise drives this wage disparity.
Job Market Demand and Employer Expectations
Employers increasingly value professional experience for its direct impact on productivity and proven skills in real work environments. Apprenticeship experience offers structured training and practical knowledge, but often lacks the depth and diversity found in professional roles, making it less prioritized in competitive job markets. Job seekers with extensive professional experience align more closely with employer expectations for immediate contribution and advanced problem-solving capabilities.
Which Path Is Right for Your Career Goals?
Professional experience offers direct exposure to industry responsibilities, enhancing skills through real-world challenges and often leading to faster career advancement. Apprenticeship experience combines on-the-job training with structured education, providing hands-on learning while earning credentials that can be crucial for trades and technical careers. Choosing between the two depends on your career goals: prioritize professional experience for roles requiring immediate expertise and apprenticeships for skill-building in specialized fields with formal certification.
Related Important Terms
Micro-apprenticeship
Micro-apprenticeships provide job seekers with structured, short-term professional experience tailored to develop specific industry skills, bridging the gap between traditional apprenticeships and full professional roles. Unlike long-term professional experience, micro-apprenticeships offer flexible, project-based learning opportunities that enhance employability and practical knowledge in a condensed timeframe.
Experiential credentialing
Professional experience demonstrates verified skills and achievements through formal employment, providing widely recognized credentials that enhance job seekers' credibility in the labor market. Apprenticeship experience offers hands-on training and practical knowledge under expert supervision, serving as a valuable experiential credential that bridges skill gaps and supports workforce readiness.
Shadowship
Shadowship offers job seekers immersive learning opportunities by observing professionals in real work environments, bridging the gap between Apprenticeship Experience's hands-on tasks and the broader scope of Professional Experience. This method enhances practical understanding and industry insight, making candidates more adaptable and valuable during their initial career stages.
Hybrid experience profile
Hybrid experience profiles that combine Professional Experience with Apprenticeship Experience enable job seekers to showcase both practical industry skills and hands-on training, enhancing their adaptability and problem-solving capabilities. Employers value this blend for fostering well-rounded candidates who can quickly integrate theoretical knowledge with real-world applications, increasing overall job performance and growth potential.
Gig-based apprenticeship
Gig-based apprenticeships provide hands-on, real-world experience that bridges the gap between traditional professional experience and entry-level training, offering job seekers practical skills aligned with industry demands. Unlike conventional roles, these apprenticeship experiences emphasize flexible, project-focused tasks that enhance employability through measurable outcomes and portfolio development.
Applied-skills portfolio
Professional experience demonstrates a candidate's competence through real-world project outcomes and measurable contributions, making it a vital component of an applied-skills portfolio; apprenticeship experience, while often less extensive, provides structured, hands-on training that builds foundational skills and industry-specific knowledge essential for skill development. Employers prioritize portfolios showcasing diverse, tangible accomplishments from professional roles, but value apprenticeship experience as evidence of formal skill acquisition and adaptability in practical settings.
Returnship experience
Returnship experience bridges the gap between professional experience and apprenticeship by providing job seekers with structured, short-term opportunities to refresh skills and demonstrate competence in their field. This type of experience is especially valuable for those re-entering the workforce, offering practical, project-based work that often leads to full-time employment.
Skill-first trajectory
Professional experience demonstrates practical application of advanced skills and industry knowledge, reflecting a candidate's ability to deliver results in real-world settings. Apprenticeship experience emphasizes hands-on learning and skill development under mentorship, fostering foundational expertise crucial for a skill-first career trajectory.
Digital apprenticeship badge
Digital apprenticeship badges provide verifiable credentials that showcase hands-on skills and real-world project experience, offering job seekers a competitive edge over traditional professional experience alone. These badges highlight mastery in specialized digital competencies, increasing employability by aligning practical training with industry standards.
Experience stacking
Professional experience demonstrates practical application of skills in real-world settings, while apprenticeship experience provides structured, hands-on training under expert supervision; combining both creates experience stacking that enhances a job seeker's versatility and marketability. Stacking diverse experiences signals adaptability and a continuous learning mindset, making candidates more competitive in dynamic job markets.
Professional Experience vs Apprenticeship Experience for job seekers. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com