Experience focuses on the practical skills and knowledge gained through hands-on involvement in specific roles, enhancing real-world problem-solving abilities. A portfolio career, by contrast, combines multiple part-time or freelance roles, showcasing a diverse range of experiences and adaptability across different industries. Emphasizing experience allows professionals to demonstrate depth of expertise, while a portfolio career highlights versatility and continuous learning.
Table of Comparison
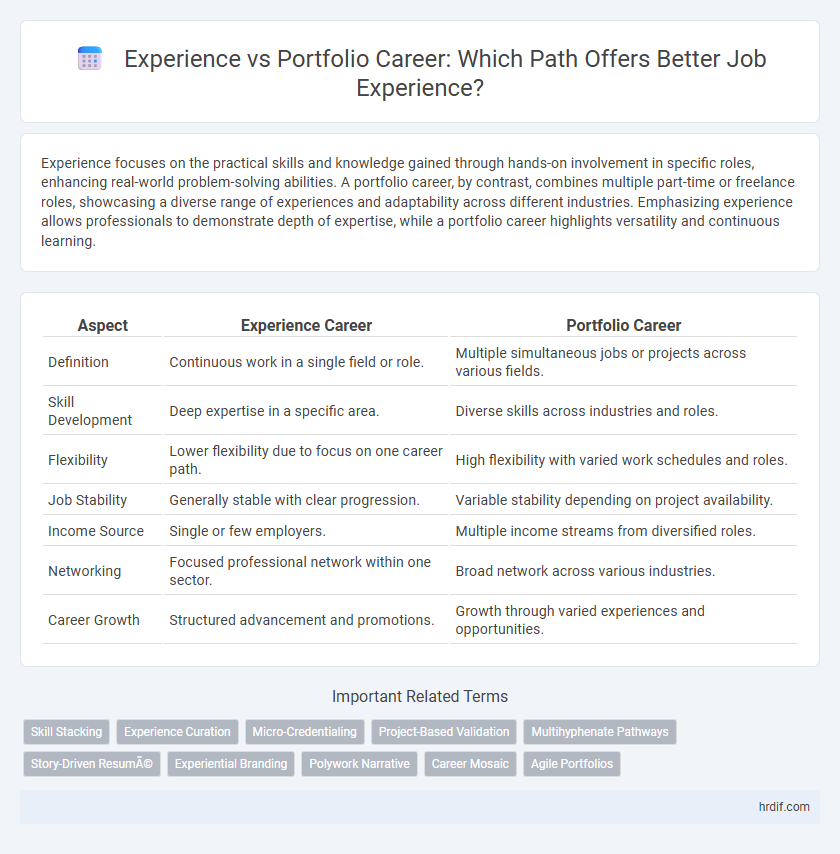
| Aspect | Experience Career | Portfolio Career |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous work in a single field or role. | Multiple simultaneous jobs or projects across various fields. |
| Skill Development | Deep expertise in a specific area. | Diverse skills across industries and roles. |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility due to focus on one career path. | High flexibility with varied work schedules and roles. |
| Job Stability | Generally stable with clear progression. | Variable stability depending on project availability. |
| Income Source | Single or few employers. | Multiple income streams from diversified roles. |
| Networking | Focused professional network within one sector. | Broad network across various industries. |
| Career Growth | Structured advancement and promotions. | Growth through varied experiences and opportunities. |
Defining Traditional Experience and Portfolio Careers
Traditional experience typically involves a linear career path within a single organization or industry, emphasizing job stability and progressive skill development over time. Portfolio careers consist of multiple concurrent roles or projects often across different fields, reflecting adaptability, diverse skill sets, and entrepreneurial mindset. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for professionals navigating job markets where flexibility and specialization increasingly intersect.
Key Differences Between Experience and Portfolio Careers
Experience emphasizes depth in a specific role or industry, showcasing long-term skills development and expertise. Portfolio careers highlight versatility by combining multiple part-time roles or projects across different fields, demonstrating adaptability and diverse competencies. Key differences include stability versus variety, specialization versus breadth, and conventional career progression versus entrepreneurial or freelance flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Experience
Traditional experience offers structured career progression, providing deep expertise and industry-specific skills that enhance job stability and credibility. However, it often limits flexibility and adaptability, potentially hindering diversification and innovation compared to portfolio careers. Employers may value consistent experience, but such paths can constrain opportunities for exploring varied roles or entrepreneurial ventures.
Advantages of Pursuing a Portfolio Career
Pursuing a portfolio career offers diverse skill development by engaging in multiple roles across various industries, enhancing adaptability and marketability. This career approach fosters continuous learning and networking opportunities, which can lead to unique job prospects and professional growth. Employers often value the broad experience and problem-solving abilities gained from managing a portfolio career compared to traditional linear job experience.
Which Offers Greater Career Flexibility?
Experience offers deeper specialization and mastery in a specific role, while a portfolio career provides diverse skills across multiple fields, enhancing adaptability. Portfolio careers deliver greater career flexibility by allowing professionals to pivot between industries and projects with ease, responding dynamically to market demands. Employers increasingly value this versatility as it cultivates resilience and broad problem-solving capabilities.
Impact on Skill Development: Experience vs Portfolio
Experience in a traditional career often provides deep, specialized skill development through prolonged exposure to specific tasks, enhancing technical proficiency and industry knowledge. A portfolio career, by contrast, cultivates a broader range of transferable skills such as adaptability, project management, and networking through varied roles and industries. The impact on skill development differs as traditional experience hones expertise within a niche, whereas a portfolio approach fosters versatility and continuous learning across multiple disciplines.
Marketability: Recruiters’ Views on Experience vs Portfolio Careers
Recruiters often prioritize proven experience over portfolio careers when assessing marketability, valuing consistent industry-specific expertise and demonstrated achievements. Experience provides tangible evidence of skills applied in real-world situations, which enhances credibility and reduces perceived hiring risk. Portfolio careers, while showcasing versatility, may be viewed as lacking depth in a single domain, potentially impacting a candidate's appeal for specialized roles.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Experience in a traditional career often leads to structured career progression with clear advancement opportunities through promotions and increased responsibilities. A portfolio career, which involves multiple part-time roles or projects, can showcase diverse skills and adaptability but may lack the linear progression seen in conventional employment. Balancing experience gained from a portfolio career requires strategic documentation to demonstrate cumulative value for future career advancement.
Financial Security and Risk Comparison
Experience offers financial security through steady income streams and predictable career progression, while a portfolio career diversifies income sources but introduces variable earnings and higher risk. Traditional employment provides benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, which enhance financial stability, whereas portfolio careers rely on multiple freelance or contract roles that may lack such safety nets. Balancing a portfolio career requires rigorous financial planning to mitigate income volatility and secure long-term financial well-being.
Deciding the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Evaluating job experience involves weighing the depth of a traditional experience career against the diverse skill set of a portfolio career, considering factors like industry stability, long-term goals, and adaptability. Key elements include the value of specialized expertise versus versatility, potential income fluctuations, and the desire for creative freedom or structured growth. Understanding personal priorities and market demands ultimately guides the decision on the optimal career path for sustained professional development.
Related Important Terms
Skill Stacking
Skill stacking in experience careers enhances deep expertise in specific roles, while portfolio careers benefit from diverse skill combinations across multiple industries. Building complementary skills through varied projects accelerates adaptability and innovation in both career paths.
Experience Curation
Experience curation involves strategically selecting, organizing, and showcasing diverse job roles and skills to demonstrate depth and adaptability, enhancing credibility beyond a traditional portfolio career. This approach emphasizes meaningful growth through deliberate career choices, which fosters continuous learning and positions professionals as versatile experts in their field.
Micro-Credentialing
Micro-credentialing enhances job experience by validating specific skills within both experience-based and portfolio careers, offering targeted proof of competency that traditional resumes often overlook. This approach accelerates career progression by providing verifiable, skill-focused evidence that complements diverse work experiences and project-based achievements.
Project-Based Validation
Project-based validation in experience emphasizes the practical outcomes and skills demonstrated through completed projects, offering concrete evidence of abilities beyond traditional job roles. Portfolio careers showcase a diverse range of projects and expertise, allowing for a dynamic presentation of accomplishments tailored to evolving market demands.
Multihyphenate Pathways
Multihyphenate pathways blend diverse skill sets from multiple professions, allowing individuals to build a rich tapestry of job experience beyond traditional portfolio careers. This approach leverages cross-disciplinary expertise, creating dynamic, adaptable professionals with multifaceted career trajectories.
Story-Driven Resumé
A Story-Driven Resume effectively bridges Experience and Portfolio Career by highlighting transferable skills through narrative examples, showcasing a candidate's adaptability across diverse roles. Emphasizing accomplishments and lessons learned within varied projects creates a compelling career story that resonates with employers seeking dynamic expertise.
Experiential Branding
Experiential branding leverages hands-on experience to create authentic connections with target audiences, highlighting the depth of skills gained through diverse roles rather than a traditional portfolio career's list of positions. This approach emphasizes measurable outcomes and real-world problem-solving abilities that enhance personal and professional credibility in competitive job markets.
Polywork Narrative
Polywork Narrative emphasizes the depth and diversity of Experience by showcasing multifaceted roles and projects beyond traditional job titles, highlighting skills development and interdisciplinary contributions. Unlike a Portfolio Career, which often lists varied jobs or gigs, Polywork captures continuous growth and context, enabling professionals to present dynamic, evolving narratives that resonate with modern employers.
Career Mosaic
Career Mosaic emphasizes the value of diverse job experience over a traditional portfolio career by highlighting how varied roles across industries build adaptable skills and resilience. This approach fosters continuous learning and flexibility, enabling professionals to navigate evolving job markets more effectively than a fixed portfolio career.
Agile Portfolios
Agile portfolios emphasize ongoing, adaptive project management skills and measurable outcomes over traditional resume experience, highlighting versatility across multiple roles and industries. This approach aligns with a portfolio career by showcasing diverse, iterative learning and value delivery rather than linear job tenure.
Experience vs Portfolio Career for job experience. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com