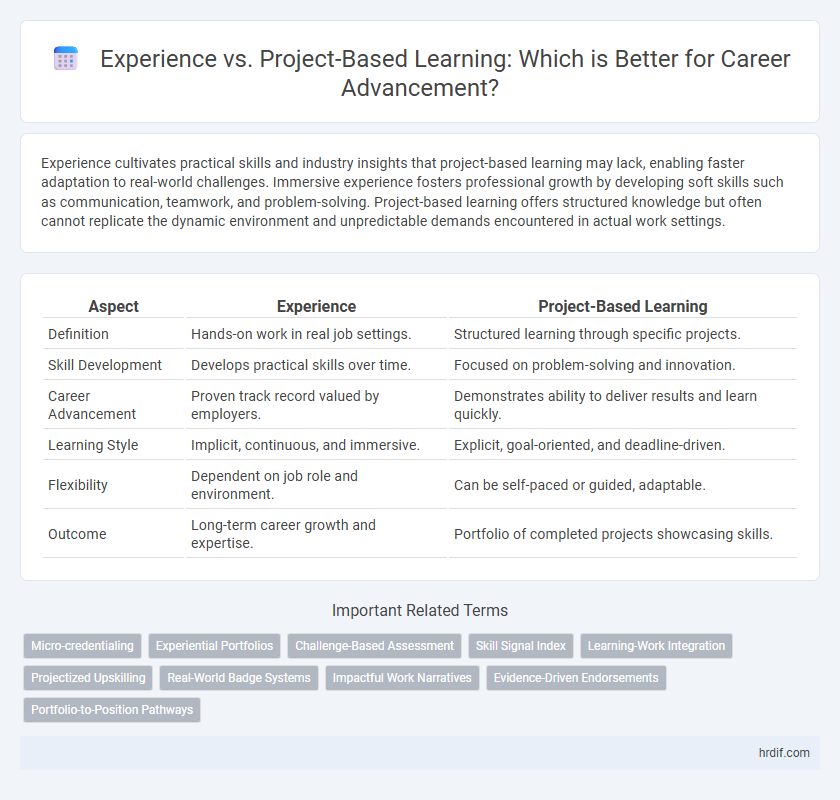
Experience cultivates practical skills and industry insights that project-based learning may lack, enabling faster adaptation to real-world challenges. Immersive experience fosters professional growth by developing soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Project-based learning offers structured knowledge but often cannot replicate the dynamic environment and unpredictable demands encountered in actual work settings.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Experience | Project-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on work in real job settings. | Structured learning through specific projects. |
| Skill Development | Develops practical skills over time. | Focused on problem-solving and innovation. |
| Career Advancement | Proven track record valued by employers. | Demonstrates ability to deliver results and learn quickly. |
| Learning Style | Implicit, continuous, and immersive. | Explicit, goal-oriented, and deadline-driven. |
| Flexibility | Dependent on job role and environment. | Can be self-paced or guided, adaptable. |
| Outcome | Long-term career growth and expertise. | Portfolio of completed projects showcasing skills. |
Defining Experience and Project-Based Learning
Experience encompasses the accumulation of skills and knowledge gained through direct involvement in tasks and real-world situations over time, while project-based learning emphasizes structured, goal-oriented activities designed to develop specific competencies within a limited timeframe. Experience fosters adaptability, problem-solving, and contextual understanding by navigating diverse challenges in professional environments. Project-based learning promotes focused skill acquisition through targeted projects, enabling learners to apply theoretical concepts and produce tangible outcomes that demonstrate proficiency.
Key Differences Between Experience and Project-Based Learning
Experience involves accumulated knowledge and skills gained over time through real-world work, while project-based learning centers on structured tasks designed to develop specific competencies. Experience often provides a broader understanding of industry practices and soft skills such as communication and problem-solving. Project-based learning enables targeted skill acquisition and immediate application, making it valuable for demonstrating expertise in particular areas during career advancement.
Advantages of Traditional Work Experience
Traditional work experience provides hands-on skills and industry-specific knowledge that employers highly value for career advancement. It offers consistent exposure to workplace dynamics, professional networking, and mentorship opportunities that build practical competence and reliability. Many studies show that candidates with substantial work experience often secure higher-paying roles and faster promotions compared to those relying solely on project-based learning.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning for Career Growth
Project-based learning develops practical skills through real-world challenges, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking abilities crucial for career growth. It fosters collaboration and adaptability, preparing professionals for dynamic work environments and increasing employability. Hands-on experience gained from project-based tasks accelerates knowledge retention and showcases measurable achievements to potential employers.
Skill Acquisition: Experience vs. Projects
Hands-on experience enables deeper skill acquisition through real-world problem solving and adapting to dynamic work environments, enhancing critical thinking and decision-making abilities. Project-based learning offers structured opportunities to develop specific skills and knowledge within a defined scope, promoting focused expertise and time management. Combining both approaches accelerates career advancement by blending practical adaptability with targeted skill mastery.
Impact on Employability and Job Market Readiness
Experience enhances employability by providing real-world problem-solving skills and industry insights that employers prioritize, making candidates more adaptable and effective from day one. Project-based learning develops critical thinking and teamwork through hands-on tasks but may lack the depth of continuous application found in prolonged professional experience. Consequently, a blend of extensive experience and targeted projects optimizes job market readiness, aligning candidate capabilities with employer expectations.
Real-World Application: Case Studies and Examples
Real-world application through case studies and examples in experience-based learning provides tangible evidence of problem-solving skills and adaptability, crucial for career advancement. Projects in real workplace settings often highlight practical challenges, enabling professionals to develop solutions that directly impact organizational goals. This hands-on approach usually results in deeper understanding and retention compared to project-based learning limited to theoretical or simulated environments.
Employer Perspectives on Experience and Projects
Employers prioritize real-world experience over solely project-based learning when evaluating candidates for career advancement, valuing hands-on problem-solving and demonstrated adaptability. Experience provides tangible evidence of an employee's ability to navigate complex work environments and deliver consistent results under pressure. While project-based learning builds skills, experiential knowledge often signals readiness for higher responsibility and leadership roles in the workplace.
Blending Experience with Project-Based Learning
Blending hands-on experience with project-based learning accelerates career advancement by fostering practical skills and critical problem-solving abilities. This hybrid approach enhances adaptability and industry-relevant expertise, making professionals more competitive in dynamic job markets. Employers value candidates who demonstrate both real-world experience and the ability to apply knowledge through collaborative projects.
Choosing the Right Path for Career Advancement
Choosing between experience and project-based learning for career advancement depends on individual career goals and industry demands. Experience provides practical, hands-on knowledge that enhances problem-solving skills and professional credibility, while project-based learning offers structured opportunities to develop specific competencies and demonstrate measurable achievements. Aligning your career path with the right balance of real-world exposure and targeted projects maximizes skill development and accelerates career growth.
Related Important Terms
Micro-credentialing
Micro-credentialing enhances career advancement by validating specific skills gained through both experience and project-based learning, offering flexible, targeted recognition that aligns with industry demands. This approach bridges the gap between practical expertise and formal education, empowering professionals to showcase competencies in real-time, skill-focused credentials.
Experiential Portfolios
Experiential portfolios showcase real-world skills and accomplishments, offering tangible proof of competency beyond theoretical knowledge, which enhances career advancement opportunities more effectively than traditional project-based learning alone. By compiling comprehensive evidence of hands-on experiences, these portfolios provide employers with a clearer understanding of a candidate's practical abilities and professional growth.
Challenge-Based Assessment
Challenge-Based Assessment enhances career advancement by simulating real-world problems that require critical thinking and adaptive skills beyond traditional project-based learning. This experiential approach fosters deeper competence and resilience, attributes highly valued in dynamic professional environments.
Skill Signal Index
Experience offers a continuous Skill Signal Index that showcases long-term competency development, while project-based learning provides discrete, targeted skill demonstrations with immediate applicability. Employers use the Skill Signal Index to evaluate consistent performance through experience, whereas project-based achievements highlight specific abilities critical for career advancement.
Learning-Work Integration
Integrating learning directly within work environments accelerates career advancement by enabling the application of theoretical knowledge to real-world challenges, fostering skill development through active problem-solving and continuous feedback. Experience-based learning, contrasted with project-based approaches, emphasizes ongoing professional growth by blending practical tasks with reflective practice, ensuring skills are honed in situ rather than isolated projects.
Projectized Upskilling
Projectized upskilling accelerates career advancement by providing hands-on experience through real-world projects, enhancing practical skills and problem-solving abilities more effectively than traditional experience accumulation. This targeted approach aligns learning outcomes with industry demands, fostering adaptability and immediate applicability in dynamic job markets.
Real-World Badge Systems
Real-world badge systems validate practical skills and verified experiences that enhance career advancement more effectively than traditional project-based learning by providing tangible proof of competencies recognized by employers. These digital credentials facilitate continuous professional development, allowing individuals to showcase verified expertise directly aligned with industry standards and job market demands.
Impactful Work Narratives
Experience-driven career advancement emphasizes the development of impactful work narratives by showcasing real-world achievements and problem-solving skills, which resonate strongly with employers. Project-based learning offers structured opportunities to build relevant competencies, but authentic experience provides deeper insights and credibility through demonstrated results in professional contexts.
Evidence-Driven Endorsements
Evidence-driven endorsements reveal that experiential learning significantly boosts career advancement by enhancing practical skills and problem-solving abilities, while project-based learning primarily develops specific task-oriented competencies; studies show employers prioritize candidates with diverse, real-world experience validated by measurable outcomes over those with isolated project involvement. Data from LinkedIn and the National Association of Colleges and Employers confirm that professionals with documented experiential learning receive higher salary offers and faster promotions compared to peers relying solely on project-based methods.
Portfolio-to-Position Pathways
Portfolio-to-position pathways emphasize leveraging diverse project-based learning experiences to showcase practical skills and problem-solving abilities, accelerating career advancement more effectively than traditional experience alone. Employers increasingly value tangible project outcomes in portfolios, making demonstrated results a critical factor in hiring and promotion decisions.
Experience vs Project-Based Learning for career advancement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com