Experience pet offers a distinctive advantage by valuing diverse skill sets beyond traditional gig experience, empowering individuals to leverage their passions in flexible careers. This approach fosters deeper engagement and adaptability, allowing professionals to transition smoothly between roles while building meaningful expertise. Emphasizing experiential learning over gig solely broadens career opportunities and enhances long-term growth.
Table of Comparison
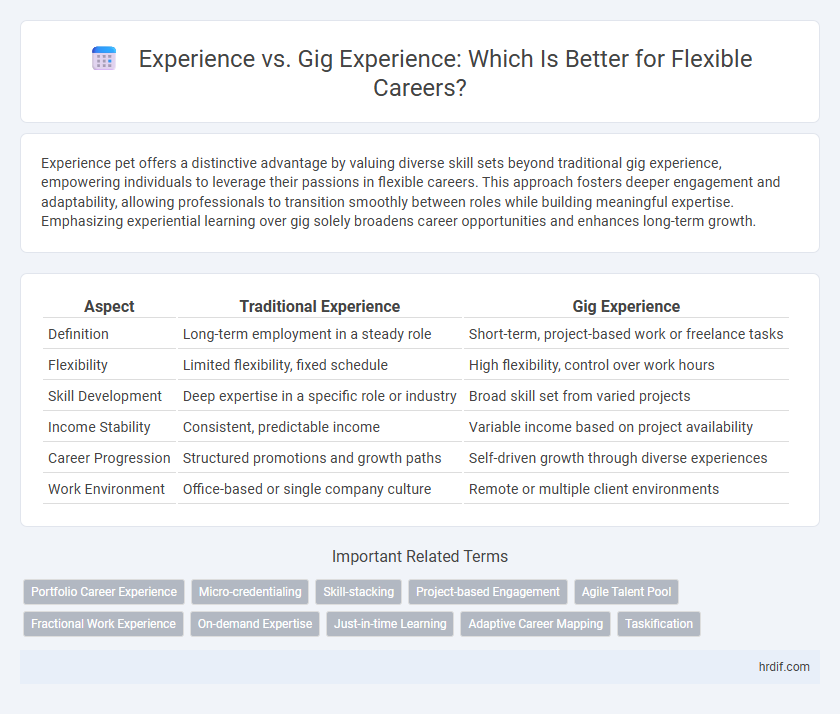
| Aspect | Traditional Experience | Gig Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term employment in a steady role | Short-term, project-based work or freelance tasks |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, fixed schedule | High flexibility, control over work hours |
| Skill Development | Deep expertise in a specific role or industry | Broad skill set from varied projects |
| Income Stability | Consistent, predictable income | Variable income based on project availability |
| Career Progression | Structured promotions and growth paths | Self-driven growth through diverse experiences |
| Work Environment | Office-based or single company culture | Remote or multiple client environments |
Defining Traditional Experience vs. Gig Experience
Traditional experience encompasses long-term employment with a single employer, emphasizing consistent skill development and career progression within a structured work environment. Gig experience involves short-term, project-based engagements often through digital platforms, highlighting adaptability, diverse skill sets, and client-oriented deliverables. Understanding the distinctions between these forms of experience is crucial for optimizing flexible careers and aligning workforce capabilities with evolving market demands.
Key Differences Between Full-Time and Gig Roles
Full-time experience typically involves long-term commitments with structured roles, predictable income, and benefits such as healthcare and retirement plans, while gig experience centers on short-term, project-based engagements offering flexibility and diverse skill development. Full-time roles emphasize stability and career progression within a single organization, whereas gig roles prioritize adaptability and exposure to multiple industries. Understanding these key differences helps professionals tailor their resumes and career strategies for flexible careers, balancing secure employment with varied gig opportunities.
How Employers Value Experience Types
Employers often prioritize traditional experience over gig experience due to its perceived depth in skill development and long-term commitment. However, gig experience demonstrates adaptability, diverse expertise, and self-motivation, qualities increasingly valued in flexible career environments. Balancing both forms of experience can strengthen a candidate's appeal by showcasing reliability alongside versatile problem-solving abilities.
Building Transferable Skills through Gig Work
Gig experience offers a dynamic platform for building transferable skills such as time management, communication, and problem-solving, which are highly valued across diverse industries. Unlike traditional experience, gig work exposes professionals to varied projects and client needs, fostering adaptability and a growth mindset. This hands-on experience accelerates skill diversification, making gig workers competitive candidates in flexible career markets.
Stability vs. Flexibility: Weighing Career Outcomes
Experience in traditional careers often provides stability through consistent roles and long-term growth, while gig experience offers flexibility by enabling diverse projects and adaptable schedules. Balancing these paths requires assessing career outcomes such as job security, skill variety, and income consistency. Professionals seeking steady advancement may favor typical experience, whereas those prioritizing autonomy and dynamic work environments might prefer gig experience.
Impact on Professional Growth and Networking
Experience gained through traditional roles often provides deep skill development and stable professional growth, while gig experience cultivates adaptability and diverse industry exposure. Gig work enhances networking by connecting professionals to a wider variety of clients and collaborators, fostering agile relationship-building. Both pathways contribute uniquely to career flexibility, blending structured expertise with expansive, dynamic connections.
Earning Potential: Salaried Jobs vs. Gig Economy
Traditional salaried jobs often provide stable earning potential with predictable pay and benefits, attracting individuals seeking financial security. Gig economy experiences offer flexible work opportunities but can result in fluctuating income due to task-based payment models and variable demand. Understanding the trade-off between consistent earnings and scheduling freedom is essential for maximizing income in flexible career paths.
Adapting to Changing Job Market Demands
Adapting to changing job market demands requires balancing traditional experience with gig experience, as the latter offers real-time skills development in dynamic environments. Gig experience cultivates versatility and rapid learning, enhancing one's ability to navigate flexible careers where project-based roles are prevalent. Employers increasingly value combined experience that demonstrates both depth in specific fields and agility across diverse tasks.
Portfolio Careers: Blending Experience Types
Portfolio careers combine traditional experience and gig experience to create a versatile professional profile that adapts to flexible career demands. Integrating diverse gig projects with established roles enhances skill variety and marketability, reflecting a dynamic range of expertise. Emphasizing both experience types in portfolios signals adaptability and continuous learning, essential for thriving in evolving job markets.
Choosing the Best Experience Path for Your Goals
Choosing between traditional experience and gig experience depends on your career objectives and industry demands. Traditional experience offers structured skill development and long-term growth, while gig experience provides flexibility and a diverse portfolio of projects. Aligning your experience path with your goals enhances career adaptability and market competitiveness in flexible careers.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Career Experience
Portfolio career experience often provides a broader skill set and adaptability compared to traditional gig experience, which tends to focus on specific, short-term tasks. This diversified experience enhances long-term career resilience and marketability in flexible careers.
Micro-credentialing
Micro-credentialing enhances gig experience by validating specific skills and competencies, offering flexible career professionals targeted recognition that traditional experience resumes may overlook. This approach accelerates career growth in dynamic markets by aligning verified micro-credentials with employer demands and evolving industry standards.
Skill-stacking
Skill-stacking in flexible careers leverages diverse gig experience to build a robust portfolio of complementary abilities, enhancing adaptability and marketability across industries. Traditional experience often emphasizes depth in one field, while gig experience cultivates breadth, enabling professionals to navigate dynamic job markets with versatile, interconnected skills.
Project-based Engagement
Project-based engagement allows professionals to accumulate diverse gig experience by working on specific assignments without long-term commitment, enhancing adaptability in flexible careers. Unlike traditional experience, gig experience emphasizes skill application and rapid learning across varied projects, accelerating expertise in dynamic work environments.
Agile Talent Pool
Agile Talent Pools prioritize gig experience over traditional experience by valuing diverse, project-based skills that adapt quickly to changing market demands. Emphasizing gig experience enables companies to tap into a flexible workforce with specialized expertise, driving faster innovation and responsiveness in dynamic industries.
Fractional Work Experience
Fractional work experience in flexible careers emphasizes diverse project-based roles across multiple industries, offering deeper skill versatility compared to traditional gig experience, which often centers on short-term, task-specific jobs. This approach enables professionals to build a robust portfolio of strategic contributions, enhancing employability and long-term career growth in dynamic market environments.
On-demand Expertise
On-demand expertise emphasizes specialized skills acquired through varied gig experiences, enabling professionals to adapt rapidly across flexible careers. This approach prioritizes practical, task-specific knowledge over traditional long-term experience, driving efficiency in dynamic job markets.
Just-in-time Learning
Just-in-time learning enhances gig experience by enabling professionals to acquire specific skills exactly when needed, increasing agility and efficiency in flexible careers. This targeted approach contrasts with traditional experience, which may rely on accumulated knowledge over time rather than immediate application.
Adaptive Career Mapping
Adaptive Career Mapping leverages both traditional experience and gig experience to create a dynamic, flexible career trajectory tailored to evolving market demands. Integrating diverse gig roles enriches skill portfolios, enabling professionals to pivot roles efficiently and thrive in fluid, project-based work environments.
Taskification
Taskification transforms gig experience into modular, skill-specific tasks that enhance flexibility and specialization in careers. This approach enables professionals to accumulate diverse, verifiable expertise across projects, making gig experience as valuable as traditional job experience in dynamic work environments.
Experience vs Gig Experience for flexible careers. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com