On-the-job learning immerses employees in real work tasks, fostering practical skills through direct experience, while experiential learning emphasizes reflection and conceptual understanding from hands-on activities. Both approaches enhance advancement by promoting skill mastery and adaptability, but experiential learning often leads to deeper insight and critical thinking. Integrating these methods accelerates professional growth and prepares individuals for complex challenges in their careers.
Table of Comparison
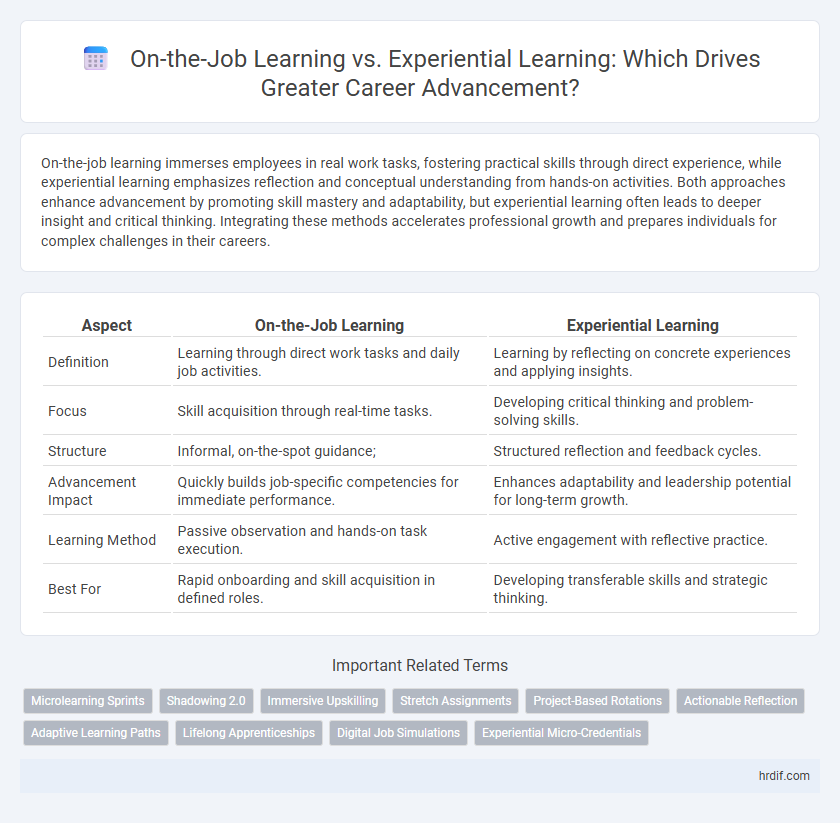
| Aspect | On-the-Job Learning | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct work tasks and daily job activities. | Learning by reflecting on concrete experiences and applying insights. |
| Focus | Skill acquisition through real-time tasks. | Developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. |
| Structure | Informal, on-the-spot guidance; | Structured reflection and feedback cycles. |
| Advancement Impact | Quickly builds job-specific competencies for immediate performance. | Enhances adaptability and leadership potential for long-term growth. |
| Learning Method | Passive observation and hands-on task execution. | Active engagement with reflective practice. |
| Best For | Rapid onboarding and skill acquisition in defined roles. | Developing transferable skills and strategic thinking. |
Defining On-the-Job Learning and Experiential Learning
On-the-job learning involves acquiring skills and knowledge directly through performing job tasks and responsibilities within a work environment. Experiential learning encompasses a broader process where individuals gain expertise through active reflection on hands-on experiences, often including problem-solving and real-world challenges. Both approaches facilitate professional advancement by enhancing practical competencies and critical thinking abilities, but experiential learning emphasizes a continuous cycle of action and reflection beyond routine job duties.
Key Differences Between On-the-Job and Experiential Learning
On-the-job learning immerses employees directly in workplace tasks, enhancing job-specific skills through real-time practice, while experiential learning encompasses a broader scope of activities beyond the workplace, including simulations and reflective exercises that foster critical thinking and problem-solving. On-the-job learning emphasizes immediate application and efficiency, whereas experiential learning prioritizes deep understanding and transferable competencies. The key differences lie in context, scope, and the depth of cognitive engagement, impacting advancement opportunities by shaping practical proficiency versus adaptable expertise.
Impact on Skill Development and Career Advancement
On-the-job learning directly enhances practical skills through real-time problem-solving, leading to faster career advancement by demonstrating immediate competency. Experiential learning fosters deeper understanding and critical thinking by reflecting on diverse experiences, promoting long-term professional growth and adaptability. Combining both methods maximizes skill development and accelerates upward mobility in competitive job markets.
Advantages of On-the-Job Learning for Professionals
On-the-job learning provides professionals with practical, hands-on experience that directly aligns with their daily tasks, accelerating skill acquisition and job proficiency. This immersive approach enhances problem-solving abilities and adaptability within real work environments, fostering immediate application of knowledge. Employers benefit from increased productivity and employee engagement as workers gain relevant expertise while contributing to organizational goals.
Benefits of Experiential Learning in the Workplace
Experiential learning in the workplace accelerates skill acquisition by immersing employees in real-world tasks, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. This approach enhances retention and adaptability by engaging multiple senses and promoting active reflection on experiences. Organizations benefit from increased innovation and employee motivation, as experiential learning cultivates a deeper understanding and practical mastery essential for career advancement.
Challenges Faced in Both Learning Approaches
On-the-job learning often presents challenges such as limited feedback and the risk of errors affecting real projects, which can hinder skill development and confidence. Experiential learning, while immersive, may involve difficulties in abstracting lessons from complex scenarios and requires structured reflection to maximize growth. Both approaches demand balancing practical engagement with critical analysis to overcome obstacles and effectively advance professional competencies.
Selecting the Right Learning Approach for Your Career Goals
Selecting the right learning approach for career advancement depends on aligning on-the-job learning with experiential learning to maximize skill acquisition and practical application. On-the-job learning offers direct exposure to real work challenges and immediate feedback, while experiential learning emphasizes reflective practice and broader problem-solving skills. Balancing both methods enhances professional growth, ensuring relevant competencies meet specific career goals and industry demands.
Employer Perspectives: Training and Talent Development
Employers prioritize on-the-job learning for its direct alignment with real-time job requirements, accelerating skill acquisition and immediate productivity. Experiential learning supports talent development by fostering critical thinking and adaptability, essential for leadership roles and innovation. Combining both approaches enhances workforce capability, driving effective performance and career advancement within organizations.
Integrating Both Approaches for Maximum Growth
Integrating on-the-job learning with experiential learning accelerates skill acquisition by combining practical tasks and reflective practice, fostering deeper understanding and adaptability. Using real-world challenges alongside structured experiences enhances problem-solving abilities and promotes continuous improvement. Organizations leveraging this dual approach see significant advancements in employee capabilities and leadership development.
Future Trends in Workplace Learning Methods
On-the-job learning remains a cornerstone for skill acquisition, enabling real-time application and immediate feedback in dynamic work environments. Experiential learning methods, such as simulations and role-playing, are gaining traction due to their ability to foster critical thinking and adaptability essential for future job roles. Emerging trends emphasize integrating augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) to create immersive, personalized learning experiences that accelerate professional advancement.
Related Important Terms
Microlearning Sprints
Microlearning Sprints enable faster skill acquisition by delivering targeted, bite-sized content directly aligned with job tasks, enhancing on-the-job learning efficiency. Experiential learning through these sprints accelerates professional advancement by immersing employees in real-time problem-solving scenarios that reinforce practical knowledge application.
Shadowing 2.0
Shadowing 2.0 enhances on-the-job learning by providing immersive, real-time observation combined with interactive feedback, accelerating skill acquisition and professional growth. Experiential learning through this method deepens understanding by actively engaging learners in complex tasks, fostering practical expertise critical for career advancement.
Immersive Upskilling
Immersive upskilling through on-the-job learning provides real-time problem-solving and immediate application of skills, driving faster advancement by embedding knowledge within authentic work contexts. Experiential learning complements this by fostering reflective practice and critical thinking, enhancing adaptability and long-term professional growth in dynamic industries.
Stretch Assignments
Stretch assignments provide immersive experiential learning opportunities that accelerate skill acquisition and drive career advancement by challenging employees to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Unlike traditional on-the-job learning, these assignments expand capabilities through purposeful responsibility beyond current roles, fostering adaptability and leadership development.
Project-Based Rotations
Project-based rotations accelerate career advancement by immersing employees in diverse, real-world challenges that enhance practical skills and adaptability. This experiential learning approach surpasses traditional on-the-job training by fostering critical thinking and cross-functional expertise essential for leadership roles.
Actionable Reflection
On-the-job learning emphasizes real-time skills acquisition through direct task execution, while experiential learning integrates actionable reflection to deepen understanding and foster continuous improvement. Incorporating structured reflection after practical experiences enhances skill retention and accelerates professional advancement.
Adaptive Learning Paths
Adaptive learning paths in on-the-job learning tailor skill development directly to role-specific challenges, accelerating career advancement through real-time problem-solving. Experiential learning enhances this process by integrating reflective practices, enabling individuals to internalize lessons and adapt strategies for sustained professional growth.
Lifelong Apprenticeships
On-the-job learning fosters practical skills directly within the work environment, accelerating career advancement through real-time problem solving and immediate application. Lifelong apprenticeships in experiential learning create continuous growth opportunities by combining mentorship and hands-on experiences, ensuring sustained professional development.
Digital Job Simulations
Digital job simulations enhance on-the-job learning by providing immersive, experiential learning environments that replicate real-world challenges, accelerating skill acquisition and practical problem-solving. These simulations enable continuous advancement by allowing learners to practice and refine digital competencies in a risk-free setting, bridging gaps between theoretical knowledge and applied expertise.
Experiential Micro-Credentials
Experiential micro-credentials offer targeted, skill-specific validation that accelerates career advancement by emphasizing real-world application over theoretical knowledge. On-the-job learning provides practical experience but lacks the formal recognition and structured assessment that micro-credentials deliver for measurable professional growth.
On-the-job learning vs Experiential learning for advancement Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com