Freelancers enjoy the freedom to select projects and clients while maintaining a stable home base, allowing for consistent work schedules and reliable income streams. Digital nomads combine work with travel, leveraging remote technology to explore new locations, which fosters creativity but may introduce challenges in maintaining steady client relationships and productivity. Both paths offer unique opportunities for self-employment, requiring individuals to balance flexibility with discipline to ensure business success.
Table of Comparison
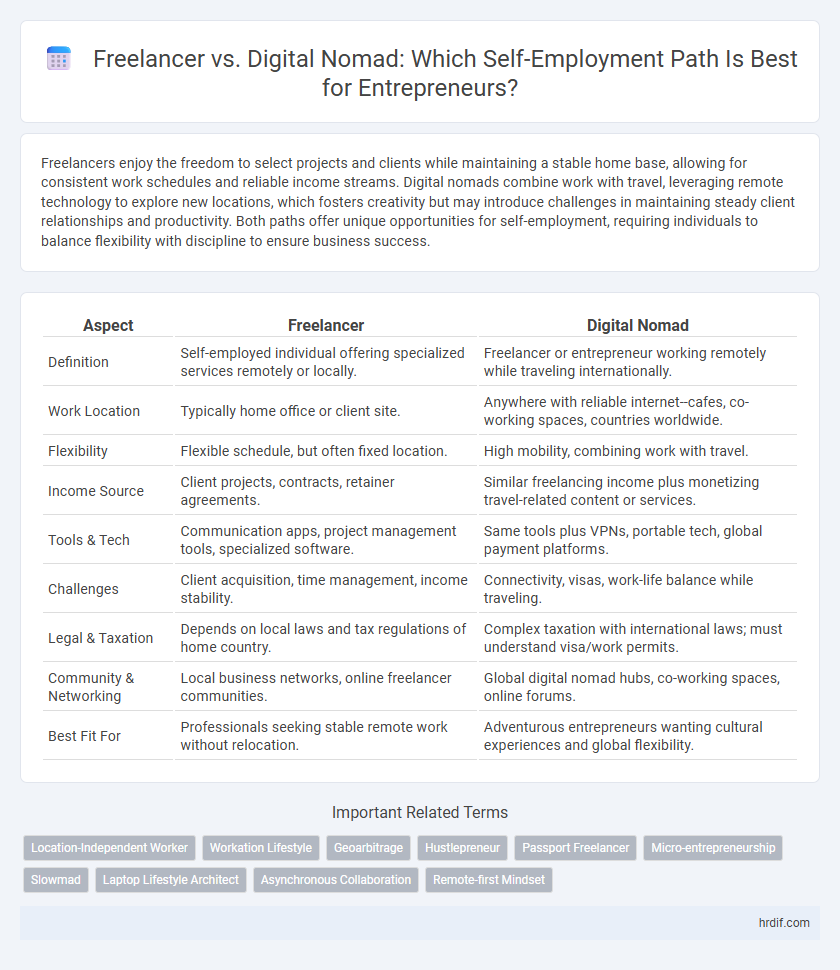
| Aspect | Freelancer | Digital Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-employed individual offering specialized services remotely or locally. | Freelancer or entrepreneur working remotely while traveling internationally. |
| Work Location | Typically home office or client site. | Anywhere with reliable internet--cafes, co-working spaces, countries worldwide. |
| Flexibility | Flexible schedule, but often fixed location. | High mobility, combining work with travel. |
| Income Source | Client projects, contracts, retainer agreements. | Similar freelancing income plus monetizing travel-related content or services. |
| Tools & Tech | Communication apps, project management tools, specialized software. | Same tools plus VPNs, portable tech, global payment platforms. |
| Challenges | Client acquisition, time management, income stability. | Connectivity, visas, work-life balance while traveling. |
| Legal & Taxation | Depends on local laws and tax regulations of home country. | Complex taxation with international laws; must understand visa/work permits. |
| Community & Networking | Local business networks, online freelancer communities. | Global digital nomad hubs, co-working spaces, online forums. |
| Best Fit For | Professionals seeking stable remote work without relocation. | Adventurous entrepreneurs wanting cultural experiences and global flexibility. |
Defining Freelancers and Digital Nomads
Freelancers are self-employed individuals who offer specialized services such as graphic design, writing, or programming, typically working remotely for multiple clients without long-term contracts. Digital nomads combine freelancing or remote work with a lifestyle of continuous travel, leveraging technology to work from various global locations. Both models emphasize independence and flexibility, but digital nomads prioritize mobility and cross-cultural experiences as part of their entrepreneurial identity.
Key Similarities in Self-Employment
Freelancers and digital nomads both embrace self-employment by offering specialized skills directly to clients, enabling flexible work schedules and location independence. Their revenue generation depends primarily on project-based assignments or hourly contracts, fostering entrepreneurial autonomy. Both leverage digital platforms and technology to market services, communicate with clients, and manage workflows efficiently in a competitive gig economy.
Major Differences Between Freelancers and Digital Nomads
Freelancers primarily focus on offering specialized services remotely, often working from a fixed location, while digital nomads combine work with travel, constantly relocating to new destinations. Freelancers maintain a stable client base and predictable income streams, whereas digital nomads prioritize flexibility and lifestyle over consistent work hours. Time zone management, work environment adaptability, and reliance on internet connectivity are critical challenges distinguishing digital nomads from traditional freelancers in the self-employment landscape.
Work Arrangements and Flexibility
Freelancers typically operate from a fixed location or home office, maintaining client deadlines and project scopes with highly flexible schedules tailored to their workload. Digital nomads leverage remote work technology to conduct business from various global locations, prioritizing maximum geographic flexibility alongside work commitments. Both arrangements offer self-employment freedom, but digital nomads emphasize location independence, whereas freelancers often focus on controlled, consistent work environments.
Income Streams and Financial Stability
Freelancers often rely on multiple income streams by serving diverse clients across various projects, enhancing financial stability through workload flexibility and varied revenue sources. Digital nomads tend to focus on scalable, location-independent ventures like remote consulting or digital products, which can lead to passive income but may involve fluctuating cash flow. Both paths demand consistent client acquisition and financial discipline to sustain long-term profitability in self-employment.
Skill Sets and Professional Opportunities
Freelancers leverage specialized skill sets such as graphic design, coding, or content writing to secure diverse projects across industries, enabling flexible self-employment options. Digital nomads combine these skills with adaptability and remote work proficiency, expanding professional opportunities globally by tapping into international markets and remote job platforms. Both paths demand strong digital literacy and time management but differ in lifestyle integration and networking scope, shaping distinct entrepreneurial trajectories.
Work-Life Balance and Lifestyle Choices
Freelancers often enjoy flexible schedules tailored to project deadlines, enabling a customizable work-life balance that suits various personal commitments. Digital nomads prioritize mobility, integrating travel with remote work to embrace diverse cultures and environments while maintaining productivity. Both paths require strong self-discipline and time management skills but offer distinct lifestyle choices centered on autonomy and work flexibility.
Legal Considerations and Tax Implications
Freelancers must navigate local business licenses and tax registrations based on their home country, often facing income tax and self-employment tax obligations. Digital nomads encounter complex legal challenges with cross-border taxation and visa restrictions, requiring careful management of tax residency and compliance with diverse international tax treaties. Both must maintain thorough documentation to optimize tax deductions and avoid penalties while ensuring adherence to varying employment and business laws.
Tools and Resources for Success
Freelancers rely on specialized platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, along with project management tools such as Trello and Slack, to streamline client communication and task organization. Digital nomads prioritize versatile tools including VPNs, cloud storage like Google Drive, and global payment systems such as Payoneer to maintain productivity across diverse locations. Mastery of these digital resources significantly enhances efficiency and competitiveness in self-employment entrepreneurship.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career
Freelancers typically offer specialized services such as writing, graphic design, or software development, freelancing provides flexibility in project selection but often requires building a steady client base and managing administrative tasks. Digital nomads leverage remote work to travel while maintaining income streams from freelancing, entrepreneurship, or remote jobs, emphasizing location independence and lifestyle freedom. Choosing between freelancing and being a digital nomad depends on your priorities for stability, mobility, and work-life balance in building a sustainable self-employed career.
Related Important Terms
Location-Independent Worker
Freelancers and digital nomads both thrive as location-independent workers, leveraging technology to offer services globally without being tied to a fixed office. While freelancers typically concentrate on project-based work with flexible schedules, digital nomads prioritize mobility, combining remote work with travel to maintain an entrepreneurial lifestyle.
Workation Lifestyle
Freelancers balance client projects with flexible schedules, enabling productivity from any location, while digital nomads integrate extensive travel into their work-life routine, leveraging remote work to sustain a workation lifestyle. Both models prioritize autonomy and location independence, but digital nomads emphasize immersive cultural experiences as part of their entrepreneurial journey.
Geoarbitrage
Freelancers leverage geoarbitrage by offering specialized services remotely from low-cost locations, maximizing profit margins through reduced living expenses and flexible client sourcing. Digital nomads prioritize constant relocation to capitalize on favorable economic conditions worldwide, balancing work with lifestyle preferences while optimizing income relative to varying cost-of-living indexes.
Hustlepreneur
Hustlepreneurs who choose freelancing benefit from project-based income and flexible client engagement, while digital nomads leverage geographic freedom and lifestyle mobility to build location-independent businesses. Both models emphasize self-employment growth but differ in daily operations: freelancers prioritize skill specialization and client networks, whereas digital nomads optimize digital tools and travel adaptability for continuous income streams.
Passport Freelancer
Passport Freelancer offers a flexible self-employment model that combines the independence of freelancing with the mobility of digital nomadism, allowing entrepreneurs to work globally without geographic constraints. This approach leverages digital tools and remote work opportunities to maximize income potential while maintaining lifestyle freedom.
Micro-entrepreneurship
Freelancers, often operating as micro-entrepreneurs, focus on providing specialized services remotely with flexible client engagements, leveraging platforms like Upwork and Fiverr to build scalable income streams. Digital nomads embrace micro-entrepreneurship by combining location-independent work with travel, utilizing online businesses or freelance projects to maintain self-employment while exploring global markets.
Slowmad
Slowmads embrace a balanced approach to self-employment by combining the flexibility of freelancers with intentional travel, prioritizing deep cultural immersion and sustainable work-life harmony over rapid movement typical of digital nomads. This lifestyle enhances entrepreneurial productivity by fostering meaningful connections and stability while maintaining the freedom to work remotely.
Laptop Lifestyle Architect
Freelancers typically build a stable client base offering specialized services remotely, while digital nomads prioritize location independence by combining work with travel, both embracing the Laptop Lifestyle Architect mindset to design flexible self-employment. Mastering project management tools, online marketing, and time-zone coordination is essential for success in freelancing or digital nomadism within entrepreneurship.
Asynchronous Collaboration
Freelancers thrive by leveraging asynchronous collaboration tools such as project management software, enabling flexible task execution across different time zones and increasing productivity. Digital nomads benefit from similar asynchronous communication methods but combine this with a location-independent lifestyle, optimizing self-employment through global networking and diverse market access.
Remote-first Mindset
Freelancers prioritize flexible project-based work while embracing a remote-first mindset that optimizes productivity through digital tools and asynchronous communication. Digital nomads extend this mindset by combining professional independence with location independence, leveraging global connectivity to sustain self-employment across diverse environments.
Freelancer vs Digital Nomad for self-employment. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com