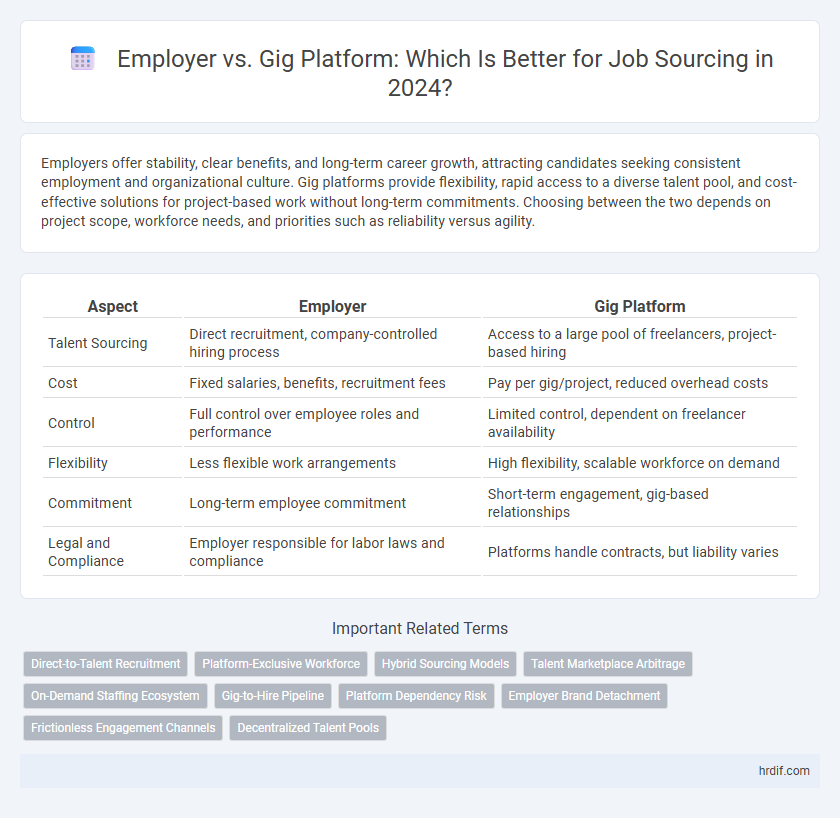
Employers offer stability, clear benefits, and long-term career growth, attracting candidates seeking consistent employment and organizational culture. Gig platforms provide flexibility, rapid access to a diverse talent pool, and cost-effective solutions for project-based work without long-term commitments. Choosing between the two depends on project scope, workforce needs, and priorities such as reliability versus agility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Employer | Gig Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Sourcing | Direct recruitment, company-controlled hiring process | Access to a large pool of freelancers, project-based hiring |
| Cost | Fixed salaries, benefits, recruitment fees | Pay per gig/project, reduced overhead costs |
| Control | Full control over employee roles and performance | Limited control, dependent on freelancer availability |
| Flexibility | Less flexible work arrangements | High flexibility, scalable workforce on demand |
| Commitment | Long-term employee commitment | Short-term engagement, gig-based relationships |
| Legal and Compliance | Employer responsible for labor laws and compliance | Platforms handle contracts, but liability varies |
Understanding Traditional Employers vs Gig Platforms
Traditional employers provide stable, long-term employment with defined roles, benefits, and workplace culture, emphasizing consistent workforce management. Gig platforms connect freelancers or contractors with short-term projects, offering flexibility and on-demand talent without long-term commitments. Employers prioritize employee retention and skill development, whereas gig platforms focus on task efficiency and scalable labor access.
Employment Models: Stability vs Flexibility
Employers offer stable employment models with consistent income, benefits, and long-term job security, making them suitable for workers seeking predictability and growth. Gig platforms provide flexibility by enabling workers to choose projects and work hours, appealing to those prioritizing autonomy over stability. Each model caters to distinct workforce needs, balancing organizational reliability with adaptable labor solutions.
Hiring Processes Compared: Direct Employment and Gig Sourcing
Direct employment offers employers greater control over the hiring process, including candidate screening, background checks, and customized onboarding procedures, which enhances long-term workforce stability. Gig platforms provide rapid access to a diverse talent pool with flexible contract terms but often limit employer influence on vetting and training, impacting job consistency. Employers prioritizing operational control and cultural fit typically favor direct hiring, while those needing scalability and project-based skills leverage gig sourcing.
Cost Implications for Employers and Job Seekers
Employers often face higher upfront costs when directly sourcing talent compared to the variable fees charged by gig platforms, which typically take a commission on each transaction. Gig platforms reduce recruitment expenses but may increase long-term labor costs due to less control over worker loyalty and productivity. Job seekers benefit from gig platforms through flexible job access, yet often encounter unstable income and limited benefits compared to traditional employment.
Quality of Work and Accountability
Employers prioritize quality of work and accountability by directly managing and training their workforce, ensuring consistent performance standards. Gig platforms often face challenges in maintaining these standards due to the temporary and dispersed nature of gig workers. Direct employer engagement fosters stronger responsibility and reliability compared to the often fragmented oversight found on gig platforms.
Employee Benefits and Protections
Employers provide comprehensive employee benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, retirement plans, and workers' compensation, ensuring long-term financial and medical security. Gig platforms often lack these protections, leaving workers responsible for their own benefits and vulnerable to income instability. Traditional employment contracts legally guarantee workplace protections, while gig platform arrangements are typically classified as independent contracting, limiting legal rights and access to social safety nets.
Scalability and Workforce Management
Employers benefit from greater scalability and streamlined workforce management by directly sourcing talent, allowing for tailored recruitment strategies and consistent employee engagement. Gig platforms offer quick access to a vast pool of freelancers but often lack long-term workforce stability and comprehensive management tools. Prioritizing direct employer sourcing enhances control over workforce quality and scalability, leading to more efficient operational outcomes.
Technological Integration in Job Sourcing
Employers leverage advanced Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to streamline job sourcing, enabling precise candidate matching and enhanced recruitment efficiency. Gig platforms utilize algorithm-driven marketplaces and mobile app interfaces to rapidly connect freelancers with short-term projects, emphasizing flexibility and scalability. The integration of cloud computing and data analytics in both models optimizes talent acquisition by providing real-time insights and automated workflows.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Employers must navigate complex legal and compliance frameworks when sourcing jobs through gig platforms, including worker classification, tax obligations, and labor law adherence. Failure to properly classify gig workers versus traditional employees can result in significant penalties and legal disputes under laws such as the Fair Labor Standards Act and IRS guidelines. Ensuring transparent contractual agreements and compliance with local labor regulations helps employers mitigate risks and maintain regulatory alignment.
Choosing the Right Approach for Business Growth
Employers seeking scalable workforce solutions weigh traditional hiring against gig platforms, with the latter offering flexibility, reduced overhead, and access to specialized talent on demand. Gig platforms provide streamlined recruitment processes and cost efficiency, enabling businesses to rapidly adapt to market fluctuations. Selecting the right job sourcing approach depends on organizational goals, project duration, and the need for skill diversity in workforce management.
Related Important Terms
Direct-to-Talent Recruitment
Direct-to-talent recruitment enables employers to bypass gig platforms, reducing intermediary fees and fostering stronger candidate relationships. This approach enhances talent retention by providing personalized engagement and aligning recruitment efforts directly with organizational culture and needs.
Platform-Exclusive Workforce
Platform-exclusive workforce refers to gig workers who rely solely on a specific digital platform for job opportunities, creating a dedicated labor pool that employers can tap into for flexible, scalable hiring. These workers often possess specialized skills tailored to the platform's demand, enabling employers to source talent quickly while maintaining control over job allocation and performance metrics.
Hybrid Sourcing Models
Hybrid sourcing models combine the strengths of traditional employers and gig platforms, enabling companies to access a broader talent pool while maintaining control over workforce quality and project allocation. This approach optimizes cost-efficiency and flexibility by blending direct hires with on-demand gig workers, enhancing scalability and responsiveness in dynamic labor markets.
Talent Marketplace Arbitrage
Employers leveraging talent marketplace arbitrage can strategically source skilled freelancers from gig platforms to reduce costs and access a wider talent pool without compromising quality. This approach enables businesses to optimize hiring efficiency by matching project needs with diverse expertise available across multiple gig platforms.
On-Demand Staffing Ecosystem
Employers leverage on-demand staffing ecosystems to rapidly source skilled workers, bypassing traditional hiring delays through gig platforms that provide access to a diverse talent pool. This shift enhances workforce flexibility and operational efficiency while gig platforms optimize matching algorithms to ensure precise talent allocation for project-specific needs.
Gig-to-Hire Pipeline
Employers leveraging gig platforms for a gig-to-hire pipeline benefit from access to a diverse talent pool, enabling real-time evaluation of skills and work ethic before full-time hiring. This approach reduces recruitment costs and time-to-hire while improving candidate fit and retention rates through practical performance exposure.
Platform Dependency Risk
Employers relying heavily on gig platforms for job sourcing face significant platform dependency risk, including reduced control over talent acquisition and increased vulnerability to platform policy changes or fee structures. This dependency can lead to higher costs, less direct access to skilled workers, and challenges in maintaining consistent workforce quality.
Employer Brand Detachment
Employers experience significant brand detachment when relying on gig platforms for job sourcing, as these platforms prioritize freelancer profiles over the company's identity, reducing opportunities to build a cohesive employer brand. This detachment hinders long-term talent engagement and weakens organizational culture visibility compared to direct hiring channels.
Frictionless Engagement Channels
Employers benefit from frictionless engagement channels by directly accessing talent pools without intermediary delays, enhancing recruitment speed and candidate quality. Gig platforms often introduce communication barriers and processing times that can hinder immediate hiring needs and disrupt workflow continuity.
Decentralized Talent Pools
Decentralized talent pools empower employers by providing direct access to a diverse and global workforce without intermediaries, increasing recruitment efficiency and reducing costs. Unlike traditional gig platforms, decentralized systems enhance transparency and control over hiring processes, fostering stronger employer-worker relationships and higher-quality job matches.
Employer vs Gig Platform for job sourcing. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com