Employers seeking to attract top talent must adapt to the rise of digital nomad employees by offering flexible work arrangements and remote-friendly policies. Traditional employers benefit from structured office environments, while digital nomad employers prioritize technology-driven collaboration and global talent access. Understanding these differences enables organizations to create inclusive workforce strategies that enhance productivity and employee satisfaction.
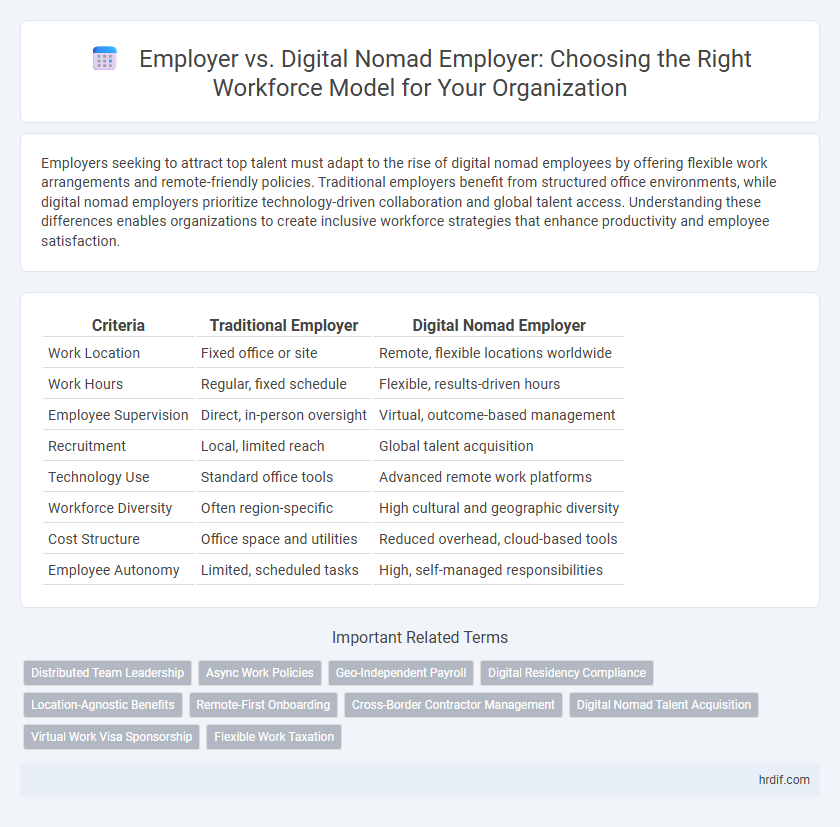
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Traditional Employer | Digital Nomad Employer |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Fixed office or site | Remote, flexible locations worldwide |
| Work Hours | Regular, fixed schedule | Flexible, results-driven hours |
| Employee Supervision | Direct, in-person oversight | Virtual, outcome-based management |
| Recruitment | Local, limited reach | Global talent acquisition |
| Technology Use | Standard office tools | Advanced remote work platforms |
| Workforce Diversity | Often region-specific | High cultural and geographic diversity |
| Cost Structure | Office space and utilities | Reduced overhead, cloud-based tools |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited, scheduled tasks | High, self-managed responsibilities |
Traditional Employer vs. Digital Nomad Employer: Key Differences
Traditional employers often require physical office presence, enforce fixed working hours, and provide structured career paths, emphasizing stability and routine. Digital nomad employers prioritize remote work flexibility, results-driven performance metrics, and adaptability, supporting diverse, location-independent talent pools. Workforce management for digital nomad employers integrates advanced collaboration tools and asynchronous communication to accommodate various time zones and working conditions.
Remote Workforce Management: Challenges and Opportunities
Employers managing a digital nomad workforce face unique challenges in remote workforce management, such as maintaining productivity across time zones and ensuring data security in decentralized environments. Digital nomad employers must implement advanced communication tools and flexible policies to optimize performance and employee engagement. Opportunities include access to a global talent pool and enhanced innovation through diverse work experiences.
Hiring Strategies: Local Employees vs. Global Digital Nomads
Employers adopting hiring strategies focused on local employees benefit from in-depth knowledge of regional labor laws, cultural alignment, and easier team integration. Conversely, engaging global digital nomads expands access to diverse talent pools, driving innovation and offering scalability through remote work flexibility. Balancing compliance, cost-efficiency, and organizational goals is essential when deciding between local workforce hiring and leveraging digital nomad talent.
Productivity Metrics: Office-Based vs. Remote Teams
Employers comparing productivity metrics between office-based and digital nomad employees observe that remote teams often deliver higher output per hour due to flexible work schedules and reduced commuting stress. Digital nomad employers leverage advanced collaboration tools and real-time performance analytics to track productivity effectively across time zones. Office-based workforce productivity remains consistent through structured environments and direct supervision, but digital nomad models offer scalability and cost-efficiency without compromising task completion rates.
Legal and Compliance Considerations for Both Employer Types
Employers must navigate distinct legal and compliance frameworks when managing traditional versus digital nomad workforces, including jurisdictional labor laws, tax obligations, and data privacy regulations. Traditional employers face established regulatory environments tied to fixed locations, while digital nomad employers must address cross-border employment laws, international tax treaties, and remote work compliance challenges. Implementing robust policies and leveraging global compliance tools ensures both employer types mitigate legal risks and uphold workforce rights effectively.
Technology Infrastructure: Supporting In-Office and Remote Staff
An employer's technology infrastructure must seamlessly support both in-office employees and digital nomad employers' remote workforce, ensuring consistent access to cloud-based collaboration tools, secure VPN connections, and reliable high-speed internet. Robust IT systems enable real-time communication and data sharing across locations, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity. Investing in scalable, cybersecurity-focused platforms is essential for managing diverse work environments while protecting sensitive company information.
Communication Styles and Collaboration Tools
Employers managing traditional workers often rely on structured communication styles such as scheduled meetings and formal reporting, whereas digital nomad employers prioritize flexible, asynchronous communication to accommodate global time zones. Collaboration tools like Slack, Zoom, and project management platforms such as Asana or Trello are essential for digital nomad employers to facilitate real-time teamwork and maintain productivity across dispersed teams. Understanding these differences enhances workforce efficiency by aligning communication strategies and technology adoption with the unique demands of each employment model.
Employee Retention and Engagement: Traditional vs. Digital Nomad Workforce
Employee retention and engagement differ significantly between traditional employers and digital nomad employers. Traditional employers often rely on in-person interactions and structured schedules to build loyalty and maintain productivity, while digital nomad employers leverage flexible work arrangements and technology-driven communication to foster a sense of autonomy and connection. Studies indicate that digital nomad workforces may experience higher engagement through personalized work environments but require strategic efforts to sustain long-term retention in a remote setting.
Cost Implications: Comparing Overheads and Benefits
Employers face differing cost implications when choosing between traditional and digital nomad workforces, as digital nomad employers often reduce expenses related to physical office spaces, utilities, and local taxes. Overheads such as office maintenance and employee relocation costs are minimized in remote setups, while benefits expenses may shift towards technology stipends, cybersecurity, and global compliance management. Strategic allocation of resources in digital nomad employment can optimize operational budgets and enhance talent acquisition flexibility without sacrificing productivity.
Building Company Culture in Hybrid and Distributed Teams
Employers face distinct challenges in building company culture within hybrid and distributed teams compared to traditional workplace settings. Digital nomad employers must leverage technology-driven communication tools and flexible policies to foster engagement and collaboration across diverse locations. Prioritizing virtual team-building activities and transparent leadership strengthens trust and alignment, crucial for sustaining a cohesive workforce culture.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Team Leadership
Distributed team leadership demands employers to implement adaptive management strategies that prioritize communication, trust, and autonomy to effectively oversee digital nomad employees. Employers embracing distributed teams benefit from diverse talent pools and increased flexibility but must invest in robust collaboration tools and performance tracking systems to maintain productivity across different time zones.
Async Work Policies
Employers adopting Async Work Policies enable digital nomad employees to maintain productivity across different time zones by prioritizing task-based outcomes over synchronous communication. Traditional employers benefit from these policies by reducing operational bottlenecks and enhancing workforce flexibility, promoting a results-driven culture.
Geo-Independent Payroll
Employers adopting geo-independent payroll systems streamline global workforce management by ensuring compliant, efficient salary distribution regardless of employee location. Digital nomad employers leverage these solutions to optimize talent acquisition and retention across borders, minimizing tax and regulatory complexities.
Digital Residency Compliance
Employers managing digital nomad workforces must prioritize digital residency compliance to avoid legal risks and ensure tax efficiency across jurisdictions. Integrating robust compliance frameworks helps digital nomad employers align with international tax laws and labor regulations while supporting flexible remote work models.
Location-Agnostic Benefits
Employers embracing digital nomad workforces benefit from location-agnostic flexibility that reduces overhead costs and expands access to global talent pools, enhancing productivity and innovation. This model supports diverse, scalable teams while enabling employees to maintain work-life balance, driving higher retention and job satisfaction rates.
Remote-First Onboarding
Remote-first onboarding streamlines integration by leveraging digital tools and asynchronous communication, enabling employers to efficiently onboard digital nomad employees regardless of location. Employers adopting remote-first approaches benefit from enhanced talent acquisition, improved employee engagement, and reduced geographic constraints within the workforce.
Cross-Border Contractor Management
Employers managing cross-border contractors must navigate complex compliance issues such as tax regulations, labor laws, and payroll across multiple jurisdictions to ensure legal and financial efficiency. Digital nomad employers provide flexible workforce solutions while leveraging technology platforms to streamline contractor onboarding, time tracking, and payment processing internationally.
Digital Nomad Talent Acquisition
Employers leveraging digital nomad talent acquisition access a global workforce unrestricted by geographic boundaries, enabling diverse skill sets and increased innovation. Digital nomad employers optimize recruitment through remote collaboration tools and flexible work policies, enhancing talent retention and reducing operational costs.
Virtual Work Visa Sponsorship
Employers offering Virtual Work Visa Sponsorship attract a diverse global talent pool by enabling digital nomads to work remotely across borders, enhancing workforce flexibility and innovation. Traditional employers face challenges competing with digital nomad employers who provide streamlined visa support and adaptable remote work policies, meeting evolving employee expectations.
Flexible Work Taxation
Employers managing digital nomad workforces must navigate complex flexible work taxation rules that differ significantly from traditional employer obligations, often involving jurisdiction-specific tax treaties and reporting requirements. Understanding these regulations ensures compliance, reduces risks of double taxation, and optimizes payroll processes for remote and mobile employees worldwide.
employer vs digital nomad employer for workforce Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com